The Royal Guinea Finch (Acryllium vulturinum), also known as the Cuckoo Guinea Finch, is a unique species of guinea fowl, renowned for its unusual appearance and characteristics. They have specific requirements regarding habitat, husbandry methods, and care. To ensure the healthy growth of Royal Guinea Finch breeders, breeders must understand their needs and provide suitable environment and care.
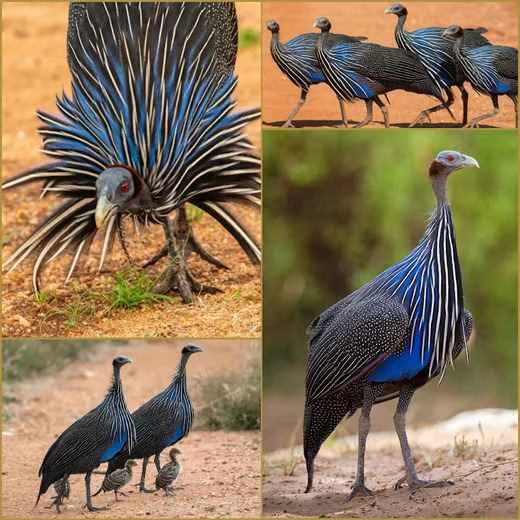

Appearance
The guinea fowl is a visually striking bird. Its head is almost entirely bare, displaying a vulture-like skin structure, with prominent bony structures and a clearly defined neck. Its plumage is deep purple or dark blue on the sides, and white on the belly with scattered spots. The guinea fowl's plumage is beautiful and glossy, especially dazzling in sunlight. Its unique appearance makes it very conspicuous among birds.
Size and weight
The guinea fowl is a medium-sized bird, with adults weighing approximately 1.5 to 2 kilograms, and males being slightly larger than females. They can reach 50-60 centimeters in length, with a distinctively long tail feather. Feather coloration varies slightly between sexes, with males having more vibrant plumage and females more subdued.
diet
The diet of the guinea fowl primarily consists of insects, seeds, small fruits, and plants. They forage on the ground, habitually pecking at food and small insects. In captivity, their diet can consist of high-quality bird feed, insects, leafy greens, grains, and some fruits and vegetables. To maintain their health, calcium and protein should be regularly added to their diet to promote bone growth and feather health.
Reproduction and growth cycle
The breeding season for the Guinea Fowl (Acryllium vulturinum) typically occurs in spring and autumn, with the choice of breeding season closely related to ambient temperature and food availability. During the annual breeding season, males attract females with loud calls and display their vibrant plumage to attract mates. Males typically stand in high positions, displaying their feathers, and are usually the most conspicuous individuals in the flock.
Egg laying and hatching
The female bird will choose a secluded spot on the ground to build her nest, usually in bushes or grass. She typically lays 3 to 5 eggs at a time; the eggs are usually light brown with some spots. The incubation period is approximately 28 days. During this time, the female bird focuses on incubating the eggs, while the male bird protects the nest from predators.
The growth of chicks
Newly hatched chicks rely on their parents for protection and food. In the first few weeks after hatching, the chicks grow rapidly and gradually begin to forage for food under their parents' guidance. Around two to three months old, the vulture guinea fowl chicks begin to become independent, able to forage for themselves and adapt to their environment.
sexual maturity
The guinea fowl typically reaches sexual maturity around 6 months of age, at which point they become capable of reproduction. Although they may exhibit some social behavior in their early years, they usually choose a suitable mate for reproduction after reaching sexual maturity.
Overall, the growth cycle of the vulture guinea fowl is relatively slow, and they need a suitable environment and sufficient food supply to ensure their healthy growth.
Ecological Habits and Survival Challenges of the Vulture Guinea Finch (Acryllium vulturinum)
Ecological habits
The guinea fowl is adapted to life in arid and grassland regions. They typically live on the ground and are highly mobile, able to quickly traverse bushes and grasslands. During the day, they primarily forage for insects and seeds, while at night they roost in shallow nests in bushes or on the ground.
Although they can fly short distances, the guinea fowl is not adept at long-distance flight; its flying ability is primarily used to escape predators or hop onto branches to avoid danger. Typically, they rely more on rapid running and sudden, short bursts of flight to evade predators.
Survival Challenge
The habitat of the guinea fowl has been gradually encroached upon by human development, particularly the over-logging of forests and grasslands in Africa and agricultural expansion, leading to severe damage to their habitat. Furthermore, the guinea fowl has a long breeding cycle and a slow population recovery rate, making them more vulnerable to environmental changes and habitat destruction. Illegal hunting is also a threat they face; although they are not widely hunted as prey, they are sometimes used for food or as ornamental birds.
Habitat distribution map and migration behavior study of the vulture guinea fowl (Acryllium vulturinum).
Habitat distribution
The guinea fowl is mainly distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, inhabiting the boundaries between grasslands, scrublands, and forests. Its habitat is primarily found in Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania. Because they live on the ground, the vegetation cover and abundance of food sources in their habitat are crucial for their survival.
Migration
While guinea fowl are not capable of long-distance migration, they do migrate to more suitable areas according to seasonal changes. During the dry season, they seek out more water and food, typically migrating to more humid climates. This migration is primarily for survival and does not follow a fixed route.
Breeding and improvement techniques, husbandry and sustainable development of the vulture guinea fowl (Acryllium vulturinum)
Variety improvement and breeding technology
In captivity, breed improvement and breeding techniques are crucial for the conservation of the guinea fowl. Scientists and breeders enhance their disease resistance and adaptability to different habitats through selective breeding. Furthermore, improved breeds can have stronger reproductive capabilities and shorter growth cycles, which positively impact species recovery and stable reproduction.
Sustainable development
The sustainable development of the guinea fowl hinges on scientific husbandry and habitat protection. Human activities have placed immense pressure on their habitats, and only through reasonable management and protection measures can the guinea fowl population be kept stable. Therefore, habitat protection, controlling hunting activities, and reducing environmental pollution are essential conditions for achieving sustainable development for the species.
Market demand and prospect analysis, economic benefit analysis of breeding
As a unique and precious bird species, the vulture guinea fowl (Acryllium vulturinum) is attracting increasing attention due to its market demand and economic benefits. It holds significant market potential, particularly in ecotourism, wildlife conservation, and high-end catering. The following is a detailed analysis of the market demand, prospects, and economic benefits of raising vulture guinea fowl:
Market demand and prospect analysis
With increasing global focus on ecological conservation and sustainable agriculture, the guinea fowl, a beautiful and uniquely shaped bird, has become a popular destination for ecotourism and nature reserves. Many ecoparks and wildlife conservation organizations use it as a tourist attraction, raising public awareness of rare species conservation through exhibitions and educational activities.
Furthermore, the beautiful feathers and unique appearance of the guinea fowl make it a popular material in some traditional feather crafts. With increasing interest in nature and unique species, the market demand for guinea fowl is likely to continue to grow. Especially in some regions where wild populations are declining, farming is gaining advocacy and support, becoming a win-win option for both species conservation and economic development.

Economic Benefit Analysis of Breeding
Market Potential for Meat and Egg Products <br />Guinea fowl meat is delicious and nutritious, making it suitable for the high-end catering market. Due to its unique wild flavor, this meat is considered to have high market value. With increasing consumer demand for natural and organic foods, guinea fowl meat is expected to become a high-end market product. Furthermore, guinea fowl eggs also have considerable market potential, especially in the high-end catering and health food industries.
Added Value of Feathers and Handicrafts <br />The colorful and beautiful feathers of the guinea fowl are suitable for making handicrafts, ornaments, and decorations. These feathers have wide applications in traditional crafts, ethnic costumes, and high-end decorative items. As consumers' appreciation for handicrafts and precious materials grows, the market demand for guinea fowl feathers has also increased, becoming a source of additional income for farmers.
Ecotourism and Educational Value <br />The guinea fowl, as a rare bird species, attracts a large number of tourists interested in ecology and nature conservation. Many protected areas and ecotourism companies generate additional revenue by showcasing this bird and providing related educational activities. Tourist visits and birdwatching activities not only promote local economic development but also raise public awareness of ecological conservation.
Farming Costs and Returns <br />While farming guinea fowl requires some technical and management investment, compared to some traditional poultry, they are more adaptable to the environment and have stronger disease resistance, making farming costs relatively controllable. Especially when provided with a suitable environment and ample food supply, guinea fowl have a shorter growth cycle and a higher chick reproduction rate. With the improvement of farming techniques and the growth of market demand, the economic benefits of raising guinea fowl will gradually become apparent.
Potential Ecological Benefits : The farming of guinea fowl not only meets market demand but also promotes species conservation and ecological balance. Through artificial breeding and rearing, the industry can reduce pressure on wild populations and help improve the species' reproductive capacity. Furthermore, farming activities can promote biodiversity conservation and enhance the ecological value of the farming areas.
Overall, the market demand for vulture guinea fowl is promising, especially in the high-end catering, ecotourism, and feather product sectors, where it offers significant economic benefits. As people's understanding of environmental protection, ecological conservation, and sustainable agriculture deepens, vulture guinea fowl farming will become a promising industry, not only bringing economic returns but also contributing to species conservation and ecological improvement.
Common diseases
As a unique bird species, the guinea fowl (Acryllium vulturinum) may face several common diseases during its rearing, affecting its health and productivity. Below are some common diseases and preventative measures:
Respiratory Infections <br />Guinea fowl have sensitive respiratory systems, especially in damp, poorly ventilated environments, making them prone to respiratory infections. Common symptoms include sneezing, coughing, and runny nose. To prevent respiratory infections, the rearing environment should be kept dry and well-ventilated, and overcrowding should be avoided.
Parasitic Infections <br />External parasites (such as ticks and lice) and internal parasites (such as roundworms and tapeworms) are common health problems in vulture guinea fowl. Parasitic infections can lead to decreased appetite, weight loss, and poor feather quality. Regular checkups and deworming are effective ways to prevent parasitic infections.
Digestive System Problems <br/>The digestive system of guinea fowl is easily affected by improper diet and environment, leading to gastrointestinal discomfort or diarrhea. To prevent digestive system diseases, suitable food, clean water, and a clean breeding environment should be provided.
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies : Deficiencies in vitamins A and D, as well as minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, can affect the growth and reproductive capacity of guinea fowl. Proper feed formulation and regular supplementation with essential nutrients can help prevent these problems.
Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease <br />Like other birds, vultures and guinea fowl can also be infected with infectious diseases such as avian influenza or Newcastle disease. These diseases are highly contagious and can cause mass mortality, so regular vaccination and strict control of external contact are very important.
History and cultural heritage
The guinea fowl is native to arid regions of Africa, particularly the savannas and grasslands of Kenya, Ethiopia, and Tanzania. Due to its distinctive appearance and behavior, the guinea fowl holds an important place in local cultures.
In some African cultures, vultures and guinea fowl are seen as symbols of courage and strength. Due to their vulture-like appearance and strong survival skills and territoriality, they are often associated with wildness and independence, becoming spiritual symbols for certain tribes and communities.
In addition, the vulture and guinea fowl also appear in some African folklore, often as a symbol of nature and survival. Their feathers have also had historical applications in traditional crafts and jewelry making, especially in local tribal clothing and rituals, where feathers are used as important symbolic items.
Advances and Prospects in Scientific Research
In recent years, scientific research on the guinea fowl has been increasing, especially in the fields of ecology, behavior, and conservation biology. As a unique bird species, the guinea fowl has attracted the attention of researchers around the world.
Behavioral Research <br />The unique behaviors of the guinea fowl have provided valuable clues for scientific research. Their group living, foraging behavior, and breeding rituals have become important subjects for ecologists and behavioral scientists studying avian social structure and behavioral adaptation. Studies have shown that guinea fowl possess a certain degree of sociality, communicating with their companions through complex vocalizations and body language.
Genetics and Breed Improvement <br/>With in-depth research into the genetics of the guinea fowl, scientists have begun to explore its genetic diversity and genomic characteristics. Through genomic research, scholars can not only help us better understand its evolutionary history, but also promote the development of artificial breeding and breed improvement technologies, thereby improving its breeding efficiency and adaptability.
Conservation Research <br />As a threatened species, the guinea fowl has attracted considerable attention from conservation biologists. Research focuses primarily on habitat protection, population recovery, and genetic conservation. With global environmental changes and habitat destruction, the guinea fowl faces severe challenges to its survival; therefore, conservation research is crucial to ensuring the species' continued existence.
Ecotourism and Education <br/>With the rise of ecotourism, the guinea fowl, as a species with high ornamental value, has gradually become an important part of some ecotourism projects. Related ecological research provides a scientific basis for the education and promotion of the guinea fowl, increasing public awareness of species conservation by demonstrating its ecological importance to tourists.
Top 10 Interesting Facts about the Guinea Fowl (Acryllium vulturinum)
The bald heads of the vulture guinea fowl are completely different from those of other guinea fowl, resembling those of a vulture.
They like to walk quickly on the ground, and sometimes they will suddenly take flight and escape.
Although they can fly, they rely more on rapid movement on the ground.
Their calls are very loud, especially during the breeding season, when the males use their calls to attract females.
They typically live in groups and rely on the strength of the group for protection.
The guinea fowl has very brightly colored plumage, with the male having the most magnificent plumage.
They are omnivorous birds with a diverse diet, including insects, plants, and fruits.
The incubation period is relatively long, taking about 28 days, during which the chicks gradually adapt to their environment.
The vulture guinea fowl is adapted to arid and hot environments and can survive in extreme weather.
They are considered an important part of the African savanna ecosystem and help control insect populations.
in conclusion
The guinea fowl (Acryllium vulturinum) not only holds an important position in ecological research and species conservation, but its unique cultural symbolism and beautiful appearance also give it undeniable value in both traditional culture and modern society. Through further scientific research and technological advancements, the conservation and utilization of the guinea fowl will become more diversified, promoting its application in ecological protection, education, tourism, and other fields, thus contributing to global biodiversity conservation.