Sharks are often called the kings of the ocean, but there are many fish in the ocean and freshwater rivers that are much smaller than sharks, yet equally ferocious, deadly, or even more dangerous.
They may live in the deep sea, tropical rivers or lakes, and are known for their unique hunting methods and terrifying teeth.

This article will take you to learn about the world's most dangerous fish and introduce you to these terrifying aquatic predators.
1. Piranhas
Distribution: Primarily found in the Amazon River basin and its tributaries in South America.
Characteristics and hazards:
Piranhas are typically only 20–35 centimeters long, but they travel in groups.
They possess sharp, triangular teeth , enabling them to quickly tear apart their prey.
When food is scarce or when provoked, swarms of piranhas will launch a fierce attack on injured animals or people who have fallen into the water.
Although fatal attacks on humans are not common, the risk increases during the dry season when water levels drop and fish are hungry.

2. Anglerfish
Distribution: They mostly live in dark waters below 200 meters in the deep sea .
Characteristics and hazards:
The most distinctive feature of the anglerfish is the bioluminescent "fishing rod" on its head , which it uses to attract prey.
When small fish are attracted by light, anglerfish will open their huge mouths and swallow their prey with lightning speed.
Although it poses no direct threat to humans, it is one of the most fearsome predators in the deep-sea ecosystem.

3. Moray Eel
Distribution: Widely distributed in coral reefs and caves in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.
Characteristics and hazards:
Moray eels are ambush predators, often hiding in reef crevices and waiting for their prey to approach.
They have two sets of jaws : the outer jaws are used to bite the prey, while the "pharyngeal jaws" in the throat pull the prey further into the body.
Some moray eels carry bacteria or secrete mild toxins, making wounds susceptible to infection.
Eel bites are often accompanied by severe lacerations and secondary infections, so divers need to be extra careful.
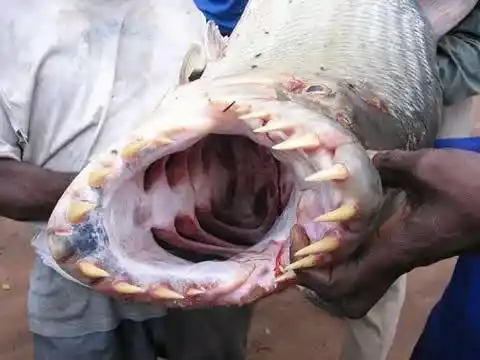
4. Tigerfish
Distribution: Mainly inhabits freshwater basins such as the Congo River and Zambezi River in Africa .
Characteristics and hazards:
Tigerfish possess enormous, sharp teeth disproportionate to their size, making them one of the most fearsome predators in Africa's freshwater rivers.
They are swift and powerful, capable of preying on fish of their own size or even larger.
It is known as the "man-eating shark of African freshwater".

5. Snakehead
Distribution: Native to freshwater areas in Asia and Africa , but has invaded North America and other regions.
Characteristics and hazards:
Snakehead fish have mouths full of sharp little teeth and can swallow almost any animal in the water, including small mammals and bird chicks.
It can briefly leave the water to breathe air and crawl , thus becoming an invasive species.
It is not directly aggressive towards humans, but will retaliate fiercely if threatened.

6. Viperfish
Distribution: Primarily inhabits dark waters at depths of 200–5,000 meters .
Characteristics and hazards:
It has long, sharp fangs and is about 30–60 centimeters long, yet it can swallow fish much larger than itself.
They use bioluminescence to attract prey, then pierce them with their fangs and swallow them quickly.
It is one of the most aggressive predators in the deep sea.
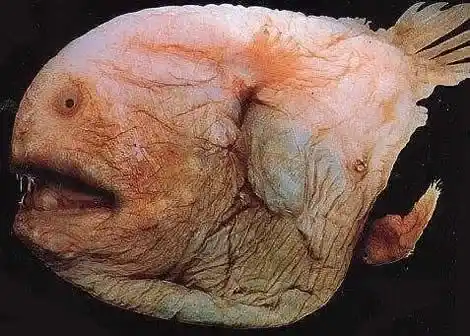
7. Fangtooth fish
Distribution: Found in tropical to temperate deep-sea regions worldwide.
Characteristics and hazards:
They are usually no more than 20 centimeters long, but have the largest fangs relative to their size .
Despite their ferocious appearance and lack of direct threat to humans, they are important medium-sized predators in the deep-sea environment.

8. Dragonfish
Distribution: Commonly found in the deep seas of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans .
Characteristics and hazards:
It has a huge jaw and sharp teeth , and its body can emit bioluminescence.
They typically hide in the darkness of the deep sea, using their bioluminescence to attract prey before quickly swallowing them.
It is an important predator at the top of the deep-sea food chain.

9. Gulper Eel
Distribution: Inhabits depths of hundreds to thousands of meters in the deep sea .
Characteristics and hazards:
It has a small body but a huge, expandable mouth , which can swallow prey much larger than itself.
Although it poses no threat to humans, it is a key species studied by deep-sea biologists.

10. Conger Eel
Distribution: Widely found in the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and shallow coastal waters .
Characteristics and hazards:
It belongs to the large carnivorous eel family, with a body length exceeding 2 meters and a weight reaching tens of kilograms.
Known for their strength and sudden attacks, fishermen have suffered bites many times during fishing operations.
Summary: Understanding and Respecting Aquatic Predators
These fish species each have their own unique characteristics; some live in the deep sea, while others inhabit freshwater rivers.
Although some of these fish pose limited direct threat to humans, they have become apex or important predators in aquatic ecosystems due to their unique hunting methods and strong adaptability.
When encountering these fish in the wild, humans should exercise caution and respect, avoiding provocation or excessive interference.
Many dangerous fish species are facing population decline due to overfishing, habitat loss, and climate change, and require scientific protection.
Understanding their ecological roles helps us better understand the complexity and vulnerability of marine and freshwater ecosystems.
This article introduces the world's most dangerous fish and reminds us that protecting biodiversity and ecological balance is key to the coexistence of humans and nature.


