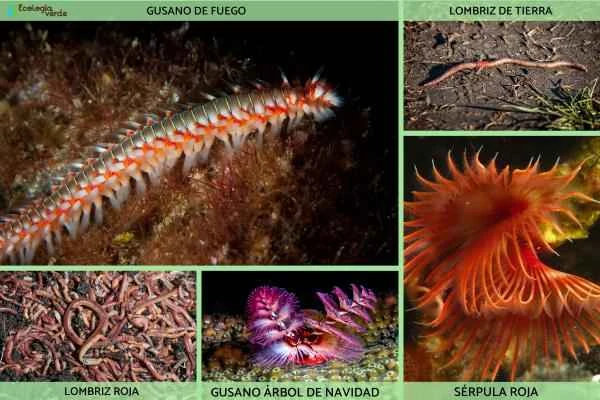
Worms are a group of slender, soft-bodied, and simple-structured invertebrates, including well-known earthworms, intestinal parasites, and small worms found on fruits. Actually, "worm" is not a strict biological classification, but rather a collective term for several animal phyla, encompassing annelids (such as earthworms), flatworms (such as tapeworms and flukes), and nematodes (such as roundworms and hookworms). This article will provide a systematic understanding of the classification, morphological characteristics, and life habits of various common worms, helping you identify the "insects" commonly found in your home and in nature.
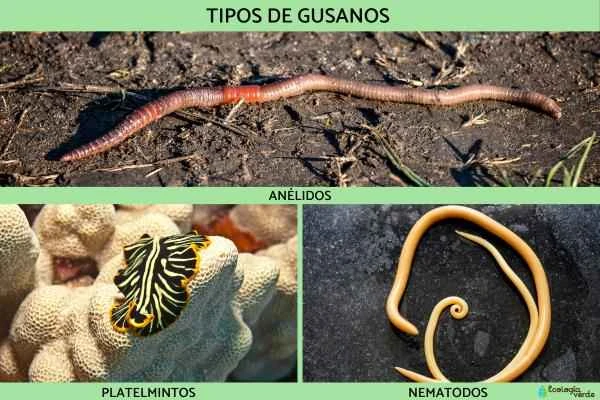

Main characteristics of worms
Slender body, worm-like or tubular
Soft, without skeleton
No obvious motor appendages such as feet or hands
Obvious dorsoventral and anterior differentiation
All are invertebrates
Mostly damp or aquatic environments, some are infested with parasites.
I. Phylum Annelida – “Higher-level worms” with segmented bodies
Annelids are the most structurally complex worms, with bodies composed of many ring-like segments, possessing a closed vascular system, a coelom, and a well-developed muscle layer. Common species include:
1. Red earthworm (Eisenia foetida)
Commonly used for composting, they live in humus-rich soil and decaying plant matter. Their excrement (earthworm castings) is a high-quality organic fertilizer.
2. Hermodice carnuculata
Also known as "fire worms," they belong to the polychaete class and have numerous bristles on their bodies that cause intense stinging upon contact. They primarily prey on corals and are common predators in tropical waters.
3. Serpula vermicularis
It can secrete calcium carbonate to form a shell, lives on the seabed, collects food with its tentacles, and can retract into its tube when it encounters danger.
4. Giant ringed caterpillar (Glossocolex sp.)
A unique annelid found in the South American rainforest, it can reach 50 centimeters in length.
5. Other representatives
Green polychaete (Eulalia viridis)
Christmas tree worm (Spirobranchus giganteus)
Sea cucumber polychaete (Gastrolepidia clavigera)
Soil earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris)

II. Phylum Platyhelminthes – Parasitic and Free-living Worms with “Flat Body”
Flatworms are characterized by their flattened bodies and simple structures. Most live in humid environments or as parasites, while some species can directly absorb nutrients.
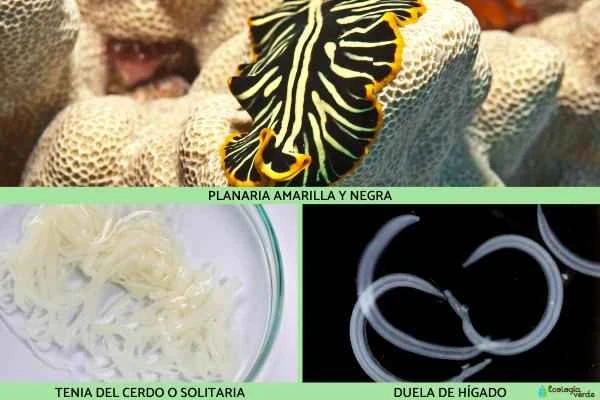
1. Porcine tapeworm (Taenia solium)
One of the most notorious parasites, its larvae can infest the human intestines and muscles, leading to malnutrition and even more serious health problems.
2. Yellow and black planarian (Pseudoceros dimidiatus)
A brightly colored, free-living flatworm in the Indo-Pacific region, which uses its vibrant warning colors to deter predators.
3. Nasal fluke (Schistosoma nasale)
It parasitizes livestock, is transmitted through freshwater snails, and harms cattle and sheep, causing respiratory difficulties and nasal secretions.
4. Other representatives
Provitellus turrum
Epidermal symbiotic planarian (Waminoa sp.)
Common planarians (Dugesia spp.)
Kaburakia excelsa
III. Nematoda – The most abundant group of "round worms"
Nematodes are cylindrical in shape, extremely diverse in species, and live in a wide range of environments, from soil to ocean, from parasitic to free-living. Some can lay hundreds of thousands of eggs every day, demonstrating an extremely strong ability to adapt.
1. American hookmouth nematode (Necator americanus)
It can penetrate the skin and infect the human body, entering the bloodstream, lungs, and digestive tract, eventually maturing in the intestines, leading to anemia, digestive and respiratory problems.
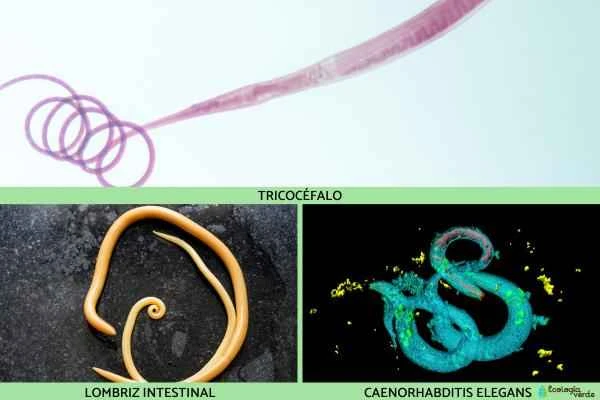
2. Human roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides)
One of the most common intestinal parasites in humans, it is transmitted through unclean food and can cause abdominal pain, indigestion, or even obstruction.
3. Soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines)
Colorless nematodes damage the root systems of leguminous plants, leading to reduced agricultural yields.
4. Other representatives
Whipworm (Trichiuris trichiura)
Caenorhabditis elegans (a commonly used laboratory animal)
Loa loa (a parasite found in the human eye)
Pinworms (Enterobius spp., a common parasite in children)
Conclusion
The term "worm" encompasses a rich variety of animal types, from earthworms that improve soil to parasites that threaten health, and even beautiful marine polychaetes. Understanding the types, structures, and ecological significance of these worms helps us scientifically understand nature and effectively control household pests. If you have further questions about the identification and control of a particular worm, parasite, or household pest, please follow our science popularization column!


