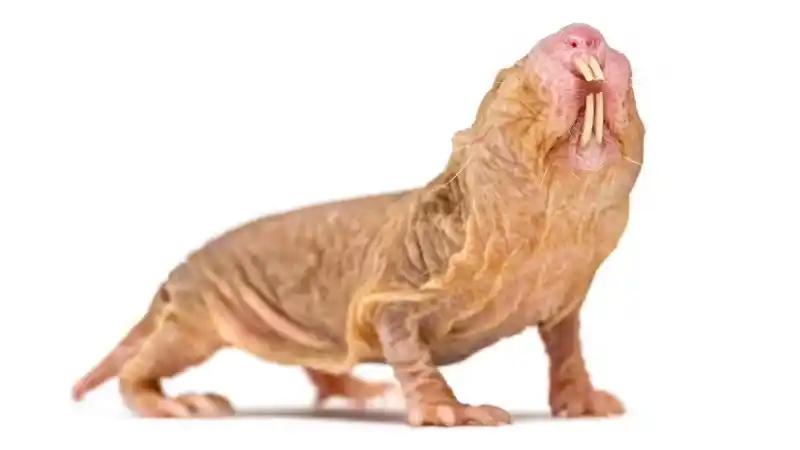
In short: Naked mole-rats (Heterocephalus glaber) are small, almost hairless rodents from East Africa, with wrinkled bodies. They exhibit eusocial behavior rarely seen in humans (queen + breeding male + worker/soldier mole), thrive in oxygen-deficient, high-carbon dioxide underground environments, are insensitive to certain types of pain, and can live up to 30 years.

External features
It is about 8–10 cm long and weighs only a few tens of grams; its eyes are small and its vision is poor.
The incisors can move independently, the lips are behind the incisors, and it digs without swallowing soil.
They have few hairs to avoid overheating; their whiskers and skin receptors are used for "adherent navigation".
Distribution and Habitat
Arid and savannas in East Africa: Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, etc.
The underground cave system stretches for hundreds of feet and is divided into sections including nurseries, granaries, toilets, main roads, and feed-gathering branches.
The underground environment has small temperature differences and good cover, allowing it to avoid predators and high temperatures and drought.
Diet and water content
Herbivores primarily consume underground tubers and roots.
Regularly girdle the tubers, trying not to kill them, to facilitate continuous regeneration.
They have a low metabolic rate, obtain water mainly from plants, and hardly need to drink water.
Social structure (eusociality)
The queen is the sole breeding female; a few breeding males mate with her.
The worker mole and the soldier mole have different roles: the smaller ones dig and move things, while the larger ones defend.
Chemical signals and behavior maintain order; when the queen is absent, individual worker moles may become breeders.
Reproduction and lifespan
Each litter produces approximately 10–30 offspring, with the worker mole raising them together.
The cubs grow quickly and should be assigned to digging, carrying, and guarding roles as soon as possible.
They can live for about 30 years in captivity, far exceeding the common lifespan of rodents of the same size.
"Hardcore Physiology"
It is tolerant of low oxygen and high carbon dioxide levels; it can also cope with cave air with ease.
It reduces some of the pain responses caused by acids, capsaicin, etc.
Natural tumors have an extremely low incidence rate and strong cellular and gene homeostasis, making them a hot topic in anti-aging and anti-cancer research.
Their ability to maintain a constant temperature is relatively weak, and they rely on group heating and selecting specific temperature zones to regulate their body temperature.
Regional differences
Currently, they are collectively referred to as Heterocephalus glaber, and there are genetic differences among populations in different regions, which may reflect local adaptations.
The naked mole-rat family includes other species, but only the naked mole-rat exhibits eusociality and these extreme physiological characteristics.
Preserve the status quo
It is not listed as endangered overall, and its population is relatively stable.
They are relatively sensitive to habitat changes (agricultural reclamation and climate change affect soil and plant resources).
It has ongoing scientific research value in areas such as aging, cancer, pain pathways, hypoxia tolerance, and social evolution.
Quick Answer
Are they "blind"? Not to the point of being blind, but their eyesight is very poor, and they rely mainly on touch and smell.
Do they really not drink water? They mainly rely on plant moisture and low metabolism to meet their water needs.
Can worker moles become queens? When a queen is absent or replaced, some worker moles may switch to a breeding role.
The reasons for longevity are believed to be a combination of factors, including low metabolism, cave protection, and strong cellular/gene homeostasis, but this is still under investigation.
Key findings: Naked mole-rats reverse many common-sense notions about mammals—they live in groups like ants, tolerate poor air quality, are insensitive to some types of pain, and are small in size yet live a long life, making them highly inspiring "underground elders" for scientific research.