All living things in nature are called organisms. Generally speaking, organisms can be divided into three main categories: plants, animals, and microorganisms.

Starfish - a type of echinoderm
There are approximately 300,000 known plant species, which can be broadly classified into algae, fungi, lichens, mosses, ferns, and seed plants. Most plants utilize sunlight through photosynthesis to obtain the energy they need for life, while simultaneously producing organic matter from inorganic substances such as water, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts, and releasing oxygen; these plants are called autotrophic plants. Some plants (such as fungi) can decompose existing organic matter to provide energy, releasing carbon dioxide and water. Autotrophic plants are the producers of organic matter and energy in the entire ecosystem, and therefore constitute the most fundamental link in the material cycle and energy flow of the ecosystem.
Spirogyra - a type of algae

Silver ear fungus - a type of edible fungus

lichen

moss
There are approximately one million known animal species, which can be divided into major groups such as protozoa, sponges, coelenterates, flatworms, nematodes, annelids, mollusks, arthropods, echinoderms, and chordates. Animals generally cannot synthesize organic matter from inorganic matter and can only rely on plants, other animals, or microorganisms as food to provide nutrition and energy for various life activities.

fern

Seed plants

A protozoan - Paramecium
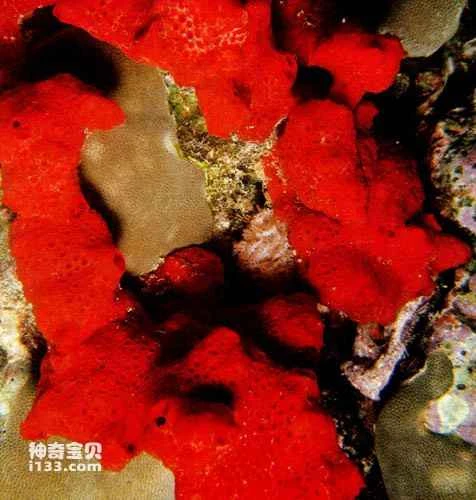

sponge
Microorganisms, including bacteria, actinomycetes, molds, yeasts, spirochetes, rickettsiae, mycoplasma, and viruses, are all tiny, simple single-celled or multicellular organisms, with viruses even lacking cellular structure altogether. The vast majority of microorganisms are so small that they can only be observed with a microscope, or even an electron microscope. On Earth, traces of microorganisms are everywhere—in the air, water, soil, on the surface of various organic matter, and within the bodies of organisms. Microorganisms exhibit a wide variety of life activities and reproduce at an exceptionally rapid rate, thus playing a vital role in the material transformation and energy flow of Earth's ecosystems.
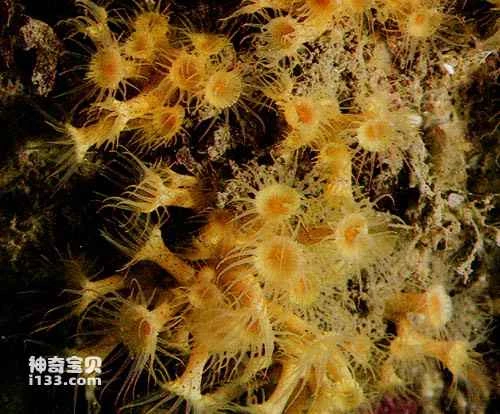

A type of coelenterate - coral

An annelid - earthworm

Snails are a type of mollusk.

Dragonfly - a type of arthropod


