Table of contents
Five characteristics of the Mediterranean Feather Star
Distribution range and habitat analysis of Mediterranean feathered star
The food chain and main predators of the Mediterranean feathered star
Breeding methods and life cycle of Mediterranean feathered star
How to determine the health status of Mediterranean feather stars
A deeper understanding of the ecological role of the Mediterranean feather star and its relationships with other marine life.
Scientific progress on the Mediterranean feather star
The relationship between the Mediterranean Feather Star and humans
How to care for Mediterranean Feather Star aquariums
Five characteristics of the Mediterranean Feather Star
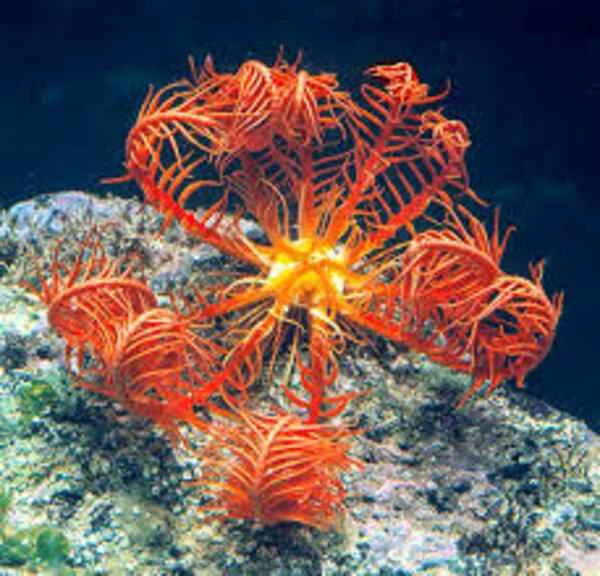

The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) is a marine invertebrate belonging to the phylum Echinodermata. It is beautiful in appearance and highly ornamental. Its five key characteristics give it a unique place in the marine ecosystem and make it a focus of attention for researchers and marine enthusiasts.
1.1 Morphological characteristics
The Mediterranean feathered starfish possesses unique feather-like arms, typically five arms surrounding its central disc. These arms exhibit an extremely slender structure, with edges covered in tiny, tentacle-like appendages resembling feathers. These arms not only provide an elegant appearance but also serve an important filtering function, helping them obtain nutrients from the water.
1.2 Filtered feeding
As filter feeders, Mediterranean feathered starfish use their long arms and tentacles to capture organic matter and plankton through water currents. Their diet mainly consists of phytoplankton, zooplankton, and other small organic particles, relying on the constant water flow to help them obtain food.
1.3 Self-protection mechanism
Mediterranean feathered stars possess strong self-protection abilities. When threatened, they retract their arms to reduce their chances of being preyed upon. Furthermore, their arms have regenerative capabilities, able to regrow after breakage, ensuring the individual's survival and reproduction.
1.4 Habitat Adaptability
Mediterranean feathered starfish primarily inhabit hard substrates on the seabed, such as rocks, coral reefs, and the surfaces of other marine life. They are adaptable to different water depths and currents, and particularly prefer clear waters rich in plankton.
1.5 Reproduction Methods
Mediterranean feathered starfish reproduce through external fertilization. They typically lay and fertilize a large number of eggs during seasons with suitable water temperatures. The released eggs and sperm meet through water currents, fertilization occurs, and larvae develop. After a planktonic phase lasting a few days or weeks, the larvae sink and attach to a suitable substrate, entering adulthood.
Distribution range and habitat analysis of Mediterranean feathered star
Mediterranean feathered starfish are mainly distributed in the Mediterranean Sea and its surrounding waters. They are one of the typical benthic animals in the region and are closely related to the local marine ecosystem.
2.1 Distribution range
Mediterranean feathered starfish are widely distributed, mainly found in the warm waters of the Mediterranean Sea, especially in areas with stable coastlines and strong currents. They can also find habitats in subtropical and temperate waters, typically at depths between 20 and 100 meters. In deeper waters, they prefer to attach to hard substrates such as rocks and coral reefs.
2.2 Habitat
Mediterranean feathered starfish typically inhabit hard substrates on the seabed, such as rocks and coral reefs, where they attach themselves. Their habitat requires clear water rich in plankton and with moderate currents. In these environments, the organic matter in the water can adequately meet their food needs.
2.3 Habitat Protection
The habitat of the Mediterranean feathered star faces threats from environmental pollution, overfishing, and climate change. To protect their habitat, it is crucial to take measures to reduce marine pollution, avoid damaging coral reefs and other hard substrates, and safeguard marine biodiversity.
The food chain and main predators of the Mediterranean feathered star
The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) is a filter feeder that plays a vital role in marine ecosystems. Understanding its food chain and predators is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of its ecological function and its place in the marine food web. This article will explore the Mediterranean feathered starfish's feeding methods, food sources, and potential predators, starting with its food chain.
1. The food chain of the Mediterranean feathered star
Filter feeding behavior
The Mediterranean feathered starfish is a typical filter feeder, using its feather-like tentacles to filter plankton, bacteria, and organic matter from seawater. They live near the shallow seabed, typically inhabiting crevices in rocks and coral reefs, using water currents to help them capture food.
Plankton : The Mediterranean feather star primarily feeds on plankton filtered from the water using its tentacles. Plankton includes phytoplankton (such as algae) and zooplankton (such as crustaceans, larvae, rotifers, etc.). These tiny organisms are carried by the water current into the feather star's tentacles for consumption.
Organic particles and bacteria : In addition to plankton, the Mediterranean feather star also ingests organic particulate matter and bacteria from the water. These substances are essential for their survival, especially when plankton levels are low, as they rely on these smaller particles for energy.
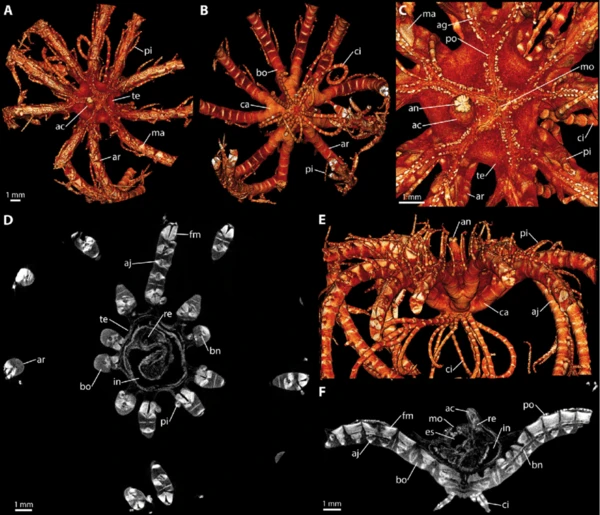
Position in the food chain
In the marine food chain, Mediterranean feather stars are primary consumers, located at the lower end of the food chain. They obtain energy by capturing tiny plankton and organic particles, which are typically provided by plant-based plankton (such as algae) and even smaller marine organisms (such as single-celled algae).
Therefore, the Mediterranean feather star forms a close food network with plant-based plankton (such as algae) and animal-based plankton (such as crustaceans, rotifers, etc.), and their roles as predators and prey can change.
2. The main natural enemies of the Mediterranean feathered star
Despite possessing a degree of defense in nature due to its strong tentacles and unique shape, the Mediterranean feathered star still faces threats from several predators. These predators are typically marine organisms that feed on it or use its habitat for resources. The following are some of the Mediterranean feathered star's main predators:
(1) Fish
Some fish, especially small predatory fish, may prey on Mediterranean feathered starfish. Since feathered starfish typically inhabit rock crevices and coral reefs, their main predators are fish that can dive into these crevices in search of food. These fish will often attempt to prey on the tentacles of the feathered starfish, especially when it is dormant or inactive.
Carnivorous small fish : Some small carnivorous fish living on the seabed may prey on the tentacles of the feathered star. Because the tentacles of the feathered star contain nutrient-rich cells, some fish will attempt to catch these tentacles.
Large predatory fish : Although Mediterranean feathered starfish are not often direct prey for large predatory fish, their location in their habitat may make them targets. For example, some large predatory fish (such as cod and sea bass) may occasionally target feathered starfish.
(2) Marine invertebrates
Mediterranean feathered starfish may also face predation threats from certain marine invertebrates, particularly certain species of crabs, sea urchins, or other benthic invertebrates. These animals may enter the rock crevices where the feathered starfish inhabits and use their pincers or other organs to seize it, especially when the starfish is relaxed.
Crabs : Some crabs, especially more aggressive species, may attack the tentacles of the Feather Star. While crabs won't easily eat the entire Feather Star, they can tear its tentacles, causing damage.
Sea urchins : Some sea urchins obtain their nutrients by directly damaging the feathered star. Sea urchins may injure the feathered star by attacking its body or tentacles.
(3) Other predatory invertebrates
Some smaller predatory marine invertebrates, such as starfish and certain species of octopus, may also be predators of the Mediterranean feathered star. While starfish may not directly attack feathered stars, some species may prey on juvenile or small individuals.
Starfish : Starfish are filter feeder predators. Their stomachs can extend into their prey to digest it. Some more omnivorous starfish may attack feathered starfish.
Octopus : As a highly predatory mollusc, the octopus may also feed on feathered stars. Octopuses have very strong grasping abilities and can use their powerful suckers to capture and tear apart the tentacles or body of feathered stars.
(4) Human activities
Human activities, particularly environmental pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction, also pose an indirect threat to the Mediterranean feathered star. Although humans do not directly prey on the feathered star, marine pollution, habitat destruction (such as the destruction of coral reefs), and temperature changes may adversely affect the Mediterranean feathered star's living environment.
Water pollution : Chemical pollutants in the ocean (such as heavy metals and plastic pollution) may affect the growth and reproduction of feathered stars. Deterioration of water quality may lead to a reduction in their habitat and even directly endanger their lives.
Habitat destruction : For example, the destruction of coral reefs has deprived the Mediterranean feathered starfish of its ideal habitat. Habitat reduction directly affects their reproduction and foraging.
Mediterranean feathered starfish play a vital role in the food chain, helping to maintain the cleanliness and stability of marine ecosystems by filtering plankton, bacteria, and organic particles. While they are lower-level consumers, they also face numerous predators, including fish, marine invertebrates, and even human activities. To protect the Mediterranean feathered starfish, we need to pay attention to their habitat, reduce pollution, and take measures to protect the health of marine ecosystems.
Breeding methods and life cycle of Mediterranean feathered star
The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) is a unique marine organism with highly specialized physiology and reproductive methods. As a filter-feeding organism, the Mediterranean feathered starfish plays a vital role in the ecosystem, and its reproductive methods and life cycle are key aspects of biological research. This article will detail the reproductive methods, life cycle, and various stages of the Mediterranean feathered starfish's life cycle.
1. Breeding methods of Mediterranean Feathered Star
Mediterranean feathered stars are dioecious organisms, meaning they have a clear distinction between sexes, with each individual typically having one sex—male or female. They reproduce through sex-specific external fertilization, that is, by releasing gametes into the water.
(1) Breeding season
The breeding season for Mediterranean feathered starfish typically occurs during the spring and summer when water temperatures rise, which is when they are most active. Warmer water temperatures promote their physiological activities and reproductive processes. Mediterranean feathered starfish usually reach sexual maturity between their second and third year of life, and the timing of the breeding season is influenced by water temperature and environmental conditions.
(2) Gamete release and fertilization
Males and females of the Mediterranean feathered star release gametes (sperm and egg) into the seawater. The sperm are carried by the water currents to the female's egg cell, where fertilization takes place. Because it is external fertilization, the sperm and egg meet in the water, and a zygote is formed after fertilization. This process occurs near the coral reefs or rock crevices where the Mediterranean feathered star inhabits, and the natural currents of the water help their sperm and egg mate.
(3) Egg development and hatching
After fertilization, the eggs float with the currents until they hatch into larvae. Mediterranean feathered star eggs typically require a period of incubation before hatching into early planktonic larvae. These larvae usually begin their life as planktonic animals, drifting in the water with the help of currents, searching for suitable habitats.
2. The life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered star
The life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered starfish comprises multiple stages, from egg to larva, and then to mature individual. Each stage has different physiological characteristics and ecological requirements. The following are the stages of the Mediterranean feathered starfish life cycle.
(1) Egg stage
The life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered star begins with an egg. The fertilized eggs typically float in the water; these eggs are usually small and have some buoyancy. Water flow is crucial at this stage, helping the eggs disperse in the water and find a suitable hatching environment.
Hatching process : After an incubation period of several days to several weeks, the eggs hatch into planktonic larvae. The specific hatching time is affected by environmental factors such as water temperature, salinity, and water flow.
(2) Planktonic larval stage
The planktonic larvae of the Mediterranean feathered star (Euphorbia milii) are free-floating organisms that briefly drift in the water after hatching. Their planktonic life lasts for several weeks, during which time they feed on marine plankton. The larval stage is a critical period in their life cycle, as individuals at this stage must successfully find a suitable habitat to continue their growth.
Habitat selection : Planktonic larvae drift in the sea propelled by water currents. Once they find a suitable habitat (such as rocks, coral reefs or other solid surfaces), they attach themselves to these places and gradually develop into the early stages of adulthood.
(3) Attachment stage
Planktonic larvae will begin to attach to solid surfaces on the seabed under suitable environmental conditions. After attachment, the larvae will enter the next stage—the larval growth stage.
Transition to a sessile lifestyle : The transition from a planktonic to a sessile state is a significant shift in the life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered starfish. They attach themselves to the surface of rocks or coral reefs by secreting mucus, at which point they begin to develop fully formed feather-like tentacles for filtering organic matter and plankton from the surrounding water.
(4) Larval growth stage
After the attachment stage, the Mediterranean feathered starfish enters its growth process. They continue to develop, gradually growing into adults with feather-like tentacles and more filter-feeding structures. As the tentacles grow, they begin to function as filters, preying on tiny plankton in the water. At this point, the Mediterranean feathered starfish has fully adapted to its seabed-fixed lifestyle and gradually reaches sexual maturity.
Tentacle development : Tentacle development is not only a physiological characteristic of the Mediterranean feathered starfish, but also its primary means of obtaining food. The feather-like tentacles can spread out over a wide area to maximize the capture of food in the water.
(5) Sexual maturity and reproduction
Sexual maturity typically occurs in the second or third year of the Mediterranean feathered star's life. At this stage, they prepare for reproduction, complete sexual differentiation, and produce sperm and eggs. After reaching sexual maturity, the Mediterranean feathered star participates in external fertilization, reproducing by releasing gametes.
(6) Adulthood and lifespan
The Mediterranean feathered starfish spends many years in the marine environment during its growth period. Their lifespan is typically 5 to 10 years, with some individuals living longer. Adult Mediterranean feathered stars maintain a stable growth and reproductive pattern later in their life cycle, but their reproductive capacity gradually decreases with age.
Lifespan : The lifespan of the Mediterranean feathered star is greatly influenced by environmental factors, especially water temperature, habitat stability, and water quality. Generally speaking, they can live for many years under ideal habitat conditions.
3. Summary of the life cycle of the Mediterranean Feather Star
The Mediterranean feathered starfish (Spodoptera litura) undergoes a life cycle consisting of multiple stages, including egg, planktonic larva, attachment, larval growth, sexual maturity, and adulthood. Each stage has different physiological characteristics and ecological requirements. The reproduction and life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered starfish are highly dependent on environmental factors, particularly water currents, temperature, and the stability of its habitat. Understanding their life cycle is crucial for protecting this species and its habitat, and for promoting marine ecological balance.
In summary, the life cycle of the Mediterranean feathered star is a long and stable process, from hatching to maturity and reproduction, maintaining the balance among species in the marine ecosystem, while also providing habitats and food resources for other organisms.
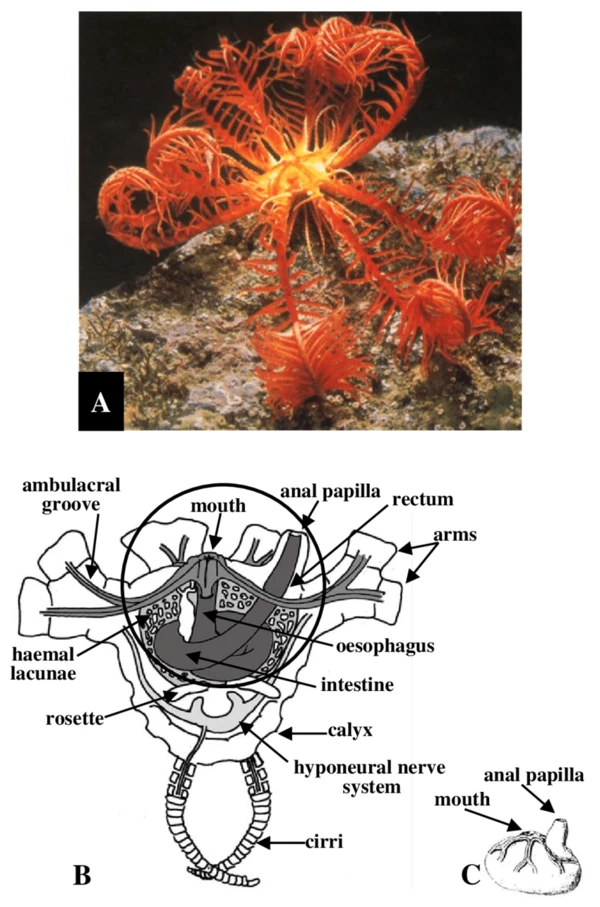
How to determine the health status of Mediterranean feather stars
The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) is a beautiful yet fragile marine organism that plays a vital role in the ecosystem. As a filter feeder, the Mediterranean feathered starfish relies on a healthy habitat for its survival and reproduction. Therefore, understanding how to assess the health of the Mediterranean feathered starfish is crucial for the conservation of this species.
When assessing the health of the Mediterranean feathered starfish, several aspects need to be considered, including its appearance, behavior, and habitat. Below are some common health assessment methods and indicators:
1. Observe the state of the feather-like tentacles.
The most distinctive feature of the Mediterranean feathered starfish is its feather-like tentacles. These tentacles not only help it hunt but also maintain its physiological functions in the water. The condition of the tentacles is an important indicator of the Mediterranean feathered starfish's health.
Normal tentacles : A healthy Mediterranean feathered starfish will have complete, extended, feather-like tentacles. The tentacles should be symmetrical and able to spread flexibly in water currents to prey on tiny plankton.
Abnormal tentacles : If the feathery tentacles fall off, change color, deform, or shrink, it usually means that the Mediterranean feathered starfish is under stress or sick. For example, the discoloration of the tentacles may be due to insufficient nutrition or pollution; while the loss of tentacles may indicate water quality problems or invasion by pathogenic microorganisms.
2. Check the adhesion and movement status.
Mediterranean feather star typically grows attached to rocks, coral reefs, or other hard surfaces. If it cannot attach stably, health problems may occur.
Normal attachment : Healthy Mediterranean feathered star will attach firmly to the surface of rocks or corals, with its body close to the surface and its tentacles extending in the water.
Abnormal attachment : If the Mediterranean feathered starfish cannot attach to the surface, appearing loose or floating, it may be facing environmental stress or declining physical strength. Loss of attachment may be caused by strong water currents, unstable habitat, or other physiological problems.
3. Observe the integrity and form of the body.
The body of a Mediterranean feathered starfish should be sturdy and intact, without any obvious damage or deformity. Its physical health is fundamental to its normal growth and reproduction.
Normal condition : A healthy Mediterranean feathered starfish should have a symmetrical body shape and no obvious cracks, wounds or tissue necrosis.
Abnormal Conditions : If the Mediterranean Feathered Star shows signs of asymmetry, damage, or decay on its body, it may indicate that it is experiencing some kind of illness or external injury. Any wounds or decay on the body surface can lead to infection, further affecting its overall health.
4. Observe the movement of the tentacles.
The Mediterranean feathered star uses its tentacles to prey on plankton in the water. If the tentacles exhibit abnormal activity patterns, it may be a sign of health problems.
Normal activity : In a healthy Mediterranean feathered star, its tentacles actively extend in the water, filtering food resources from the surrounding water. When water flows by, its tentacles actively extend and prey on plankton.
Abnormal activity : If the tentacles of the Mediterranean feathered star cease to extend voluntarily, or exhibit paralysis or relaxation, it indicates that the star may be in poor health. Inactivity of the tentacles could be due to insufficient nutrition, environmental pollution, or disease infection.
5. Inspect the quality of the habitat.
The health of the Mediterranean feathered starfish largely depends on the quality of its habitat. Factors such as water quality, temperature, salinity, and water flow rate can all affect its physiological state.
Suitable Environment : Mediterranean Feather Star thrives best in clear water with moderate flow. The ideal water temperature is 18-24°C, the salinity should be around 35‰, and the pH should be between 7.8 and 8.4.
Unsuitable environments : Deteriorating water quality or habitat pollution can put immense stress on the Mediterranean feathered starfish. High concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water, excessive pollutants, or excessively high or low temperatures can all threaten its health. Strong or weak water currents can also affect its normal filter feeding and respiration.
6. Observe for diseases or parasites.
Like many other marine creatures, the Mediterranean feathered starfish can be susceptible to pathogens or parasites. Examining its body and tentacles for obvious signs of disease or parasites is an important step in assessing its health.
Health characteristics : A healthy Mediterranean feathered starfish has a smooth surface without significant parasites or lesions. The tentacles should also be clean and free of abnormal diseases.
Symptoms of disease : If lesions, black spots, rot, inflammation, or other symptoms appear on the tentacles or body surface, it may be due to bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infestation. Common parasites include small crustaceans or marine worms that may attach to the body surface of the Mediterranean feathered star and affect its normal growth.
7. Monitor appetite and eating behavior
The Mediterranean feathered starfish is a filter feeder, sustaining itself by catching plankton in the water. When healthy, it should be able to consistently engage in both filter feeding and predation.
Normal feeding : Healthy Mediterranean feathered stars will filter organic matter in the surrounding water through their tentacles, demonstrating good feeding behavior.
Decreased appetite : If the tentacles of the Mediterranean Feathered Star become less active or completely immobile, this usually indicates a suppressed appetite, possibly due to environmental stress or health problems. Prolonged loss of appetite can lead to physical decline and even death.
8. Changes in reproductive capacity
Reproductive capacity is one of the important indicators of the health of Mediterranean flinted stars. A healthy Mediterranean flinted star should be able to reach sexual maturity and complete the reproductive process normally. If the reproductive capacity of a Mediterranean flinted star declines, it may mean that there is a problem with its physiological health.
Normal Reproduction : Healthy Mediterranean feathered starfish typically releases sperm and eggs during the appropriate season, entering a reproductive state. If it is observed to be in its reproductive period and successfully releases gametes, this usually indicates that it is in good health.
Reproduction issues : If the reproductive capacity of Mediterranean feathered starfish decreases, or if it does not enter the breeding season for a long time, it may be due to a variety of reasons such as water quality problems, malnutrition, and disease.
The health of Mediterranean feathered starfish can be assessed from several aspects, including the condition of its tentacles, attachment status, body integrity, habitat quality, and examination for diseases and parasites. Timely detection and diagnosis of health problems not only helps protect this beautiful marine creature but also contributes to maintaining the balance and diversity of the ecosystem. Therefore, regular health checks are crucial for keepers and researchers.
A deeper understanding of the ecological role of the Mediterranean feather star and its relationships with other marine life.
The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) is a typical marine filter feeder, widely distributed in the Mediterranean Sea and surrounding waters. It plays a vital role in the marine food chain by capturing tiny plankton, phytoplankton, and organic particles with its feathery tentacles. As an important member of the ecosystem, the Mediterranean feathered starfish has formed complex interactions with its surrounding environment and other marine organisms. In this article, we will explore the ecological role of the Mediterranean feathered starfish, its interactions with other marine life, and its function in maintaining marine ecological balance.
1. Filter feeding habits and ecological role of the Mediterranean feathered star
The Mediterranean feathered starfish is a filter feeder that uses its feathery tentacles to capture plankton from the water. Its foraging behavior not only provides it with nutrition but also plays a crucial role in the marine food chain.
Filter feeding behavior
The Mediterranean feathered starfish uses its tentacles to capture suspended organic particles and tiny plankton in the water. By spreading its tentacles in the water flow, it can effectively filter organic matter from the water, including phytoplankton (such as algae) and zooplankton. These organic particles not only provide the Mediterranean feathered starfish with the necessary nutrients but also help it maintain its physiological functions.
Ecological role
As filter feeders, Mediterranean feather starfish act as "cleaners," helping to maintain water quality. By filtering plankton, they regulate the abundance of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the water, preventing their overgrowth and thus maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Especially in waters rich in phytoplankton, the filter feeding of Mediterranean feather starfish is crucial for controlling excessive algal growth, thereby reducing eutrophication caused by algal proliferation.
2. The relationship between the Mediterranean feathered star and other marine life.
The Mediterranean feathered star not only impacts the environment, but also forms close relationships with other marine life, exhibiting both cooperation and competition. It coexists with other species in its surrounding ecosystem, collectively maintaining the stability of the marine ecosystem.
Relationship with plankton
The Mediterranean feathered star primarily obtains its nutrition through filter feeding on plankton. Plankton, including phytoplankton and zooplankton, are an important food source for it. The foraging behavior of the Mediterranean feathered star directly affects the abundance of these plankton.
Phytoplankton : Mediterranean Feather Star effectively regulates the amount of phytoplankton, avoiding the negative effects of explosive algal growth. Especially during warmer seasons, when phytoplankton grow rapidly, the presence of Mediterranean Feather Star helps balance the amount of phytoplankton, preventing eutrophication of the water.
Zooplankton : Zooplankton, such as small crustaceans and water fleas, are an important food source for the Mediterranean feathered star. The Mediterranean feathered star obtains its food by filtering these zooplankton from the water using its tentacles.
Relationship with marine life
Mediterranean feathered stars often inhabit rocks, corals, or other hard surfaces on the seabed, which creates diverse ecological connections between them and marine life.
Epiphytes : The Mediterranean feathered starfish often inhabits rocky, coral reef, and other similar locations where various epiphytes thrive, such as seaweed, soft corals, and other filter-feeding organisms. These epiphytes provide a stable habitat for the Mediterranean feathered starfish and also offer it shelter, helping it avoid predators.
Competition with other filter-feeding organisms : Due to its filter-feeding habit, the Mediterranean feather star may compete with other similar filter-feeding organisms (such as sponges and sea anemones) for food resources in the same habitat. When there is a shortage of plankton in the water, this competition may affect the survival of the Mediterranean feather star.
Relationship with predatory organisms
The Mediterranean feathered star's natural enemies mainly include some predatory fish and marine invertebrates. Although the Mediterranean feathered star itself does not have strong self-defense capabilities, it can quickly retract its tentacles when threatened, thus avoiding being preyed upon, through its flexible tentacles and rapid reaction ability.
Predatory fish : Some fish, such as certain bass and moray eels, may prey on Mediterranean feathered starfish. When attacked, the Mediterranean feathered starfish quickly retracts its tentacles to reduce its exposed surface area, thus protecting itself.
Marine invertebrates , such as some large snails or starfish, may devour the body of the Mediterranean feathered star, especially when the tentacles of the Mediterranean feathered star are damaged or loose.
Interaction with benthic organisms
The rocks and coral reefs where Mediterranean feather stars inhabit are often also habitats for other benthic organisms, creating a multi-layered ecological interaction.
Symbiotic relationships : The Mediterranean feather star may form symbiotic relationships with other marine organisms, such as certain types of algae or microorganisms, under certain circumstances. These symbiotic organisms provide habitat for the Mediterranean feather star or help it obtain nutrients, while the Mediterranean feather star may also help remove harmful substances from its habitat.
Resource sharing and competition : In abundant habitats, Mediterranean feathered starfish may share resources with other benthic organisms, engaging in mutually beneficial resource exchanges. However, when resources are scarce, they may compete with other organisms, especially when food sources are limited.
3. The role of the Mediterranean feathered star in the ecosystem
Mediterranean feathered starfish, as filter feeders in marine ecosystems, not only regulate the abundance of plankton and microorganisms in the water but also promote marine environmental cleanliness and help maintain ecological balance. They are integral to many food chains, serving as both predators of plankton and prey for some predatory fish and invertebrates. Their presence is crucial for maintaining the health of the entire ecosystem.
Maintaining ecological balance
Mediterranean feather starfish effectively controls phytoplankton populations through their filter-feeding behavior, preventing ecological imbalance caused by overgrowth. In this role, they help clean seawater and reduce the accumulation of harmful substances. Especially in eutrophic waters, they help improve water quality by filtering organic matter such as phytoplankton.
Maintaining biodiversity
The rocks and coral reefs inhabited by the Mediterranean feathered star provide habitats for numerous marine species, forming a diverse ecosystem. They coexist with the surrounding organisms, maintaining the diversity and stability of the seabed ecosystem. Through interactions with other marine life, the Mediterranean feathered star helps maintain the biodiversity of the marine ecosystem.
The Mediterranean feathered starfish ( Antedon mediterranea ) plays a vital role in marine ecosystems. As filter feeders, they not only regulate the food chain by preying on plankton but also promote ecosystem stability through interactions with other marine life. Their presence helps maintain a clean marine environment and preserve biodiversity. To protect the Mediterranean feathered starfish and its habitat, we need to address threats such as marine pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing, and take measures to safeguard this species' habitat to ensure its continued important ecological role in the future.
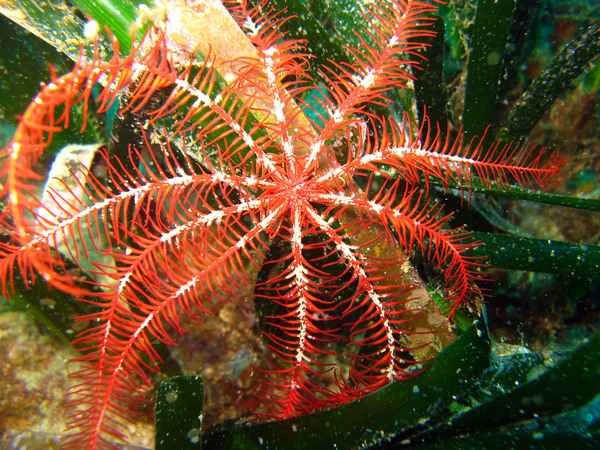

Scientific progress on the Mediterranean feather star
The Mediterranean feathered star ( Antedon mediterranea ), a unique marine organism, has attracted considerable attention from scientists in recent years. Through studies on its ecological habits, reproductive methods, and environmental adaptability, scientists have gradually revealed the crucial role of the Mediterranean feathered star in the marine ecosystem. The following are some of the main aspects of the scientific research progress on the Mediterranean feathered star.
1. Research on ecological role and environmental adaptability
Mediterranean feathered starfish, as filter feeders, play a crucial role in the marine food chain. Studies have found that they obtain nutrients by filtering plankton from the water, helping to maintain water cleanliness. In some marine ecosystems, the abundance and distribution of Mediterranean feathered starfish are closely related to water clarity and current speed. Therefore, scientists are also studying how they adapt to different habitats and how they survive environmental changes such as rising water temperatures and pollution.
Some scholars have conducted in-depth research on the adaptability of Mediterranean feathered stars to different waters through experiments and field observations. For example, how do they find suitable habitats in eutrophic and oligotrophic waters, and how do they cope with changes in water flow speed and temperature? These studies are of great significance for understanding the operational mechanisms of marine ecosystems and developing effective marine conservation strategies.
2. Research on reproduction and life cycle
The reproductive methods of the Mediterranean feathered starfish have long been a focus of scientific research. They reproduce through external fertilization, where eggs and sperm combine in the water to produce planktonic larvae, a process particularly pronounced during seasonal variations. Researchers have observed the reproductive behavior of different populations, revealing the reproductive adaptability of the Mediterranean feathered starfish under varying water temperature and salinity conditions.
In recent years, scientists have used molecular marker technology to further analyze the genetic diversity and population structure of the Mediterranean feathered star. These studies provide important data for understanding its reproductive strategies and its adaptive evolution on a global scale.
3. Research on regenerative capacity and repair mechanisms
The Mediterranean feathered star possesses a remarkable regenerative capacity, rapidly recovering damaged arms upon injury. This property has attracted the interest of many biologists. Regeneration studies have shown that arm regeneration in the Mediterranean feathered star is not merely a matter of cell division and tissue repair, but also involves the regulation of cell signaling and gene expression.
By studying their regeneration process, scientists hope to better understand the basic principles of animal regeneration mechanisms and apply these findings to medical research, particularly in the fields of wound repair and regenerative medicine.
4. Sensitivity studies to environmental pollution
Mediterranean feather starfish inhabits relatively stable marine environments, but they are highly sensitive to environmental pollution, such as oil spills and heavy metal contamination. Therefore, the Mediterranean feather starfish serves as an effective biological indicator for assessing marine pollution levels. Studies have shown that Mediterranean feather starfish can accumulate pollutants in the water, especially heavy metals, which significantly impacts their growth and reproduction.
Some scientists are using the Mediterranean feathered star as a model organism to study the impact of water pollution on marine ecosystems. By monitoring its growth, reproduction, and behavior, researchers can assess the potential threats posed by different pollutants to marine life. This research provides a scientific basis for developing marine conservation policies and pollution control measures.
5. Genomics and Molecular Biology Research
随着基因组学的发展,科学家们开始对地中海羽毛星的基因组进行全面研究。这些研究帮助揭示了它们在繁殖、再生、环境适应等方面的分子机制。例如,研究发现,地中海羽毛星基因组中与免疫反应、再生能力和环境应激反应相关的基因具有特别的表达模式。
通过基因组学研究,科学家们还发现了地中海羽毛星在进化过程中如何积累与其他海洋生物不同的基因特征,这有助于我们理解棘皮动物群体的演化历史和适应性进化。
6. 气候变化对地中海羽毛星的影响
气候变化对海洋生态系统的影响是当前科学研究的重要课题。地中海羽毛星作为海洋生态系统中的关键物种,研究气候变化对它们的影响尤为重要。温度升高、酸化加剧、海平面上升等因素可能影响地中海羽毛星的生存环境和种群结构。
一些研究表明,气候变化可能会影响地中海羽毛星的繁殖周期、食物获取以及栖息地的稳定性。科学家们正在通过长期的监测和实验,探索气候变化对地中海羽毛星的直接和间接影响,以便为未来的保护和管理提供科学依据。
7. 海洋保护与物种复苏研究
随着对地中海羽毛星的深入了解,越来越多的保护措施开始被提上日程。科学家们通过对地中海羽毛星栖息地的研究,提出了多项海洋保护措施,包括减少污染物排放、保护海洋生物多样性、修复珊瑚礁和其他生态系统等。这些研究不仅有助于地中海羽毛星的保护,也有助于提升全球范围内对海洋生态系统保护的认识。
同时,部分科学家还在研究人工繁殖技术,以帮助恢复那些因环境污染或栖息地丧失而数量减少的地中海羽毛星种群。这些研究在实际操作中遇到了一些困难,但为未来的海洋物种复苏工作提供了宝贵的经验。
地中海羽毛星( Antedon mediterranea )作为海洋生态系统中的重要组成部分,受到了科学家们广泛的关注。通过研究其生态角色、繁殖与生命周期、再生能力以及对环境污染的敏感性,科学家们逐步揭示了这一物种的生物学特征和生态功能。随着气候变化和人类活动对海洋生态系统的影响加剧,地中海羽毛星的保护工作也显得尤为重要。未来的研究将继续深入探讨该物种在海洋生态中的作用以及如何有效保护这一珍贵物种。
地中海羽毛星与人类的关系
地中海羽毛星( Antedon mediterranea )作为一种重要的海洋生物,虽然并非直接与人类生活密切相关,但它在生态系统中的作用和对环境的敏感性,使得它与人类的关系变得尤为重要。无论是在生态保护、科学研究还是海洋资源的可持续利用方面,地中海羽毛星都与人类活动有着深远的联系。
1. 地中海羽毛星作为海洋生态指示物
地中海羽毛星是一种滤食性动物,主要通过捕食水中的浮游生物来获取养分。它的生活环境对水质和水流有较高的要求,这使得它成为了一个重要的生态指示物。当环境发生变化时,地中海羽毛星的生存和繁殖受到直接影响,因此,科学家常常利用它来评估海洋环境的健康状况。
例如,海洋污染,尤其是重金属污染、石油泄漏以及海洋酸化等因素,都会影响地中海羽毛星的生长和繁殖。地中海羽毛星的数量变化和健康状况可以反映出水域的污染程度,这对于环境监测和保护措施的制定非常重要。通过保护地中海羽毛星的栖息环境,人类也能间接地保护其他依赖该生态系统的海洋物种及整个海洋环境。
2. 促进海洋保护与生物多样性
地中海羽毛星在生态系统中的角色不仅仅是维持水质和生态平衡,它也是维持生物多样性的一部分。海洋生物多样性的保护是全球环境保护的重点之一,而地中海羽毛星作为其中的一环,对于海洋生物群落的稳定具有重要意义。
由于地中海羽毛星栖息的环境多为海底软底或岩礁地带,这些地方往往也是其他海洋生物的重要栖息地。通过研究和保护地中海羽毛星的栖息环境,可以促进整个海洋生态系统的恢复与可持续发展。这些保护行动不仅有利于地中海羽毛星的生存,也有助于保护其他海洋生物,特别是那些依赖羽毛星栖息环境的物种,如小型底栖生物和滤食性鱼类。
3. 在生物医药研究中的潜力
地中海羽毛星的再生能力是一个受科学界广泛关注的领域。它能够通过再生失去的臂部来修复自身的身体结构,这一过程不仅对生物学家了解动物再生机制具有重要意义,也为医学研究提供了宝贵的研究材料。通过研究地中海羽毛星的再生机制,科学家们可以探索到一些再生医学的潜力,甚至有可能为人类的伤口愈合和组织再生提供新的思路。
此外,地中海羽毛星的免疫系统、抗污染能力等方面也有可能为药物开发和生物技术创新提供新的突破。特别是在环境污染和气候变化加剧的背景下,探索海洋生物的适应机制,或许能够为人类社会提供应对环境挑战的新策略。

4. 旅游业与教育的潜在影响
地中海羽毛星是海洋生态系统中具有重要生态价值的物种,虽然它的外形并不引人注目,但它在自然保护区和海洋生态旅游中的角色不可忽视。随着环保意识的增强和生态旅游的兴起,许多海洋生物的观察和学习成为了人们了解海洋生态系统的重要途径之一。
地中海羽毛星的栖息地,尤其是地中海和近海地区,吸引了大量的潜水员和生态旅游者。通过向游客介绍地中海羽毛星的生物学特征和生态价值,相关的旅游业和教育活动可以增加公众对海洋生态保护的重视。同时,这也为当地的经济发展提供了支持,尤其是在以海洋保护为核心的生态旅游中,地中海羽毛星作为标志性物种之一,具有不可替代的象征意义。
5. 对渔业资源的间接影响
地中海羽毛星虽然本身不直接为人类所食用,但它对海洋生态系统的稳定和渔业资源的保护具有重要作用。通过维持水质的清澈和减少水体中的有害物质,地中海羽毛星有助于提升海域的生物多样性,进而影响渔业资源的丰度。例如,地中海羽毛星为其他小型海洋生物提供栖息环境,这些生物是许多商业性鱼类的食物来源。因此,保护地中海羽毛星的栖息环境,不仅有助于该物种本身的生存,也间接地有助于渔业资源的恢复和可持续利用。
然而,由于人类活动的不断扩展,过度捕捞、栖息地破坏和污染等因素正威胁着地中海羽毛星及其生态系统的健康。为确保渔业资源的可持续发展,人类必须采取有效的保护措施,避免破坏海洋生态平衡,保护像地中海羽毛星这样的关键物种。
6. 未来的科学研究和保护需求
地中海羽毛星的生态研究仍在继续,科学家们希望进一步了解其在海洋生态系统中的复杂角色。随着人类活动对海洋环境的不断影响,保护像地中海羽毛星这样的物种不仅仅是为了物种本身的生存,也是为了维护整个海洋生态系统的健康。因此,加强国际合作和跨学科研究,制定和实施有效的海洋保护政策,是当前和未来亟需解决的问题。
科学研究表明,气候变化、海洋污染和过度开发正在严重威胁地中海羽毛星的栖息地。为了避免这些威胁的加剧,国际社会需要加强对地中海羽毛星及类似物种的保护工作,包括加强对海洋环境污染的监管、开展生态修复项目、加强生物多样性保护等。
地中海羽毛星( Antedon mediterranea )作为海洋生态系统中的重要物种,虽然并非直接为人类所依赖的资源,但它在维持海洋生态平衡和生物多样性方面具有不可替代的作用。无论是在作为生态指示物、促进海洋保护、还是推动科学研究与生物医药开发方面,地中海羽毛星都与人类的生活息息相关。通过加强对地中海羽毛星的保护,推动相关的科学研究和环保措施,不仅有助于这一物种的生存,也能为人类提供更多的生态价值和科学突破。
如何在水族箱中养护地中海羽毛星
地中海羽毛星( Antedon mediterranea )是一种美丽的海洋生物,其在自然环境中以滤食为主,依靠其独特的羽毛状触手捕捉水中的微小浮游生物。由于它对水质和环境条件的要求较高,因此在水族箱中养护地中海羽毛星并非易事。正确的环境设置和细心的照顾是保持地中海羽毛星健康生长的关键。以下是一些养护地中海羽毛星的要点,帮助你创建一个理想的水族箱环境。
1. 了解地中海羽毛星的基本需求
首先,了解地中海羽毛星的自然习性和生存环境是非常重要的。它们原产于地中海及其附近的水域,通常生活在浅海底部,栖息在岩礁和沙泥交界处,喜欢水流较强的环境。它们是滤食性动物,主要以水中的浮游生物为食,因此在水族箱中需要保证水质清澈并且有足够的微小颗粒物质供其捕食。
2. 设置合适的水族箱环境
Water quality requirements
地中海羽毛星对水质要求较为严格,以下是一些基本的水质标准:
水温:地中海羽毛星的最佳水温范围为18°C至24°C(64°F至75°F)。由于它们主要栖息在温暖的海域,过高或过低的温度都可能导致其健康问题。
盐度:地中海羽毛星生活在海水环境中,因此需要盐度在1.020至1.025之间的海水。确保定期测试盐度,并保持稳定。
pH值:地中海羽毛星对pH值较为敏感,理想的pH值范围为7.8至8.4。定期监控水族箱中的pH值,避免水质过酸或过碱。
氨、亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐:这些物质对地中海羽毛星的健康至关重要,过高的氨和亚硝酸盐浓度会导致其死亡。因此,在设置水族箱时,应确保进行彻底的循环和过滤,以保持水质清洁。
水流要求
地中海羽毛星喜爱水流较强的环境,这有助于它们更好地捕食浮游生物。在水族箱中,可以通过合适的泵浦和水流装置来模拟自然水流。确保水流不至于过于猛烈,否则可能会损伤羽毛星的触手和身体。
底材和岩石
在水族箱中,使用沙子或细沙作为底材是理想选择。底部应放置一些岩石和珊瑚结构,模拟其天然栖息地的地形。这些岩石和珊瑚不仅可以为羽毛星提供隐蔽空间,还可以为其提供附着点,帮助其稳定在底部。
3. 饲养和喂养地中海羽毛星
food sources
地中海羽毛星是滤食性动物,主要通过捕捉水中的浮游生物、细菌、微小的有机颗粒等来获取食物。为确保其充足的营养,可以在水族箱中培养浮游生物,或者通过定期补充液态的藻类或浮游动物来为其提供食物。
你还可以选择为水族箱中加入一些细微的藻类或浮游生物,模拟自然环境中的食物来源。有些水族箱主人会添加一些专门为滤食性海洋生物设计的颗粒食品,或者用磷虾、幼体浮游生物等直接喂食。
喂食频率
地中海羽毛星并不需要频繁喂食,它们主要依靠水中的自然浮游生物进行摄食。在水族箱中,如果没有足够的自然食物,建议每隔几天喂一次,并确保食物颗粒足够细小,能被其羽毛状触手有效捕捉。
4. 定期清洁和维护水族箱
地中海羽毛星对水质的变化非常敏感,因此保持水族箱的清洁和稳定至关重要。定期检查和清洁水族箱的设备、过滤系统以及底部,确保没有积累过多的有机废物。
Filtration system
高效的过滤系统对于维持水族箱中的水质至关重要。地中海羽毛星对污染物的耐受力较低,因此需要一个强力的过滤系统来去除有害物质,保持水质清洁。
定期换水
建议每2到4周进行一次部分换水,以维持水质的稳定。换水时要小心避免剧烈变化,逐步调整水温和盐度,避免对地中海羽毛星造成刺激。
5. 避免常见的养护问题
水温波动
地中海羽毛星对水温的波动非常敏感,因此避免温度剧烈变化是至关重要的。水族箱中的加热器或冷却装置应当定期检查,确保温度保持在18°C至24°C之间。
高污染和水质不稳定
水质不稳定是导致地中海羽毛星健康问题的常见原因之一。要确保水中的氨、亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐浓度处于安全范围内,并保持pH值、盐度等在正常范围内。
搭配合适的伙伴
由于地中海羽毛星性格温和,避免与具有攻击性的鱼类或其他海洋生物一起饲养。理想的伴侣是那些体型较小、性格温顺且不会干扰羽毛星活动的物种。
6. 注意观察与健康管理
定期检查地中海羽毛星的身体状况是非常重要的,健康的地中海羽毛星应当展示出羽毛状触手的扩张和活动。如果其触手出现萎缩、掉落或颜色暗淡等问题,可能意味着水质出现问题或者食物不足,需要立即调整养护条件。
Summarize
在水族箱中成功养护地中海羽毛星需要细心的照料和稳定的环境条件。通过提供适合的水质、合适的水流以及充足的食物来源,可以确保地中海羽毛星健康生长并发挥其在水族箱中的美丽与功能。定期清洁水族箱、监控水质并避免环境剧烈变化,是养护地中海羽毛星的关键步骤。在适宜的条件下,地中海羽毛星将成为水族箱中一道独特的风景。


