Frogs, as amphibians, have always played a vital role in the ecosystem. Their biological characteristics, behavioral habits, and interactions with the environment make them "spectacles" of nature. Among the many frog species, some have become outliers in nature due to their peculiar appearance, unique behaviors, or amazing adaptations. They not only bring research pleasure to zoologists but also inspire awe in the general public towards nature. This article will introduce you to ten of the world's strangest frogs, each possessing its own unique charm and deserving the title of "stars" of nature.
1. Glass Frog: A peculiar frog with a completely transparent body.
Glass frogs ( Centrolenidae ) are among the most unique members of the frog family, named for their transparent bellies. They typically measure 2 to 3 centimeters in length and inhabit the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, particularly common in regions like Costa Rica and Panama. Their most captivating feature is their almost completely transparent abdomen, allowing a clear view of their internal organs, such as the heart and intestines; this physiological characteristic makes them exceptionally mysterious in the animal kingdom.
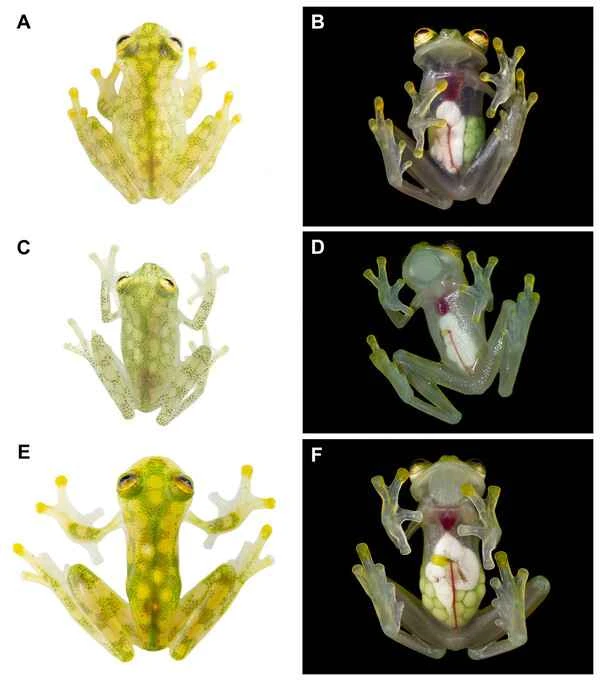
The transparency of glass frogs is an adaptive evolution that helps them hide in the shady environment of rainforests and avoid predation. Their skin is typically green or yellowish-green, similar in color to the vegetation and leaves in their environment, allowing them to blend into the landscape and achieve a camouflage effect. Their transparent abdomen, in addition to providing external cover, may also help them escape stealthily before being detected by predators.
These frogs live in moist environments, especially near streams and bodies of water. Their reproductive behavior is also quite interesting: the female lays her eggs on leaves, and the male guards them until the hatched tadpoles slide downstream into the water, completing their life cycle. The glass frog's habitat is becoming increasingly fragile due to its specific ecological requirements, making the conservation of these frogs an important task for biologists.
2. Beibu Gulf Bark Frog: A Master of Camouflage, Like Moss
The Beibu Gulf leathery tree frog ( Theloderma corticale ), also known as the Vietnamese moss frog, is a frog with exceptional camouflage abilities, widely distributed in southern China, Vietnam, and Laos. Its most distinctive feature is the abundance of protrusions and nodules on its skin, making it blend seamlessly into its environment like moss. These angular structures not only allow it to resemble the surrounding moss, bark, and dead leaves in appearance but also enhance its survival capabilities, helping it effectively evade predators.
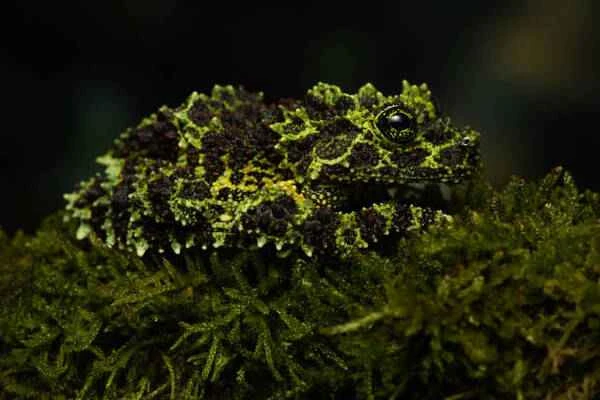

The Beibu Gulf leathery tree frog is relatively small, usually no more than 5 centimeters long. Its body color is dark green or gray, often with irregular black spots and yellow stripes. Through these color variations and textures, the Beibu Gulf leathery tree frog can remain almost undetected in the moist forest environment. They prefer to inhabit damp forest floors, hiding under rocks, tree roots, or in damp layers of dead leaves during the day, and only becoming active at night to forage.
During the breeding season, the Beibu Gulf leathery tree frog emits a deep call to attract mates. The eggs are typically laid in moist environments near bodies of water, and the hatched tadpoles quickly enter the water to begin their aquatic life. It is this unique camouflage and reproductive behavior that makes the Beibu Gulf leathery tree frog a truly remarkable species in nature.
3. Darwin's Frog: The Male "Male Mother" Who Raises His Young
Darwin's frog ( Rhinoderma darwinii ) is a tree frog native to South America, best known for the male's role in raising the young during the breeding season, essentially acting as a "male mother." This frog is relatively small, typically about 4 to 5 centimeters in length, and is green or brown with irregular spots and stripes on its back. They mainly inhabit the humid forest environments of Chile and Argentina, feeding on small insects.
Darwin's frog exhibits a very unique parenting behavior. During the breeding season, the male frog swallows the eggs laid by the female and stores them in its glottis until they hatch into tadpoles and then froglets. Throughout this process, the male frog provides oxygen to the tadpoles through its glottis, sustaining their lives. Only when the tadpoles are fully developed does the male frog release them into the air via regurgitation. This parenting behavior is extremely rare and unique among amphibians, warranting further scientific research and exploration.
In addition, Darwin's frogs have a particularly prominent and uniquely shaped snout, resembling a "duck's bill," which adds to their distinctive charm. The function of this snout is not yet fully understood, but some research suggests it may play a role in their courtship behavior. In the wild, Darwin's frogs face challenges such as habitat loss and climate change, therefore, their conservation efforts need to be further strengthened.
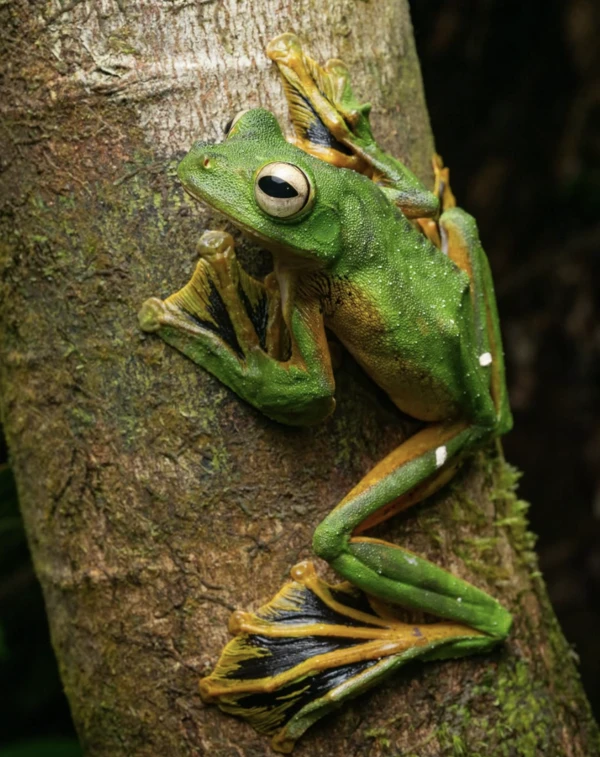
4. Black-handed tree frog: A frog that can fly.
The black-handed tree frog ( Rhacophorus nigropalmatus ) is a unique type of frog capable of gliding from trees, a characteristic that makes it a distinctive member of the amphibian family. It inhabits the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, primarily distributed in Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand. Its back is typically bright green, while its belly is white or pale yellow, creating a striking visual contrast. The black-handed tree frog is of moderate size, with adults typically measuring 5 to 7 centimeters in length.
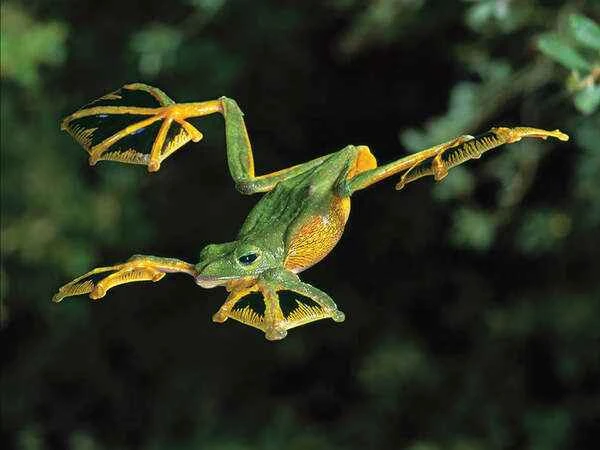

Most remarkably, the black-handed tree frog can glide between trees using the large webbing on its hind limbs and feet. As they leap between branches, the webbing on their hind limbs unfolds, allowing them to glide like paragliders, sometimes covering distances of several meters. This gliding ability is a crucial means for them to evade predators and a survival strategy adapted to their forest environment.
Furthermore, the black-handed tree frog has a unique reproductive method. The female frog lays her eggs on damp leaves, and after the tadpoles hatch, they slide off the leaves into the water. Black-handed tree frogs typically live near slow-flowing streams, and they have very high requirements for environmental humidity, especially during the breeding season. The quality and quantity of water directly affect their reproductive success rate.

5. Madagascar Rainbow Frog: A Colorful "Picasso"
The Madagascar rainbow frog ( Scaphiophryne gotlebei ) is a small frog, typically 5 to 6 centimeters in length, mainly distributed in the humid forests and streamside areas of Madagascar. Their most distinctive feature is their vibrant colors, including bright yellow, orange, red, and black, resembling an "abstract painting" in nature. This coloration not only makes the Madagascar rainbow frog visually appealing, but the color variations also likely serve as camouflage in their environment.
The Madagascar rainbow frog's call is particularly loud during the breeding season. Males typically emit a continuous, high-pitched call at night to attract females. Their breeding usually takes place around water, with eggs attached to the leaves of aquatic plants. After hatching, the tadpoles enter the water and begin their aquatic life. Despite their small size, the Madagascar rainbow frog's vibrant colors and calls secure them a place in the ecosystem, making them a highlight of the forest.
6. Vampire Flying Frog: A frog with tusks
The vampy frog ( Rhacophorus vampyrus ) is a very unique tree frog, first discovered in the misty forests of Vietnam. Known for its mysterious name, the "vampy" aspect of the frog doesn't refer to actual blood-sucking behavior, but rather to the special structure of its teeth. This tree frog is only 5 centimeters long, small in size, but possesses sharp, pointed teeth, seemingly developed as special weapons for defense and predation during evolution.
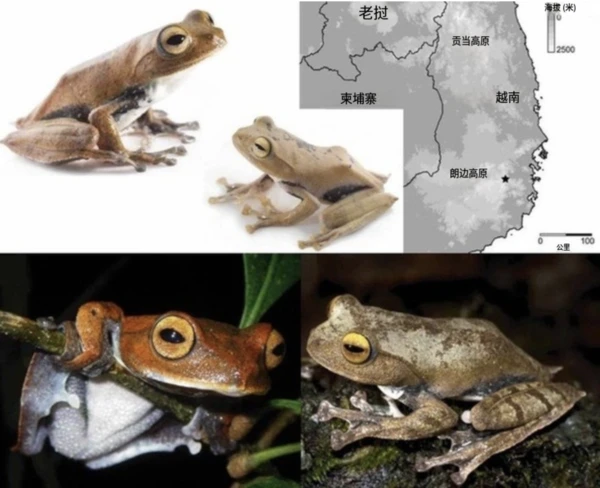

The vampire flying frog has a very unique tooth shape. Its teeth are not only sharp but also densely packed, resembling canines, which allows it to easily catch small insects and even other smaller frogs. When hunting, it quickly bites its prey and then swallows it with its flexible tongue. Vampire flying frogs are typically green or yellow, with smooth skin and a small body, but they possess exceptionally agile hunting skills.
These frogs primarily inhabit humid tropical forests, preferring to live on damp leaves, especially near streams and bodies of water. Their reproductive behavior is quite unique: the female lays her eggs on damp leaves, and the hatched tadpoles jump into the water to continue growing. Due to their habitat specificity, the vampire frog faces threats from habitat destruction and environmental change. Nevertheless, their unique physiological characteristics and adaptability give them a distinctive place among amphibians.
7. Pitcher Plant Frog: The world's smallest frog
The pitcher frog ( Microhyla nepenthicola ) is one of the smallest frogs in the world and one of the smallest frog species, with adults measuring only 1.1 cm in length. They live in pitcher plant wetlands in Malaysia and primarily inhabit pitcher plants. These tiny frogs depend on the environment provided by pitcher plants for survival, especially the moist conditions and abundant insect resources they offer.
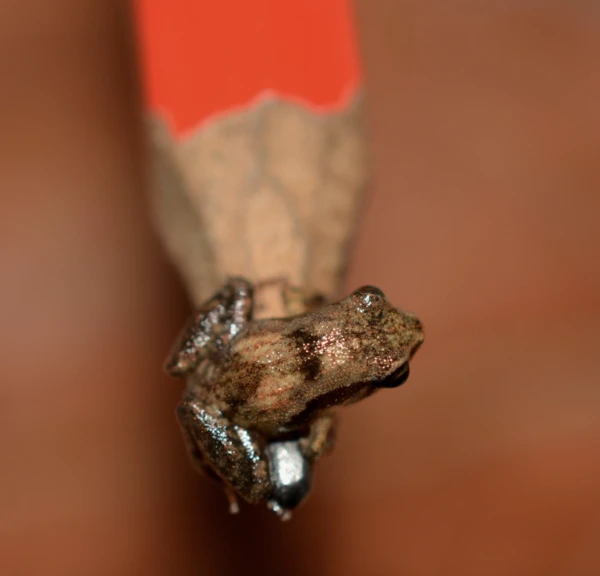

The pitcher plant frog is typically dark green or brown, blending well with its habitat—the leaves of the pitcher plant—providing excellent camouflage. The pitcher plant is a carnivorous plant whose leaves form a pitcher-like structure to trap insects. The pitcher plant frog uses this structure to avoid predators and find food within. The pitcher plant's leaves provide a rich source of insects; these small frogs feed on insects and are occasionally attracted to the plant's sticky substance, but their agile jumping ability allows them to avoid being swallowed by the plant.
Despite their tiny size, the pitcher plant frog reproduces similarly to other frogs, laying its eggs on damp leaves, and the hatched tadpoles slide into nearby water. Their existence demonstrates the complexity of countless micro-ecosystems in nature and reminds us that even the smallest species play a vital role in ecosystems.
8. African Giant Frog: The largest frog on Earth
The African giant frog ( Conraua goliath ) is one of the largest frogs in the world, with adults reaching up to 32 centimeters in length and weighing over 3 kilograms. They inhabit the tropical rainforests of Africa, particularly the rivers and lakes of Nigeria and Cameroon. Their enormous size makes them behemoths among amphibians, possessing immense strength and exceptional hunting skills.
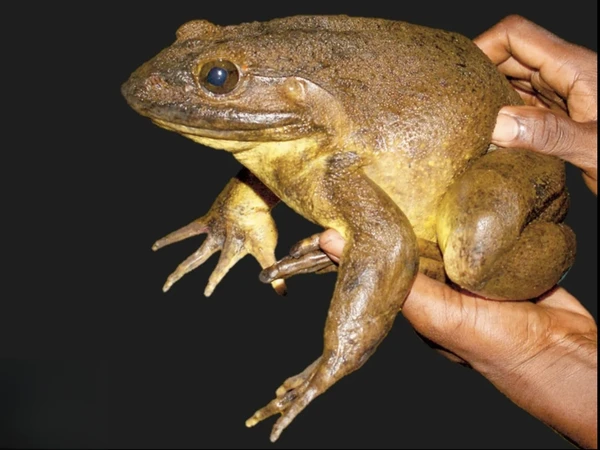

African giant frogs are extremely robust, with powerfully muscular hind legs that allow them to leap across the water to hunt aquatic animals and even small mammals or birds. Their forelimbs and mouthparts are also very strong, helping them to grasp and swallow their prey. Their skin is dark green or brown, often with irregular spots or stripes, allowing them to blend well into their environment of plants and rocks.

Despite their enormous size, the African giant frog's reproductive behavior is similar to that of other frogs. Males attract females with deep calls, and during the breeding season, they lay numerous eggs near the water's edge. The hatched tadpoles quickly enter the water to continue growing. These giant frogs face survival pressures due to habitat loss and climate change, making their conservation particularly important.
9. Hairy Frog: From Fractured Bones to Self-Defense – The "King of Hair"
The robust frog ( Trichobatrachus robustus ), also known as the hair frog, fracture frog, hairy frog, wolverine frog, terror frog, or hairy frog, is a very unique frog. They are mainly distributed in the tropical rainforests of Central Africa, and are relatively large, reaching up to 13 centimeters in length. Most striking are the hair-like structures on their backs and limbs; these "hairs" are not actually hair, but rather raised skin structures.
The most distinctive feature of the hairy frog is that when it feels threatened, it forms fracture-like cracks in its skeleton, exposing its hair-like structures. These hair-like structures not only serve as camouflage but may also be one of its defense mechanisms, helping it avoid harm when encountering predators. Furthermore, these hairs may also help it retain moisture in humid environments, enhancing its adaptability.
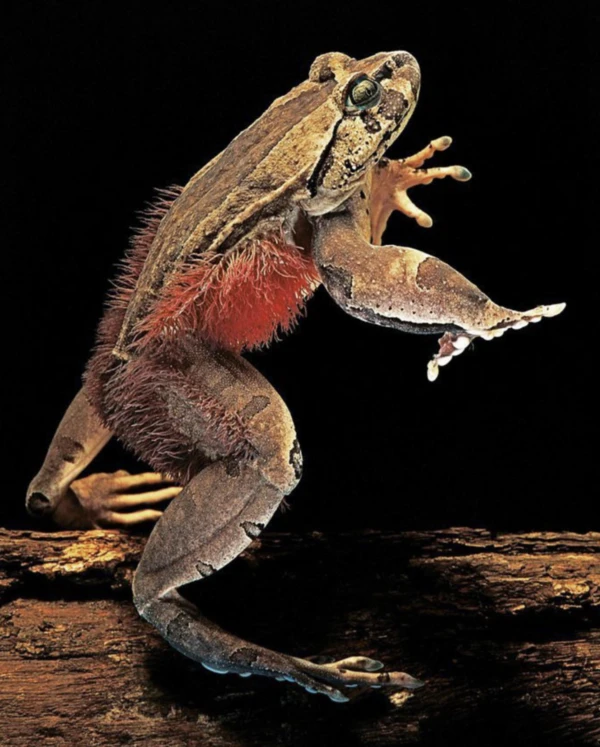

The hairy frog typically inhabits damp forest areas, inhabiting moist soil. During the day, it hides in the mud or under tree roots, emerging at night to forage. Its reproductive behavior is similar to other frogs; the male attracts the female with its calls, and the eggs are laid in damp soil or near water. Due to its unique appearance and physiological characteristics, the hairy frog has become a "strange star" in nature, and scientific research on it has revealed the vastness and wonder of biodiversity in the natural world.
10. African Bullfrog: A tough survivor and predator
The African bullhead frog ( Pyxicephalus adspersus ), also known as the African bullfrog, is the second largest frog in the world. Males can weigh over 2 kg (4.4 lbs) and reach 23 cm (9.1 inches) in length, while females are only half the size of the males. They are very robust frogs found in the grasslands and deserts of Africa. They are famous for their thick bodies, powerful leg muscles, and distinctive "box-head" shape. The African bullhead frog is enormous, reaching up to 25 cm in length and weighing a considerable amount. It possesses exceptional hunting abilities, capable of preying on almost any swallowable prey, including small mammals, birds, and insects.
The African bullhead frog feeds on insects, small rodents, reptiles, birds, and other amphibians. Cannibalism is also observed, with males occasionally eating the tadpoles they are protecting. They have a voracious appetite; one African bullhead frog at the Pretoria Zoo in South Africa once ate 17 small spitting snakes. They emit loud calls when stressed and will attack enemies with their sharp teeth when threatened; there are records of humans being bitten by them.

Their skin is brown or green with irregular spots on their backs, allowing them to camouflage themselves in arid grasslands and bushes, avoiding attacks from predators. The African bullhead frog has a very large mouth, capable of holding large prey, and its powerful limbs make it exceptionally agile when hunting. They can leap several meters, forcefully grab their prey, and swallow it whole.
The breeding of the African bullhead frog typically occurs in seasonal ponds or humid environments. Male frogs attract females with loud calls, and after laying eggs, the eggs hatch in the water, and the tadpoles grow into adult frogs. Their robust survival skills allow them to survive in extremely harsh environments, making them formidable predators in nature.
Conclusion
These frogs are not only amazing for their unique appearance, but their physiological characteristics, behaviors, and survival strategies also provide scientists with valuable research material. From the long tusks of the vampire flying frog to the formidable hunting prowess of the African bullhead frog, each frog species demonstrates the boundless creativity and adaptability of nature. Their existence not only enriches ecological diversity but also provides us with valuable biological research resources, deserving our greater attention and protection.