In nature, despite their venomous stings and defensive behaviors, wasps and bees still become prey for some animals. Numerous species, including the American brown bat (Eptesicus fuscus) , the bee-hunting fly (Mallophora ruficauda) , the jumping spider (Phidippus audax) , and the common swallow (Hirundo rustica), include wasps or bees in their diet. Below, we will introduce ten known predators and analyze their hunting methods and ecological roles.

1. American Brown Bat (Eptesicus fuscus)
This is a widely distributed insectivorous bat found throughout the Americas. While it primarily feeds on beetles, easily biting through their hard exoskeletons, it also preys on bees, wasps, moths, and other nocturnal insects. Studies show that juvenile bats have a broader diet than adults, with a preference for softer insects. They use echolocation to precisely capture their prey while flying at night.
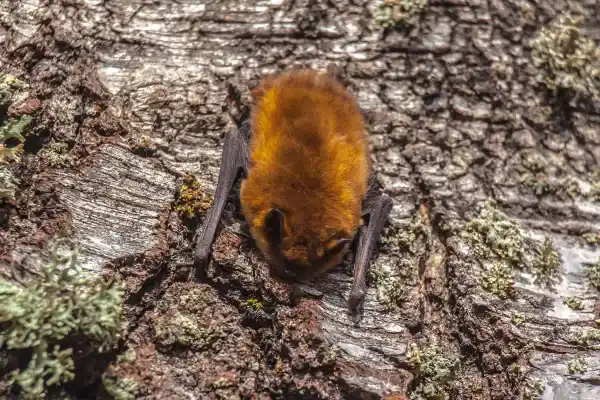

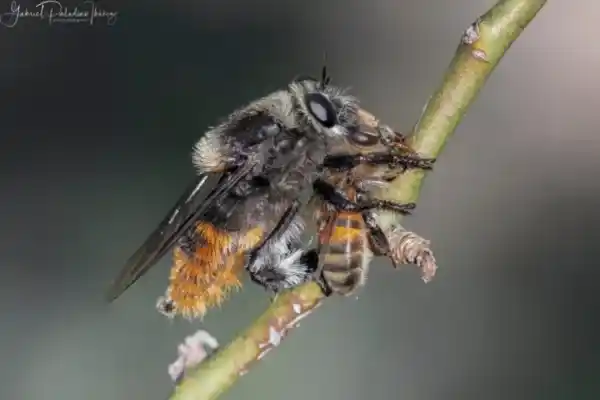
2. Bee-hunting fly (Mallophora ruficauda)
This insect is endemic to the Pampas region of Argentina. As its name suggests, it preys exclusively on bees, especially the Western honeybee (Apis mellifera) , selectively targeting them even when other insects abound in the fields. The bee predator fly is considered a pest of the country's beekeeping industry because it causes significant losses to honey production.

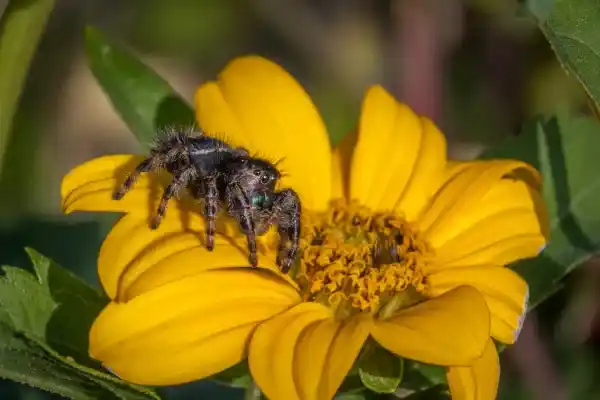
3. Jumping spider (Phidippus audax)
Jumping spiders are small hunters native to North America that do not rely on webs to catch prey, but instead actively track and leap to attack their prey. They feed on a variety of small insects, including bees and wasps. Jumping spiders can silently strike when these pollinating insects alight on flowers, and are frequently active in gardens and urban green spaces.

4. Thai shield bug (Pahabengkakia piliceps)
This is a unique insect found only in Thailand, targeting honeybees of the genus *Trigona*. The female lays her eggs in wild beehives, and the hatched larvae guard the entrance, hunting returning worker bees. It does not prey on other hymenoptera, demonstrating extremely high specialization, making it a sophisticated "hive invader."

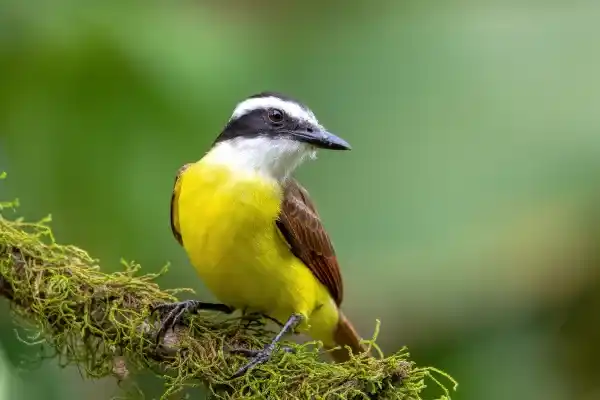
5. Common Bass Flycatcher (Pitangus sulphuratus)
This is a common bird in South America, found in a variety of ecosystems. It uses its strong beak to prey on various invertebrates, including wasps and bees. In addition, it also eats fruits, small mammals, reptiles, and even fish, making it a typical omnivorous predator.

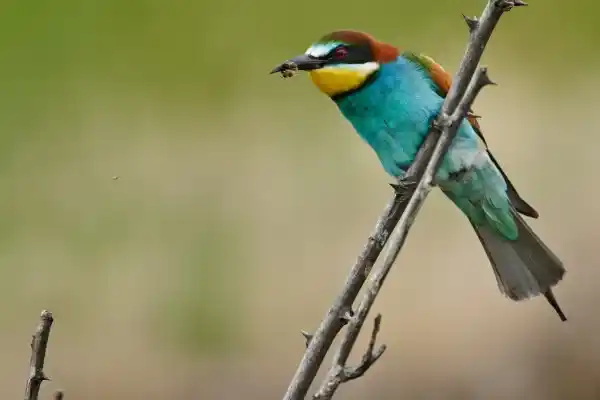
6. European bee-eater (Merops apiaster)
The brightly colored bee-eater is a professional hunter of wasps and bees, distributed across Europe, North Africa, West Asia, and South Africa. They hunt from the air, preying on bees, wasps, dragonflies, and flies, posing a potential threat to apiaries. However, encouragingly, they are also natural predators of the Asian wasp (Vespa velutina), playing a crucial role in controlling this invasive species.

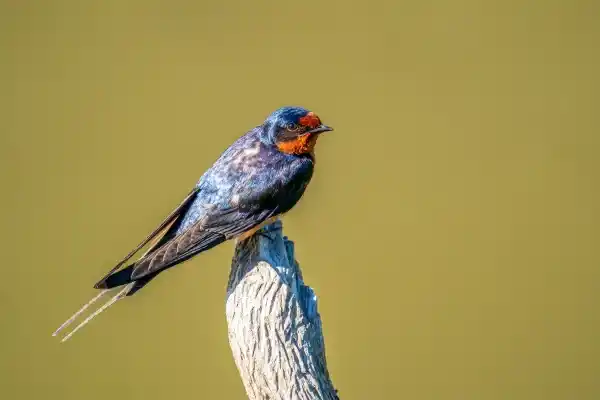
7. Common Swallow (Hirundo rustica)
This is the most widespread species of swallow, and we are very familiar with it. They primarily feed on mosquitoes and flies, but also prey on wasps, flying ants, small beetles, and other flying insects. They fly nimbly at low altitudes near their nests, chasing and hunting prey at high speeds, and occasionally form small groups to hunt cooperatively.

8. Honey bear (Tamandua tetradactyla)
The honey bear is an insectivorous mammal found in South America, ranging from Venezuela to northern Argentina. Its diet includes termites, ants, wasps, and bees, and it also consumes honey and beeswax. With its keen sense of smell and powerful forepaws, it can tear open nests and use its long tongue to lick up the insects clinging to them.
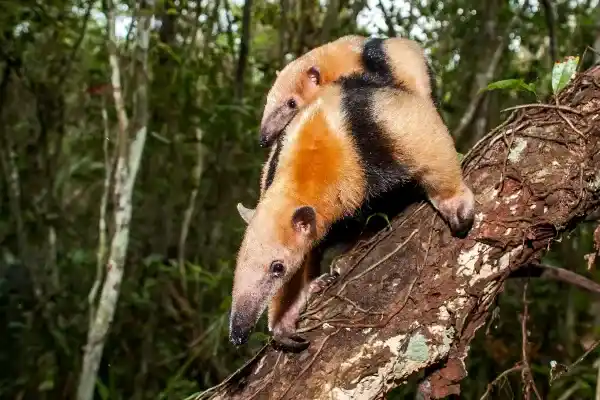

9. European Badger (Meles meles)
The European badger is an omnivorous mammal widely distributed in Europe and parts of Asia. Its diet is extremely diverse, ranging from plant matter to small animals. It is adept at digging up the nests of wasps and bees, feeding on adult wasps, larvae, honey, and waxy substances. Its thick skin and dense fur effectively protect it from insect stings.
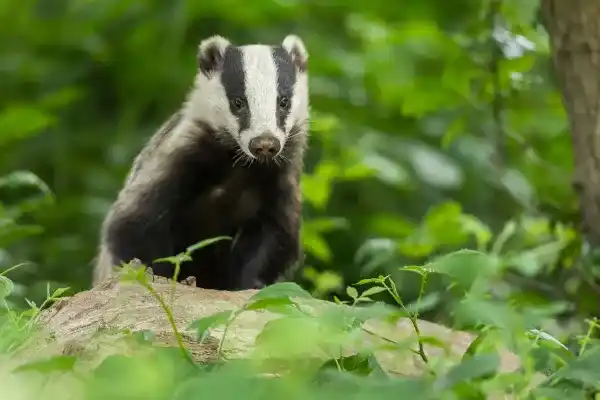

10. White-nosed long-nosed raccoon (Nasua narica)
This is an omnivorous mammal found from the southern United States to Columbia. Its diet includes insects, fruits, small vertebrates, and bird eggs. The white-nosed raccoon is adept at using its flexible nose and claws to search for and dig up wild beehives and wasp nests, consuming adult insects, larvae, and honey. Although not a monogamous predator, its interactions with these insects are frequent and skillful.

Summarize
Despite their stingers and collective defense mechanisms, wasps and bees possess numerous predators in nature that manage to overcome these defenses and prey on them. From birds in flight and ground mammals to insect hunters, a variety of predators maintain the balance of wasp and bee populations within the ecosystem.
If you are interested in this type of content, please visit the "Wildlife" section of our animal encyclopedia website for more scientific knowledge.