Bearded vultures and griffon vultures are collectively known as Old World vultures, although they do not constitute sister groups within the order Accipitriformes. Abundant fossil evidence shows that Old World vultures were widely distributed in Miocene to Late Pleistocene strata in North America; in contrast, early vulture fossils are rarely found in the Old World. Recently, researchers from the University of Texas, including Zhiheng Li, in collaboration with the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported a new species of bearded vulture fossil discovered in Linxia, China, named *Mioneophron longirostris*. This is the earliest record of bearded vultures in the Old World (Asia, Europe, and Africa), expanding the temporal and spatial range of this group's distribution. The relevant research results were published in the latest issue of *The Auk*, an academic journal published by the Ornithological Society of America.
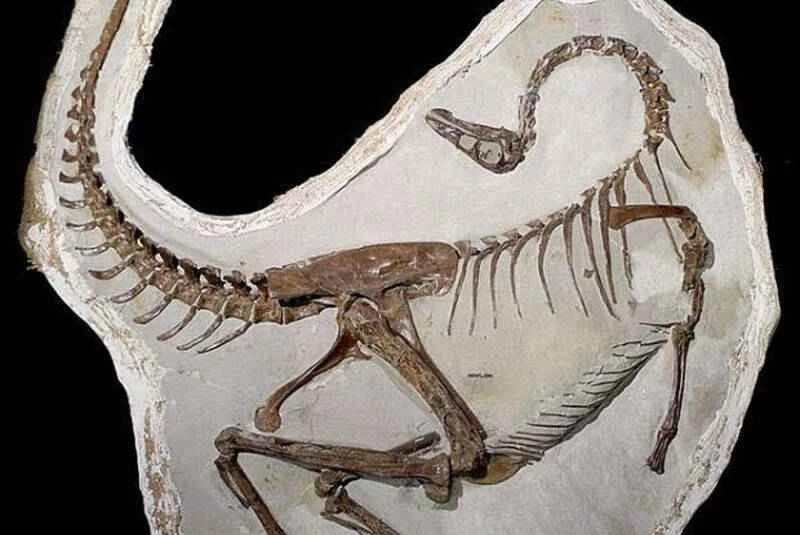
Due to the slender, hollow skeletons and large size of vultures, most discovered specimens are fragmented and scattered. This nearly complete fossil was found in the yellowish-gray siltstone layer of the Late Miocene Liushu Formation in the Linxia Basin of Gansu Province. Several other well-preserved bird fossils have been discovered and reported in the same strata, such as the Gansu vulture (a type of vulture), the predatory Hezheng falcon, and the larger flat-chested bird, the Linxia ostrich. This discovery suggests that 6-7 million years ago, the intermontane basin of the Linxia region of China was home to a rich variety of Cenozoic birds, including large ostriches adept at running on land, and various vultures soaring in the sky, such as the scavenging Gansu vulture, the omnivorous Bearded Vulture, and the agile and nimble predatory Hezheng falcon.
After analyzing and comparing the paleogeographic and geological distribution of Old World vultures, researchers found that the early species of Old World vultures mostly belonged to the Bearded Vulture, a basal group within the Accipitridae order. Their appearance and radiation in North America were closely related to the Miocene grassland expansion in North America. The radiation of more advanced cinereous vultures occurred relatively later, associated with the C3-C4 vegetation transition. The radiation evolution of the Bearded Vulture as a whole predates the C3-C4 transition, a hypothesis supported by the recent discovery of the White Vulture.
The discovery of the new specimens provides evidence for the study of the evolution and paleogeographic distribution of Old World vultures in the Old World, but more and earlier fossils are still needed to clarify the paleogeographic origins and evolutionary patterns of Old World vultures. The extinction of Old World vultures in North America, as well as their remnants and radiation in the Old World, remains an unsolved mystery in avian paleogeography.
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology's 973 Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Key Project), and the Lundelius Foundation of the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas.

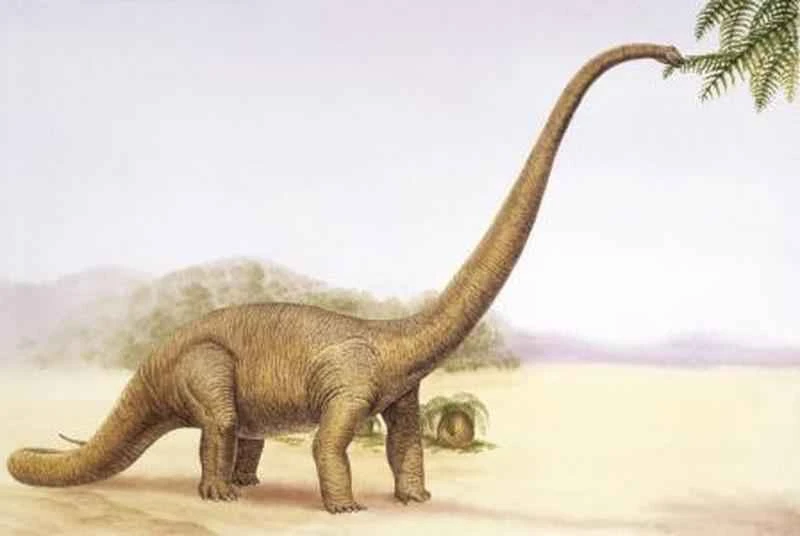
Figure 1. Reconstruction of a recently reconstructed white vulture with a long beak (illustrated by Xu Yong).
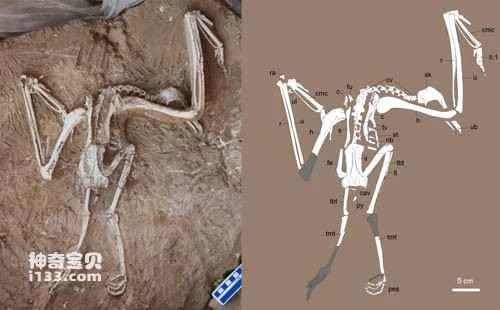
Figure 2. Photograph and line drawing of a recently discovered fossil of a white vulture with a long beak (provided by Li Zhiheng).