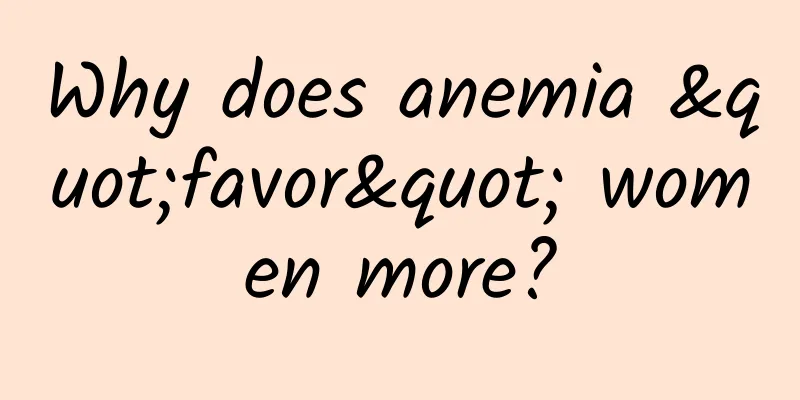One of the hardiest plants on Earth, this moss could be the key to future Mars colonization

|
Tuchong Creative In the grand blueprint of human exploration of the universe, Mars has always been one of our most desired goals. However, the environment of this red planet is extremely harsh for life on Earth: thin atmosphere, extreme temperature changes, strong radiation and lack of liquid water. How to establish a human habitat in such an environment is a question that scientists have been thinking about. Now, a kind of life from the harshest environment on Earth is opening up a new idea for us - it is the desert moss Erythromyces dentata. Syntrichia caninervis is a bryophyte commonly found in desert areas. It is widely distributed in arid, high-altitude and polar regions around the world, such as the Gurbantunggut Desert, Tengger Desert, Pamir Plateau in China, and Mojave Desert in the United States. This inconspicuous little plant is providing important inspiration for human exploration of space and even the establishment of a base on Mars in the future. Zhang Daoyuan, a researcher at the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his team conducted a series of extreme tests on Erythromyces dentata, and the results were amazing: Super strong dehydration tolerance: Even if it loses more than 99% of its cellular water, it can resume photosynthesis within a few seconds after reabsorbing water. In the experiment, it was observed that completely dry black moss body regained green color in just 2 seconds after contact with water, recovered more than 80% of its water content within 20 seconds, and fully restored its photosynthesis capacity within 2 minutes. This ability to "resurrect from the dead" allows Erythromyces serrulate to survive in long-term drought environments. Excellent freezing resistance: It can survive and regenerate after being frozen at -80℃ for 5 years or stored in liquid nitrogen (-196℃) for 1 month. This feature not only demonstrates the adaptability of Erythromyces dentata to extreme low temperatures. It is worth noting that even in a fully hydrated state (100% water content), it still shows considerable freezing resistance, although the survival rate and regeneration ability are slightly lower than those in a dry state. Amazing radiation resistance: It can withstand up to 5000 grays of gamma rays, which is more than five times the limit of ordinary plants. Its radiation resistance is comparable to that of the popular tardigrades (commonly known as "water bears"). Tolerance to multiple extreme environments: It can survive for 7 days and resume growth in a simulated Martian environment (low temperature, 95% CO2 hypoxia, dryness, and strong ultraviolet light). This test best illustrates the potential of Erythromyces serrulate as a pioneer plant on Mars. In a simulated Martian environment, Erythromyces serrulate not only survives, but also grows again after returning to normal growth conditions, showing incredible vitality. So how does Erythromyces dentata do this? Researchers have found that the amazing ability of this moss stems from its unique morphological structure, physiological biochemistry and molecular adaptation mechanisms: First, in terms of morphology, Erythromyces serrulates has evolved a series of characteristics that adapt to extremely arid environments. Its leaves can curl up when dry, reducing the surface area for water evaporation. The white tips of the leaves can not only reflect strong light, but also improve water use efficiency. These characteristics enable Erythromyces serrulates to survive in extremely arid and strong light environments. Secondly, at the physiological and biochemical level, Erythromyces serrulates also has a unique adaptation mechanism. Under stress conditions, it enters a selective metabolic dormancy state to strategically preserve key metabolites. For example, under extreme stress conditions, Erythromyces serrulates maintain high levels of sucrose and maltose, which not only act as osmotic regulators and protectors to help maintain cell structure, but also provide energy for rapid recovery after extreme stress is relieved. In addition, Erythromyces serrulates also has a strong ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species, and responds to stress by accumulating high levels of catalase, glutathione S-transferase, and peroxidase. At the molecular level, the multiple stress tolerance of E. corymbosa involves complex regulatory mechanisms. Studies have found that the expansion of stress-related late embryogenesis abundant protein (LEA) genes and catalase genes, as well as the tandem duplication of genes encoding photoprotective early light-induced proteins (ELIPs), are important molecular bases for the extreme environment of E. corymbosa. Under extreme stress conditions, these regulatory mechanisms also involve the precise regulation of genes and proteins related to key processes such as photosynthesis, protein stability, antioxidant defense and cell repair. These characteristics of Erythromyces serrulate make it an ideal pioneer plant for future Mars immigrants. Not only can it adapt to the harsh environmental conditions on Mars, it can also produce oxygen through photosynthesis, fix carbon, improve the soil, and create living conditions for other organisms. On Earth, Erythromyces serrulate is an important component of biological soil crust and plays a vital role in desert ecosystems. They can stabilize the surface of sand, enhance the soil's water retention capacity, and provide nutrients to poor desert soils through biological nitrogen fixation. These characteristics make Erythromyces serrulate an ideal candidate for transforming the Martian environment. In addition, the genes of Erythromyces serrulate may also be used to cultivate crops with stronger stress resistance. Through genetic engineering technology, we may develop new crops that can grow in extreme environments, which can not only cope with the increasingly severe environmental changes on Earth, but also provide a source of food for future interstellar immigrants. Although humans still have a long way to go to establish a self-sufficient habitat on Mars, the study of Erythromyces serrulates has opened up a new way of thinking for us. In the future, this tiny plant may really be taken to Mars or the Moon for field testing, contributing to the cause of human interstellar migration. With the success of China's "Tianwen-1" and other Mars exploration missions, I believe that in the near future, we will be able to see Erythromyces serrulates growing on the red planet, paving the way for human migration to Mars. The study of Erythromyces dentata is not only of great significance to interstellar exploration, but also has important implications for environmental protection and ecological restoration on Earth. In the context of global climate change, understanding and utilizing the survival strategies of these extreme environment organisms may provide us with new ideas and methods to cope with increasingly severe environmental challenges. The story of Erythromyces dentata is the perfect combination of human wisdom and the miracles of nature, illustrating the tenacity of life and the infinite possibilities of scientific exploration. This article is a work supported by the Science Popularization China Creation Cultivation Program Author: Yang Qilin, PhD, Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Reviewer: Wang Kang, Director of Beijing Botanical Garden Science Center, Professor-level Senior Engineer; Gu Lei, Associate Professor of School of Life Sciences, Capital Normal University Produced by: China Association for Science and Technology Department of Science Popularization Producer: China Science and Technology Press Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhongke Xinghe Culture Media Co., Ltd. |
>>: Why do so many people have this "nail house" in their stomachs?
Recommend
Why do you start reviewing a fight you didn't win during the day as soon as you take a shower?
Review expert: Yin Tielun, deputy chief physician...
[Pure practical information] Are you still worried about lack of inspiration? Click me, click me...
Many people encounter times when they can’t think...
Long-term fatigue after Yang Kang, beware of "catching COVID-19"!
More and more people say that they experience sym...
How to set keywords for iOS APP titles and find the right length and keywords
Today’s article is about the length of iOS APP na...
These phones can be upgraded to Android 5.0, but yours can't?
According to the information we have received so ...
Learn how to optimize information flow ads in one article! Applicable to all industries
Many friends asked: I have been working as an opt...
Take a sneak peek at the majestic figure of “Kuafu” and look forward to the feat of “chasing the sun” in the future!
The sun is the source of life and the symbol of l...
How to start live streaming sales for brands? Brand self-broadcasting full process design
This article is divided into three parts: 1. Full...
China Automobile Dealers Association: Analysis of vehicle data for “Xing” certification week testing and certification
Affected by the continued impact of the local epi...
Why can't the cyclamen I grow with five rabbit ears bloom?
Look at the picture below. Do these pink and tend...
A new way to play Douyin information flow ads, one-click direct access to the landing page!
From immersive viewing scenarios to capture users...
A new "sentinel" on the vast green sea! See how Beidou protects forests and grasses!
At present, the connection between Beidou and for...
Those popular internet buzzwords were actually written as Spring Festival couplets, hahahahaha…
The Spring Festival is coming again, and the Spri...
World Thyroid Day | As the saying goes, “Anger harms the body”, are thyroid nodules really caused by anger?
□ Gao Hongkai May 25th is World Thyroid Day. The ...
Testin Cloud Testing and Chukong Strategic Cooperation: Helping North American Developers Improve Game Quality
Testin, the world's largest real-device cloud...