In short: polar bears generally have the upper hand in sea ice environments and are also larger; grizzly bears (brown bears) are more agile and stronger in terrestrial environments. Which is more "fierce" depends on the terrain and situation .
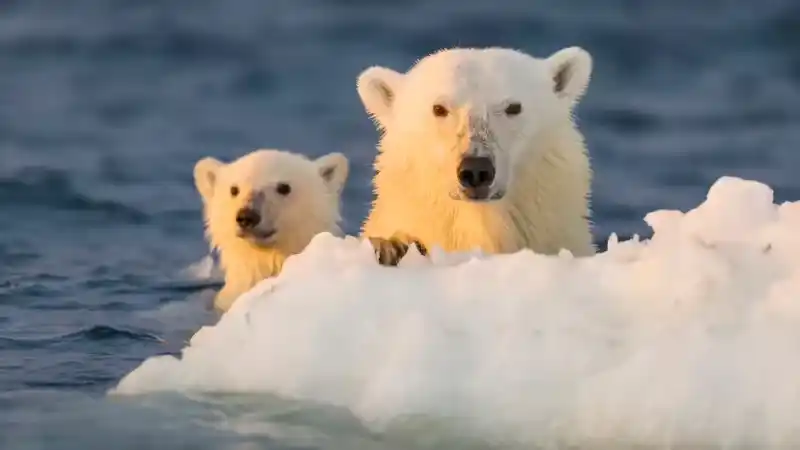

Quick Comparison
| Dimension | Polar bear ( Ursus maritimus ) | Grizzly bear/Brown bear ( Ursus arctos ) |
|---|---|---|
| Common weight of adult males | 900–1,500 lbs (410–680 kg), some larger | Inland grizzly bears weigh 400–800 lbs (180–360 kg); coastal/Kodiak bears weigh 900–1,400 lbs (410–635 kg). |
| Body type | Long neck, extra-wide forepaws, thick fat and high-density fur | A prominent acromion indicates powerful forelimb strength; long claws are good for digging/fighting. |
| Habitat | Arctic coast and sea ice | Forests, mountains, tundra, riverbanks, coastlines |
| Special skills | Sea ice ambush seals, long-distance swimming | Omnivorous diet: roots, berries, salmon, rodents, carrion, and occasional predators of large ungulates. |
| Terrain advantages | Sea ice/floating ice: Polar bear | Terrestrial/Diverse Environments: Grizzly Bear |
Their respective "winning strategies"
Polar bear: Top ocean predator
Design language: Thick grease and hollow protective fur for warmth, with a giant paw serving as "snowshoes + paddles".
Predation technique: Ambush the seal's "blowhole" and unleash a sudden slap and a deadly skull bite.
Advantages of the environment: Excellent grip on ice and ambush tactics, unmatched in endurance swimming.
Grizzly bears/Brown bears: the jack-of-all-trades on land
Design language: The acromion represents the amazing pushing/grabbing power of the forelimbs, and the long scythe claws are used for both digging and fighting enemies.
Recipe logic: Flexible switching with the seasons—carrion and calves in spring, berries/insects/salmon in summer and autumn, and opportunities to hunt elk/moose, etc.
Scenario advantages: strong terrain adaptability, versatile strategies, and stronger resource substitution capabilities.
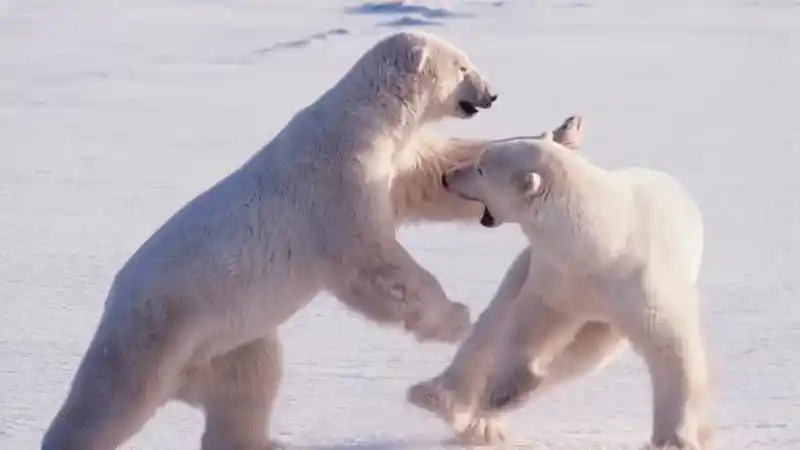

Body type and strength points
Both have a bite force of >1,000 psi , and their forelimb sweeping strikes are extremely destructive.
Kodiak brown bears (coastal type) can approach or rival smaller polar bears in weight; inland grizzly bears are generally lighter.
In real-world conflicts, most end in standoffs or avoidance of combat ; when it comes to fighting over corpses or food, individual weight, age, courage , and terrain often determine the outcome.
Dietary differences and tactical differences
Polar bears: highly specialized seal hunters, heavily reliant on sea ice platforms for ambushes; the difficulty of foraging increases dramatically when sea ice decreases.
Grizzly bears are broad-spectrum omnivores—eating everything from plants to fish, rodents, carrion, and even large mammals; they are also highly resilient and adaptable .
The "Hybrid Bear" makes its debut: Pizzly / Grolar
Causes: Climate warming leads to overlapping distributions, and occasional hybridization between polar bears and grizzly bears occurs .
Appearance/Characteristics: Light cream or light brown fur, skull and limb features are somewhere in between; diet is more omnivorous .
Reality: It remains rare in the wild (the proportion of genetic monitoring is extremely low), but it highlights the ecological convergence brought about by environmental changes.
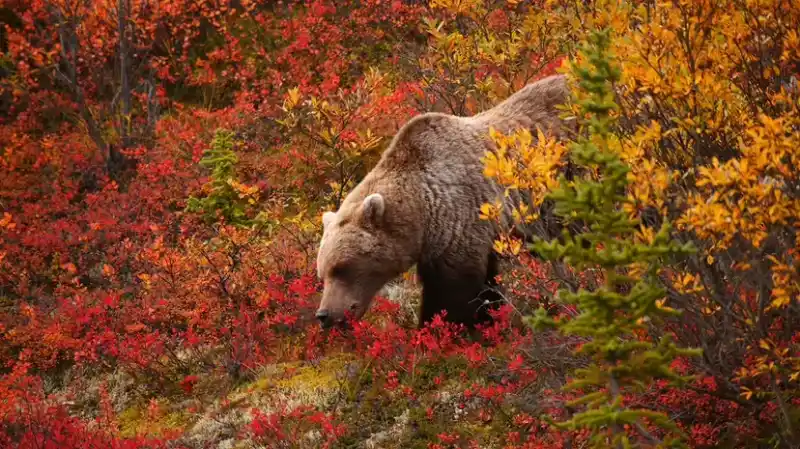

Current Status of Conservation
Polar bears: Multiple populations are subject to international treaty/quota management due to pressures such as sea ice retreat and pollution, and fluctuations in food availability.
Grizzly bears (North American interior): Regional recovery under protection, but food conflicts with human activities (garbage, feed, camping food) are a major management challenge.
Bear Safety Tips
Carry bear spray when hiking; store food/garbage in bear-proof containers ; verbally warn bears in poor visibility areas; maintain a safe distance from bears, especially female bears with cubs .
The Arctic community follows local polar bear watch and professional removal protocols.
Summary of conclusions
Larger: Overall, it is a polar bear (but the coastal/Kodiak brown bear can be approached or side by side).
Better at fighting: Look at the terrain —polar bears are stronger on sea ice, while grizzly bears have an advantage on land.
More adaptable: Grizzly bears win by adapting ; polar bears are irreplaceable experts on sea ice .