Have you ever heard of tapeworms or pork tapeworm cysticercosis? These familiar yet dreaded parasites actually belong to the same phylum— Platyhelminthes . This phylum includes many free-living or parasitic worms with extremely simple body structures, yet they have a profound impact on human health and ecosystems.
This article will take you on an in-depth journey through the definition, characteristics, habitat, reproductive methods, and representative species of flatworms, giving you a comprehensive understanding of these "ordinary yet extraordinary" invertebrates.

What are flatworms? Analysis of their main characteristics.
Flatworms are among the simplest triploblastic invertebrates , with over 20,000 known species , ranging from free-living planarians to highly parasitic tapeworms and flukes.
The typical characteristics of flatworms are as follows:
The body is symmetrical on both sides and flat , resembling a shoe sole;
Acoelous animals (i.e., "coelomates") have no true hollow organs inside;
They lack a respiratory and circulatory system , relying on the body surface to absorb oxygen and expel waste.
Excretion occurs through the protonephridia , which is the most primitive excretory system.
Most are hermaphroditic (possessing both male and female reproductive organs) ;
It possesses a basic nervous system, including anterior ganglion and two longitudinal nerve cords ;
It was the first animal to develop interneurons;
Some species are of medical importance to humans and can cause serious parasitic diseases.
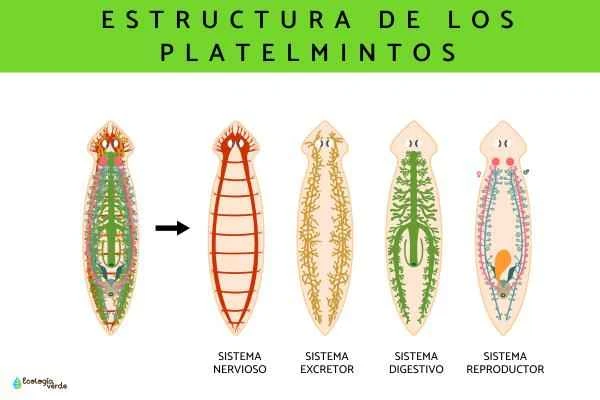
Habitat of flatworms
Flatworms are highly adaptable and commonly found in the following three types of environments:
Aquatic environments : freshwater or ocean, such as planarians and some trematodes;
In damp land or air : a few species can survive in moist soil;
Parasitic in animals : including humans and livestock, it is the habitat of most parasitic flatworms, such as tapeworms and liver flukes.
Feeding methods of flatworms
The digestive system of flatworms is extremely primitive, and most species lack a complete digestive tract structure.
It has no anus, only a mouth , and shares a passage for both food and excretion.
Some species do not have a digestive tract and absorb nutrients directly through their skin.
The digestive system branches into multiple channels that deliver nutrients directly to various tissues in the body.
Some species feed on detritus in the water using cilia ;
A small number of free-living flatworms prey on small invertebrates .

Reproduction methods of flatworms
Despite their simple structure, flatworms reproduce in a wide variety of ways, including:
Sexual reproduction:
Most species are hermaphroditic , possessing both male and female reproductive systems;
Both autofertilization and allogeneic fertilization can be achieved;
Male organs include the testes, ejaculatory ducts, prostate, and copulatory organs (cirrus).
Female organs include the oviduct, uterus, seminal vesicle, and yolk sac.
Asexual reproduction:
This includes fission and parthenogenesis ;
Planarians, which live freely, are particularly known for their remarkable regenerative abilities .
Special Reproduction of Parasitic Flatworms
Most parasitic flatworms have complex life cycles ;
Asexual reproduction occurs in intermediate hosts (such as snails), while sexual reproduction occurs in definitive hosts (such as humans and cattle).
It often goes through multiple developmental stages (egg, larva, adult) and can cause various diseases.
Representative species and examples of flatworms
According to traditional classification, flatworms can be divided into the following four categories:
| Classification | feature | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Turbellaria (a class of turbellarians) | Mostly free life | Project bugs (such as Dugesia) |
| Monogenea | Parasites on fish and amphibians | Gill fluke |
| Trematoda | Internal parasitic trematodes | Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) |
| Cestoda (a class of tapeworms) | Long, ribbon-like body shape with numerous segments | Pig tapeworm (Taenia solium) |
Common examples:
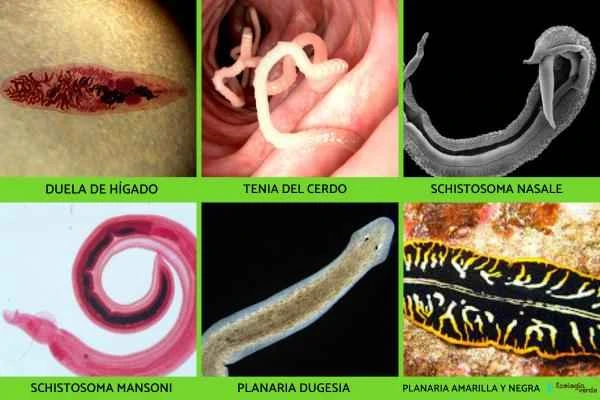
1. Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica)
The adult worms parasitize the livers of livestock such as cattle and sheep ;
The intermediate host is a freshwater snail;
It poses a huge threat to animal husbandry.
2. Pig tapeworm (Taenia solium)
It is often referred to as a " parasitic solitary tapeworm ";
Humans become infected after eating undercooked pork or contaminated food;
The larvae can form cysticercus in muscles and even the brain, causing cysticercosis.
3. Nasal blood fluke (Schistosoma nasale)
It parasitizes the respiratory tract of cattle and is transmitted through freshwater snails;
It can cause nasal congestion, runny nose, and abnormal breathing sounds.
4. Schistosoma mansoni
It causes schistosomiasis in humans by penetrating the body through the skin;
It affects the skin, lungs, and intestines , and spreads eggs through feces.
5. Planner (Dugesia spp.)
Widely distributed in freshwater environments ;
It has a triangular head and two "fake eyes";
It has an amazing regenerative ability ; even if cut into several pieces, it can regenerate into a complete individual.
6. Black and yellow bicolor planner worm (Pseudoceros dimidiatus)
Body length approximately 8 centimeters;
Its body surface has bright yellow and black stripes , and it has a beautiful appearance;
They live in the oceans of the Indo-Pacific region and are a free-living species.
In conclusion: Why should we pay attention to these "invisible creatures"?
Although flatworms are tiny and simple in structure, they play a crucial role in nature. From free-living planarians to tapeworms and flukes that endanger human health, the biological characteristics, parasitic methods, and reproductive strategies of these animals deserve in-depth study.
If you would like to learn more about diseases and prevention related to flatworms, please read the extended article: "Schistosomiasis and Human Health".
bibliography
Faculty of Science, University of the Eastern Republic of Uruguay (2009). *Platyformes*. Accessed at: http://zoologia.fcien.edu.uy/practico/03%20PLATYHELMINTHES&NEMERTINA.pdf
University of Las Palmas (2014). *Platyformes: Overview and Classification*. Accessed at: https://www2.ulpgc.es/hege/almacen/download/48/48207/leccion_11_0607.pdf
Beatty, R., Beer, A., and Deeming, C. (2010). The Book of Nature. Dorling Kindersley, UK.


