Discussions about the "world's smallest fish" often become complicated. Several fish species vie for the title, including the dwarf paddy field fish (Paedocypris progenetica), the short-tailed baby fish (Schindleria brevipinguis), and the parasitic male of the deep-sea clownfish (Photocorynus spiniceps). Depending on different metrics—such as size, maturity, lifestyle, or ecological role—each fish could be considered the "smallest."
In this article, we will explore these fascinating fish in detail to clear up the confusion.
Standard for measuring "minimum"
To determine which fish can earn this title, we need to clarify the following parameters:
Total length: Physical measurement from head to tail.
Maturity: Whether the fish has fully developed and is capable of reproduction.
Lifestyle: Whether the fish can survive independently, or whether it is parasitic or remains in a juvenile state.
Habitat and Ecology: The Role of Fish in Ecosystems.
The main competitors of the smallest fish
1. Dwarf Paddy Field Fish (Paedocypris progenetica)
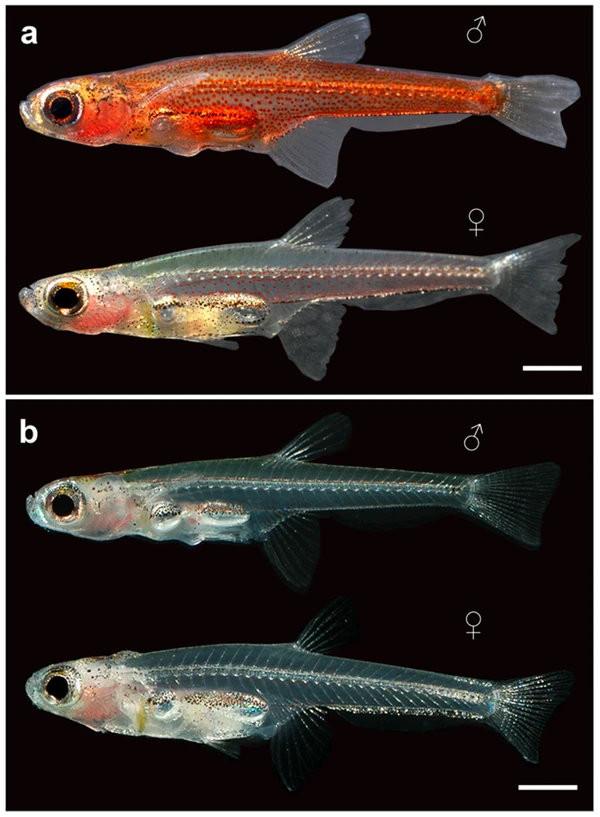

Other names: Ruby Fairy Lantern, Miniature Fish
Minimum body length of mature individuals: The smallest adult female is only 7.9 mm (0.31 inches).
Lifestyle: A completely solitary freshwater fish that lives in peat bogs and blackwater streams in Indonesia.
Key features:
The body is transparent.
Adapted to extreme survival conditions of low-oxygen environments.
Its reproductive organs are fully developed, enabling it to complete its life cycle independently.
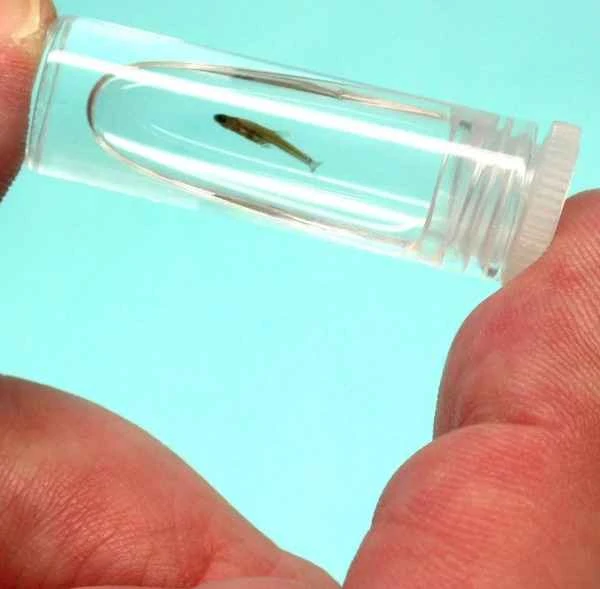

2. Short-tailed baby fish (Schindleria brevipinguis)
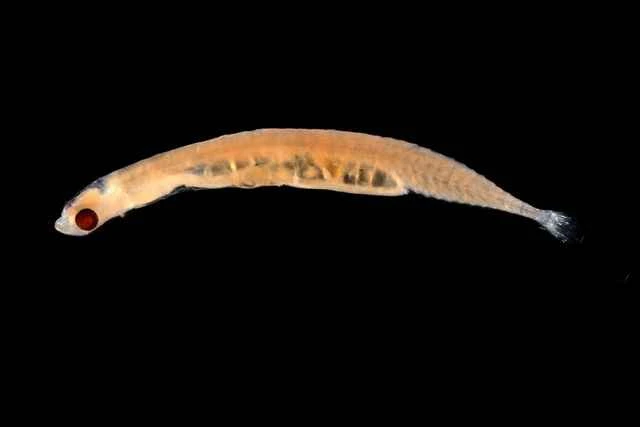

Other names: Fat Baby Fish, Short and Sturdy Sin's Microfish
Minimum body length of mature individuals: Females can be as small as 6.5 mm (0.26 inches).
Lifestyle: Pelagic fish that inhabits coral reef waters.
Key features:
Even after maturity, they retain juvenile characteristics (neomorphic continuation).
It is highly adapted to floating in open water.
3. Deep-sea clownfish (Photocorynus spiniceps)
Other names: Anglerfish
Minimum body length of mature individuals: Males can be as small as 6.2 mm (0.24 inches).
Lifestyle: Parasitic; the male attaches to the larger female and merges with her, completely losing its independence.
Key features:
Organs degenerate, existing solely for reproduction.
Its entire life cycle depends on the female host.
Comparative analysis
| fish | Minimum body length | lifestyle | Reproductive independence | Habitat | Special adaptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwarf Rice Paddy Fish | 7.9 mm | Independent freshwater fish | Completely independent | peat bogs and blackwater streams | Adaptation to low-oxygen environments |
| Short baby fish | 6.5 mm | Floating fish | Partially independent | Coral Reef Waters | Preserving larval characteristics to enhance buoyancy |
| Deep-sea clownfish | 6.2 mm | Parasites on female fish | Completely dependent | deep sea | Male fish are specialized for reproduction |
Why does confusion occur?
The confusion arises because different species excel in different "minimum" categories:
Although male deep-sea clownfish are the smallest, they are completely parasitic and cannot survive independently.
The short-bodied baby fish is smaller than the dwarf paddy field fish, but retains juvenile characteristics and has lower ecological complexity.
The dwarf paddy field fish has earned the title of the smallest completely independent fish species due to its completely independent lifestyle and ecological functions.
Conclusion: How to define the smallest fish
Based on the definition of "smallest", here are three different champions:
The smallest single fish: Dwarf paddy field fish (7.9 mm).
The smallest floating fish: the short baby fish (6.5 mm).
The smallest parasitic fish: deep-sea clownfish (6.2 mm).
By distinguishing these categories, we can avoid confusion while appreciating the unique adaptations of each fish species. "Small" in the animal kingdom is not just about body size, but also about an organism's adaptation to its ecological niche and its way of survival.
Why are these fish important?
Understanding these differences allows us to see the diversity of life on Earth and the evolutionary strategies animals use to adapt to extreme habitats. Whether it's the independent survival of the dwarf paddy fish, the larval continuation of the short-tailed baby fish, or the parasitic specialization of the deep-sea clownfish, each fish species reveals the complexity and wonder of nature.


