Introduction: Understanding Animal Instincts
What are animal instincts?
Animal instincts are generally defined as behaviors that occur naturally in response to specific stimuli, without learning or conscious thought. These behaviors are usually fixed, meaning they follow specific patterns and do not deviate from them. For example, instinctive animal behaviors include:
Courtship rituals : Many animals follow specific courtship behaviors, such as the elaborate dance of the bird of paradise or the nesting behavior of the beaver.
Migration : Birds and other animals migrate long distances without any prior training.
Hunting and foraging : Predators instinctively know how to hunt, ambush, and capture prey.
Parental care : Many animals (such as mammals and birds) exhibit instinctive behaviors to care for and protect their offspring.
But are animal instincts hereditary ? To answer this question, we need to understand more deeply the nature of instincts and how they are passed down through generations.
The genetic basis of animal instincts
Are animal instincts hereditary?
When we ask whether animal instincts are hereditary , we are actually asking whether these behaviors are encoded in the animal's DNA. While not all behaviors are purely instinctive, many animal instincts are indeed hereditary. They are passed down from one generation to the next through genes, ensuring that the species can perform the basic functions of survival and reproduction.
The idea of inherited instincts is supported by research in animal behavior and genetics. Studies show that many animal behaviors appear to be innate rather than learned, indicating a strong influence of genes on these behaviors. For example:
Salmon migration : Salmon are born in freshwater rivers, but when they mature, they instinctively swim to the sea and then return to the same river to reproduce. This behavior is hard-coded into their genes.
Birds building nests : For example, robins instinctively build nests in a specific way, even though they are never taught how to do so by their parents.
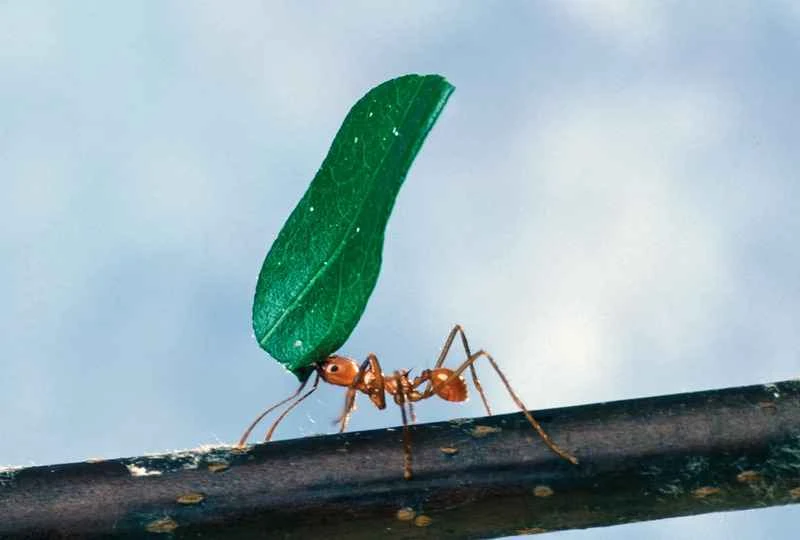
Ant foraging behavior : Ants are born knowing how to find food, communicate through pheromones, and contribute to the success of the colony.
Although these behaviors are consistent within a species, they can still be influenced by environmental factors, which complicates the question of whether animal instincts are hereditary .
How genes shape animal instincts
How do genes influence instinctive behaviors?
To understand whether animal instincts are hereditary , we must first explore how genes influence behavior. Genes are biological instructions that guide the development of organisms, and they play a crucial role in shaping instinctive behaviors. Here are some ways genes influence animal instincts:
Hereditary behavior : Certain behaviors are passed down to offspring through genes. These behaviors are usually essential for survival and reproduction, and thus have been preserved through long-term natural selection.
Neurobiological pathways : Specific genes influence the development of neural circuits in the brain, which in turn guide behavior. For example, newborn birds are born knowing how to peck at food thanks to neural pathways in the brain that are influenced by genetic factors.
Hormonal Influence : Hormones are influenced by genes and play a crucial role in regulating animal instincts. For example, mating behavior in many animals is triggered by hormonal changes that are pre-programmed by genes.
In some cases, genes may not directly encode a particular behavior, but rather support that behavior by influencing the development of physiological systems. For example, the migratory instinct in birds may not be a learned behavior, but a natural response to environmental cues (such as daylight hours) that are linked to genetic mechanisms.
Are animal instincts inherited or learned?
The role of learning in animal instincts
While a large portion of animal behavior is determined by genes, some instincts are improved or enhanced through learning. So, are animal instincts inherited , or do environmental factors also play a role in shaping behavior? The truth is, it's usually a combination of both.
Instincts provide a basic blueprint for behavior, but the environment can influence the expression of these instincts. For example, a dog's maternal instincts may be triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy, but the quality of a mother's care for her puppies may be influenced by her experiences.
Here are a few examples of learning how to interact with instincts:
Nurturing behavior in mammals : Although the basic instinct to care for offspring is inherited, the manner and level of care can be learned through interaction with other individuals.
Birdsong : Male birds are born knowing how to sing to attract mates. However, they often learn specific melodies by learning particular songs from adult males. The song itself is an instinctive behavior, but the specific melody is acquired through learning.
Escaping predators : Many animals, such as rodents, have an instinctive fear of certain predators, such as snakes. However, the intensity of this fear can increase through learned experiences, such as witnessing other animals being preyed upon.
The interaction between genes and learning helps animals adapt to their specific environments and increase their chances of survival.
How does evolution affect animal instincts?
Survival through evolution and instinct
Looking at it from an evolutionary perspective can help us understand the heritability of animal instincts. Are animal instincts inherited ? The answer is yes—many animal instinctive behaviors have evolved over millions of years. Evolution favors behaviors that increase an organism's chances of survival and reproduction, and these behaviors are encoded in its genes.
Consider the following examples of how evolution has shaped instinctive behavior:
The predator-prey relationship : Animals as prey evolve instinctive escape or fight responses. These instincts help them avoid becoming food for predators, thus ensuring their survival and reproduction.
Reproductive behavior : Mating rituals and courtship behaviors in many species are instinctive because they increase the success rate of reproduction. For example, male peacocks attract females by displaying their colorful plumage, a behavior that is an instinct passed down through their genes.
Survival strategies : Animals like meerkats have evolved complex social structures in which instinctive behaviors, such as guard duties and group cooperation, help the species thrive in harsh environments.
These evolutionary adaptations demonstrate that animal instincts are indeed rooted in genetic inheritance and passed down from generation to generation through natural selection.
The complexity of animal instincts
The role of epigenetics in animal instincts
While the answer to the question of whether animal instincts are inherited is yes—most instincts are inherited—the complete picture is much more complex. Epigenetics, that is, changes in gene expression caused by environmental factors, also plays a role in shaping animal instincts.
Epigenetic changes can alter gene expression but do not change the genes themselves. These changes can affect behavior, especially in response to environmental stress or change. For example:
Parenting behavior : In some species, the environment in which parents grow up influences how they care for their offspring. Animals living in stressful environments may develop more protective instincts.
Fear response : Some animals may pass on learned behaviors to their offspring through epigenetic mechanisms. For example, if a female mouse experiences a stressful event, its offspring may inherit a stronger fear response, even if they did not directly experience the event.
These epigenetic discoveries make it clearer that animal instincts are not a single genetic process, but a complex phenomenon involving a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Conclusion: Are animal instincts inherited?
From the perspective of the heritability of instinctive behavior, whether animal instincts are inherited is indeed a complex question. Although many animal behaviors are encoded by genes and are widespread across species, they can also be influenced by learning, environmental changes, and evolutionary pressures.
Therefore, animal instincts are both inherited and can be adjusted according to environmental changes during evolution. Inherited instincts provide the foundation for animal survival, while learning and adaptation help them cope with changing environments. When discussing animal behavior, we must not only focus on genes but also consider how the external environment and evolutionary history jointly shape these behaviors.