Hummingbirds are tiny birds known for their hovering flight and vibrant plumage, found only in the Americas. They belong to the order Apodiformes and are named for their extremely small feet, which prevent them from walking. Hummingbirds are not only important ecological pollinators but also receive considerable attention due to their unique ecological and cultural value.

However, in recent years, many hummingbird species have faced the risk of extinction, including the mangrove hummingbird (Chrysuronia boucardi), the red hummingbird (Selasphorus rufus), the Guerrero crested hummingbird (Lophornis brachylophus), the arica hummingbird (Eulidia yarrellii), and the black-breasted belt hummingbird (Eriocnemis nigrivestis). This article will provide a detailed introduction to the species characteristics, distribution, threats faced, and conservation methods of these endangered hummingbirds to help raise public awareness and action.
Hummingbirds' endangered status and major threats
There are over 300 known species of hummingbirds worldwide, of which approximately 10% are listed as vulnerable or endangered. According to the IUCN Red List, the main threats facing hummingbirds include:
Habitat loss and fragmentation : Deforestation, urban sprawl, and agricultural development have directly led to the disappearance of flower sources and nesting environments on which hummingbirds depend for survival.
Climate change : Climate fluctuations affect the synchronization of hummingbird migration and plant flowering periods, impacting food acquisition and reproduction.
Pesticides and Invasive Species : Pesticide pollution affects the health of hummingbirds, while invasive species threaten native flowers and ecological balance.
Human infrastructure : hummingbirds are killed by collisions with power lines, glass, and other structures.
Some widespread populations, such as the sword-billed hummingbird (Ensifera ensifera), are at low risk, but hummingbirds with limited distribution and dependent on specific ecosystems are highly vulnerable.
Introduction to typical endangered hummingbird species
1. Mangrove hummingbird (Chrysuronia boucardi)
Distribution and characteristics : It is found only in the mangrove ecosystems along the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Its plumage has a blue-green gradient and is named "Mangrove Diamond Hummingbird" because it sparkles like diamonds in the light.
Threat Status : There are only about 1,500 wild adult birds left in the world. The main threats are the large-scale logging of mangroves for shrimp farming and charcoal production, and habitat destruction exacerbated by the alteration of waterways by dams and roads.

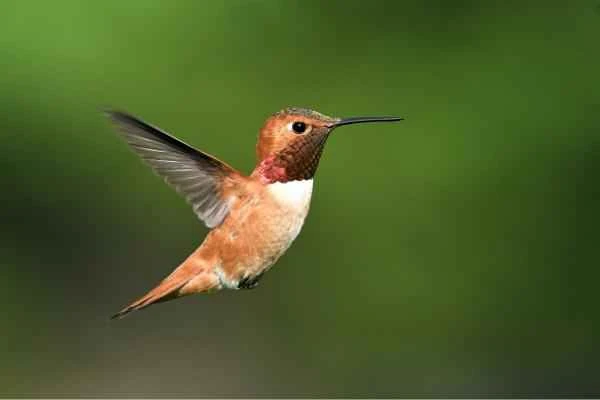
2. Red Hummingbird (Selasphorus rufus)
Distribution and characteristics : Found in the western United States and Canada, migrating to Mexico in the winter. Known for its long-distance migrations (up to 4,000 kilometers).
Threat status : Due to climate change causing its distribution area to shift northward, and deforestation reducing its flower source, it is listed as a near-threatened species.

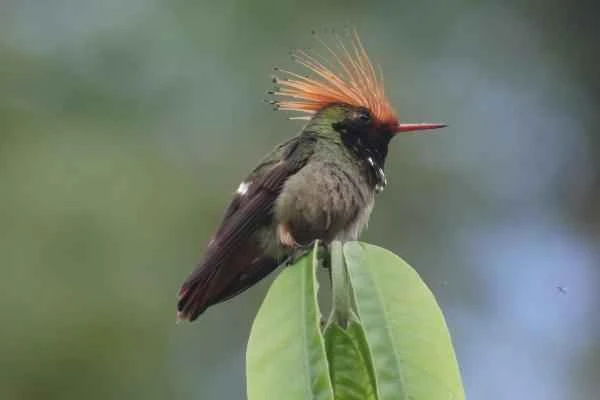
3. Guerrero Crowned Hummingbird (Lophornis brachylophus)
Distribution and characteristics : Endemic to a very small area in Guerrero, Mexico. The male has a bright red crest on its head, is small in size, and is extremely rare.
Threat status : Primarily affected by deforestation resulting from coffee, corn, and fruit cultivation, it is classified as critically endangered. It is currently protected under Mexican law and through international cooperation projects, with some individuals residing within protected areas.

4. Eulidia yarrellii (Hummingbird)
Distribution and characteristics : Endemic to Chile, with an extremely limited distribution, existing only in two small areas of the country. It relies on native shrubs such as *Geoffroea decorticans* for reproduction and food.
Threat status : Listed as critically endangered, primarily due to the clearing of native plants by farmers who consider them weeds, leading to a sharp decline in food and habitat.

5. Black-breasted Hummingbird (Eriocnemis nigrivestis)
Distribution and characteristics : It is distributed in the cloud forests of the volcanic mountains of Ecuador and relies on seasonal flowers for food.
Threat Status : Only about 100-150 individuals remain in the wild worldwide. Due to deforestation, charcoal harvesting, and cattle grazing, 94% of its habitat has been lost, leading to its classification as critically endangered. Climate change may force it to migrate to higher altitudes, where it will compete with other species for living space.

How can I participate in hummingbird conservation?
Plant native flowers : Plant trumpet-shaped flowers (such as hibiscus, impatiens, etc.) in your own backyard, balcony or garden to provide a continuous source of nectar for hummingbirds.
Use hummingbird feeders with caution : prioritize natural flowers. If using a feeder, clean it regularly and avoid using sugar water containing artificial coloring to prevent illness and behavioral changes in the hummingbird. It is recommended to make your own feeding solution using four parts boiled and cooled purified water to one part brown sugar.
Reduce pet threats : Domestic cats and other pets are one of the major reasons for the decline in the number of wild birds worldwide. Pets should be prevented from hunting wild hummingbirds as much as possible.
Focus on and support hummingbird conservation projects : Participate in or support the work of relevant conservation organizations to help ensure the sustainable management of hummingbirds and their habitats.
In conclusion , hummingbirds are vital pollinators in nature, and their survival is crucial to the health of numerous ecosystems. Protecting hummingbirds is not only about preserving beautiful natural landscapes but also about maintaining ecological balance. Let's start with our daily actions and contribute to the sustainable development of hummingbirds and the natural environment!
References
BirdLife International. (2020) *Amazilia boucardi*. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Accessible at: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22687562A168615870.en
BirdLife International. (2020) *Selasphorus rufus*. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Accessible at: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22688296A178595564.en
BirdLife International. (2018) Lophornis brachylophus. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, accessible in English: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22687196A130649157.en.
BirdLife International. (2020) Eulidia yarrellii. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, accessible in English: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22688244A181468935.en.
BirdLife International. (2020) *Eriocnemis nigrivestis*. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, accessible at: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22687909A173319425.en.
Alexandre, NM, Romero, FG, English, SG, Grames, E., Garzón‐Agudelo, F., Epperly, K., ... & Rico‐Guevara, A. (2025). Supplemental feeding is a driver of population expansion and morphological changes in Anna hummingbirds. Global Change Biology, 31(5), e70237.