Leopards, cheetahs (Guepardo, also known as "Cheetahs"), and jaguars all belong to the large cat family. They are all top predators with spotted fur and extremely powerful hunting abilities, which often leads to confusion. Many people struggle to accurately distinguish these three predators, especially when looking at photographs, where they are easily mistaken for one another. In fact, they differ significantly in size, coat color and pattern, distribution range, hunting methods, and temperament.
Understanding these differences not only deepens our knowledge of wildlife but also greatly helps in identifying these animals when traveling to the relevant countries. The scientific names of the three are:
Leopard : Panthera pardus
Cheetah : Acinonyx jubatus
Jaguar : Panthera onca
Below, we will comprehensively compare these three felines from the perspectives of appearance, distribution, hunting methods, and interesting facts.

I. Differences in appearance
1. Body type and weight
Cheetah : With long limbs, a tall and slender body, a shoulder height of about 70–90 cm, and a weight of 35–60 kg, it is well-suited for running.
Leopard : Relatively compact in build, with a shoulder height of about 45–78 cm and a weight of 30–90 kg.
Jaguar : The most robust in build, with a shoulder height of 75–85 cm and a weight of 50–100 kg or more. It has well-developed muscles and a robust skeleton.
2. Species classification
Leopards and jaguars belong to the same genus, Panthera , and are close relatives of lions and tigers.
The cheetah is the only surviving member of the genus Acinonyx , making it an "outlier" in the cat family.
It is worth mentioning that the so-called "black panther" is not a separate species, but a melanized individual of a leopard or jaguar (with "melanin deposition" and the pattern can still be vaguely seen).
3. Fur and markings
Cheetah : Its entire body is covered with individual black dots, and there are two black tear streaks from the corners of its eyes to the corners of its mouth.
Leopard : The pattern is a hollow "rose spot", with brownish-yellow patches surrounded by black circles, and the spots are of varying sizes.
Jaguar : Its stripes are similar to those of a leopard, but the patches are larger, and there is often a small dot in the black circle, making it look more imposing.
4. Claws
Cheetah : Its claws are semi-non-retractable , more like those of canines, making them suitable for gripping the ground while running at high speeds.
Leopards and jaguars : Their claws are fully retractable, making it easy for them to climb trees and grip their prey.
5. Speed and Power
Cheetah : The fastest land animal in the world, it can accelerate from 0 to 100 km/h in 3 seconds, and can reach a top speed of 110–120 km/h, but it has poor endurance and can only sprint for short distances.
Leopard : Not as fast as the cheetah, but agile and nimble, and good at climbing.
Jaguar : The strongest, with an amazing bite force, enough to crush a tortoise shell.
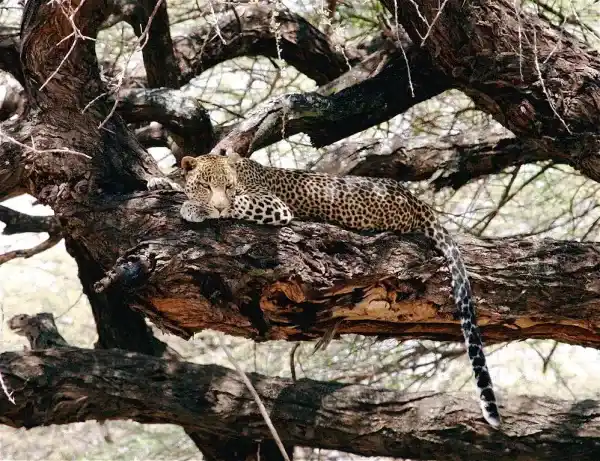

II. Distribution and Habitat
Cheetah : Mainly distributed in the savannahs of central and southeastern Africa, with a few subspecies found in Asia (Iran), where their numbers are extremely small.
Leopard : It has an extremely wide distribution, from Africa to South Asia, Southeast Asia, and even to the Russian Far East, with diverse habitats (grasslands, forests, and mountains).
Jaguar : Distributed throughout the Americas, from Mexico to Argentina, mainly living in tropical rainforests, wetlands and river valleys.
Therefore, cheetahs and leopards have overlapping distributions in parts of Africa, while jaguars live entirely in the New World.
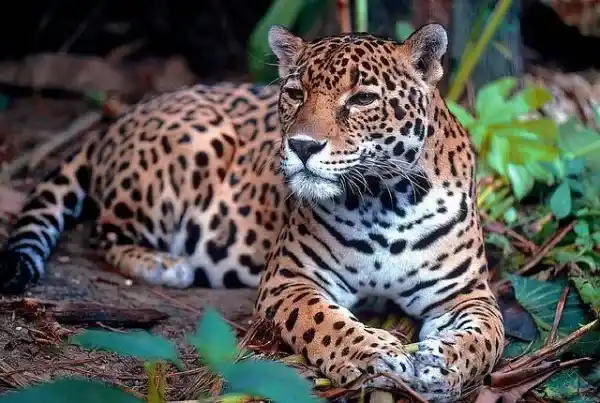

III. Differences in hunting methods
Cheetahs rely entirely on high-speed sprints to hunt prey, typically during the day, primarily targeting small to medium-sized antelopes. Due to limited stamina, they must eat quickly, otherwise their spoils will be stolen by hyenas or lions.
Leopard : Possessing both strength and agility, it can actively hunt and also scaveng. It often drags its prey up trees to prevent other predators from stealing it. It hunts flexibly, both day and night.
Jaguars : They hunt mostly at dusk or night, are adept at ambush in water, and prefer to prey on capybaras, caimans, and turtles. Their powerful bite can penetrate the skull or shell of their prey.

IV. Fun Facts
The jaguar is the third largest cat species in the world, after the tiger and the lion.
Cheetah cubs have a low survival rate, and artificial breeding is very difficult.
Jaguars can swim and climb trees, making them one of the few large cat species that are both amphibious and aquatic.
Leopards are extremely adaptable to their environment and are known as "stealth hunters".
Cheetahs, being relatively docile, were once kept as "exotic pets," which also made them targets for poaching.

V. Summary and Comparison Table
| feature | Cheetah ( Acinonyx jubatus ) | Leopard ( Panthera pardus ) | Jaguar ( Panthera onca ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| body shape | Tall and slender, the lightest | medium | The most robust and muscular |
| weight | 35–60 kg | 30–90 kg | 50–100+ kg |
| speed | Fastest, 110–120 km/h | medium | Slower pace, primarily based on strength |
| paw | Semi-inflexible | Scalable | Scalable |
| stripes | Black dots + tear stain lines | Rose-shaped pattern | Large rose spots with small dots inside. |
| Habitat | African savanna, a few Asian | Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia | Central America and South America |
| hunting methods | Daytime sprint hunting | Agile, often dragging prey up trees | It ambushes at night and has an extremely strong bite force. |
| character | Relatively docile, curious | Cautious and stealthy, highly adaptable | Fierce and daring to hunt in the water |
In summary, the differences between the three are: cheetahs rely on speed, leopards on agility, and jaguars on strength . Although they all have spots on their bodies, they can be easily distinguished by careful observation of their body shape, patterns, and behavior.