The skeleton is the backbone of a living organism, bearing body weight, protecting internal organs, and enabling us to move. While human and animal skeletal systems share similarities, they exhibit significant differences due to varying lifestyles and evolutionary paths. This article will comprehensively analyze the similarities and differences between human and animal skeletons, helping you understand the mysteries of the skeleton.
Table of contents
Basic concepts of the skeletal system
The main differences between human and animal skeletons
Similarities between human and animal skeletons
An Adaptive Analysis of Skeletal Evolution
Detailed comparison of specific parts of human and animal skeletons
Skull structure
Spinal characteristics
Limb function
Human vs. Animal Skeleton Comparison Table
Frequently Asked Questions
in conclusion
1. Basic Concepts of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the internal framework of an organism, consisting of bones, cartilage, joints, and ligaments.
Main functions:
Support: Provides the shape and framework of the body.
Protection: Protecting internal organs, such as the skull protecting the brain and the chest cavity protecting the heart and lungs.
Movement: Bones achieve a variety of movements through the cooperation of joints and muscles.
Storage: Storing minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
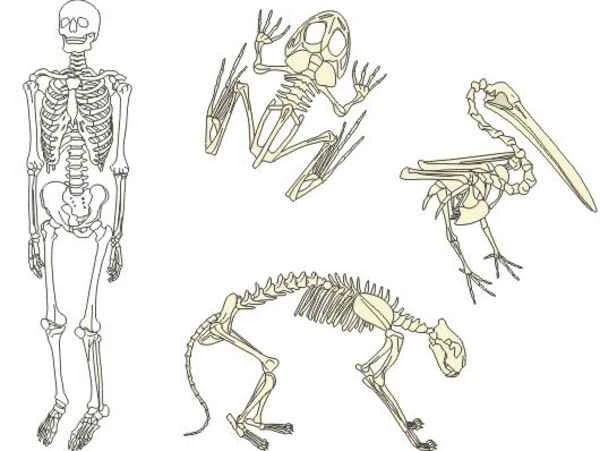
2. The main differences between human and animal skeletons
(1) Postural differences:
Humans: walk upright, have skeletons adapted to the distribution of gravity, wide pelvis, and an "S"-shaped spine.
Animals: Most walk on four legs, while some animals are adapted to flight (such as birds) or swimming (such as fish).
(2) Bone density:
Humans: Have denser bones that support standing and daily activities.
Animals: Bone density varies as needed; for example, birds have hollow bones to reduce weight during flight.
(3) Skull characteristics:
Humans: The skull is relatively large, housing a well-developed brain, while the jawbone is relatively small, adapted to an omnivorous diet.
Animals: Based on their dietary needs, predatory animals (such as lions) have strong jaws, while herbivores (such as deer) have wide jaws.
(4) Differences in limbs:
Humans: short upper limbs, long lower limbs, dexterous fingers, and the ability to oppose fingers.
Animals: Limbs are adapted to different environments, such as the hooves of horses for running and the flippers of whales for swimming.
3. Similarities between human and animal skeletons
Although humans and animals have many differences in their skeletons, their basic structure and function are very similar.
Shared skeletal framework:
Humans and most animals are vertebrates, and their skeletal system includes the skull, vertebrae, ribs, and limb bones.The exercise methods are similar:
The mechanisms by which bones, joints, and muscles work together are similar, and their principles of movement are consistent.Protective function:
In both cases, the skeleton plays a role in protecting internal organs; for example, the ribs protect the heart and lungs.
4. An Adaptive Analysis of Skeletal Evolution
(1) Evolution of the human skeleton:
Walking upright widens the pelvis, causing the spine to form an "S" shape to cushion the pressure.
The extended lower limbs freed up the hands for tool operation and fine labor.
(2) Evolution of animal skeletons:
Flying animals: have lightweight and hollow skeletons, such as birds.
Aquatic animals: with smooth skeletons and flippers that facilitate swimming in water, such as whales and dolphins.
Predators: Powerful jaws and sharp teeth are key features of their skeletal evolution.
5. Detailed comparison of specific parts of human and animal skeletons
(1) Skull structure
Humans:
The human skull is round, with a large brain capacity and a high forehead. The jaw is small and lacks canine teeth, which is adapted to complex language communication and a diverse diet.animal:
Predatory animals like tigers have strong jaws and well-developed canines. Herbivores like cattle have broad jaws and well-developed chewing muscles.
(2) Characteristics of the spine
Humans:
The human spine has an "S"-shaped curve, which helps to mitigate the impact of walking upright.animal:
Animals have straighter spines, adapted to quadrupedal walking or other modes of locomotion.
(3) Limb function
Humans:
The legs support the body weight, and the arms are flexible, making it easy to grasp and operate tools.animal:
Different animals have specialized limbs: birds have wings for flight, horses have strong hooves for high-speed running, and monkeys' tails can also be used as a "fifth limb".
6. Comparison table of human vs. animal skeletons
| feature | Human skeleton | animal bones |
|---|---|---|
| posture | Bipedal walking | Quadrupedalism or other specializations (flight, swimming, etc.) |
| skull | Round shape, large brain capacity | Diverse, with obvious hunting or chewing functions |
| Spine | The "S" shape supports upright posture. | Horizontal, adaptable to four-legged stability |
| limbs | Dexterity of the fingers facilitates tool use. | Adaptations to the environment, such as wings, flippers, or claws. |
| Bone density | High-density support upright | Bird bones are becoming lighter as needs change. |
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is the human skeleton adapted for upright walking?
A: Because humans have wide pelvises, an "S"-shaped spine, and strong and long lower limb bones, they can support an upright posture and mitigate the impact of gravity.
Q: Do animal skeletons also have hollow structures?
A: Yes, for example, birds have hollow skeletons to reduce weight during flight while maintaining a certain level of strength.
Q: Which animals have skeletons that are most similar to humans?
A: The skeletal structure of primates (such as orangutans and gorillas) is most similar to that of humans, especially the limb bones and skull.
8. Conclusion
Human and animal skeletons share many similarities in function and structure, while also demonstrating their unique adaptations. A deeper understanding of the skeletal system allows us not only to better understand humans themselves but also to comprehend the diversity of other organisms in nature.
In summary, bones are the foundation of life, and the different skeletons of different species are the masterpieces of natural selection. Let's continue to explore these fascinating biological secrets!


