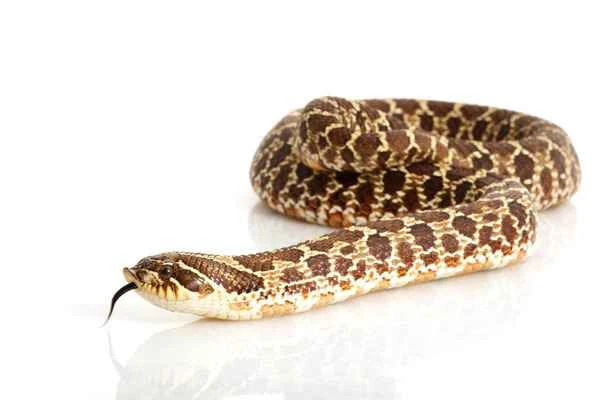
The southern hognose snake, known for its distinctive upturned snout, is one of the most striking snakes in North America. Primarily found in the southeastern United States, it possesses unique characteristics and behaviors that set it apart. This article will provide an in-depth look at everything about the southern hognose snake, including its habitat, behavior, conservation efforts, and common misconceptions.

What is the Southern Hognose Snake?
The southern hognose snake, scientifically known as *Heterodon simus* , is a small, non-venomous snake characterized by its upturned, pig-like snout. This snout is not only distinctive in appearance but also helps the snake dig in the sand, searching for food or escaping predators. Southern hognose snakes typically grow to about 14 to 24 inches in length, classifying them as small to medium-sized snakes.
Appearance characteristics: What does the Southern Hognose Snake look like?
The southern hognose snake has some unique physical characteristics:
Color : Their backs have light and dark patches that help them blend into their sandy soil habitat. The color is generally brown, gray, or reddish-brown with darker markings.
Nose : Its most distinctive feature is its upturned nose, which is used for digging in sandy or soft soil.
Abdominal color : Unlike the eastern hognose snake, the southern hognose snake has a lighter abdominal color, which usually matches the overall color of its body, and this also helps in identification.
Habitat: Where does the Southern Hognose Snake live?
The southern hognose snake is native to the southeastern United States and typically inhabits sandy pine forests, scrublands, and coastal dunes. These environments provide them with ample soft soil for digging and hiding from predators. Commonly distributed states include:
Florida
Georgia
South Carolina
Alabama
However, due to habitat loss and other environmental changes, the distribution range of the southern hognose snake has shrunk in recent years.
Diet and Behavior: What do Southern Hognose Snakes eat?
The diet of the southern hognose snake is relatively unique:
Diet : Unlike many other snakes, they primarily feed on amphibians such as frogs and toads. They have a special adaptation that allows them to neutralize the toxins secreted by toads, making them one of the few snakes that can safely consume this prey.
Hunting method : They use their upturned noses to dig in the sand, looking for hiding amphibians.
Defense mechanisms and behaviors
The southern hognose snake is non-venomous and harmless to humans. However, it exhibits some interesting defensive behaviors:
Playing dead : When threatened, the southern hognose snake may roll over, open its mouth, and play dead to scare away predators.
Hissing and swelling : These snakes may hiss and swell their bodies to mimic dangerous behavior, trying to appear larger and more threatening—but they rarely bite.
Biting : Despite having small teeth, the southern hognose snake almost never bites and usually relies on other defensive behaviors to scare away potential threats.
Conservation Status: Is the Southern Hognose Snake endangered?
The southern hognose snake is considered a species of concern due to habitat loss, climate change, and urbanization. It is listed as “Vulnerable” on the IUCN Red List and is protected in states such as Florida and Georgia. The population of the southern hognose snake continues to decline as its natural habitats, such as sandy pine forests, are developed for residential or agricultural use.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect this unique snake. Protecting sandy pine forests, raising awareness of the species, and protecting their distribution range are crucial for the survival of the southern hognose snake.
Common Misconceptions
Like many snakes, the southern hognose snake is often misunderstood:
Myth 1 : They are dangerous or poisonous. Fact : Southern hognose snakes are completely non-venomous and harmless to humans. Their threatening behavior is merely a bluff.
Myth 2 : Their bites are fatal. Fact : These snakes rarely bite, and even if they do, it's not dangerous.
Myth 3 : They are closely related to venomous snakes. Fact : The southern hognose snake belongs to the genus Heterodontidae and is very distantly related to venomous snakes such as rattlesnakes or copperhead snakes.
How to spot the Southern Hognose Snake?
If you live in or plan to travel to the southeastern United States and hope to see the southern hognose snake, you can refer to the following points:
Looking for sandy areas : pine forests, shrublands, and sand dunes are the best habitats.
Pay attention to the colors and patterns : their unique markings and upturned noses make them distinctive, but they can also disguise themselves very well.
Stay calm : These snakes are usually quite shy and will try to escape or use their dramatic displays rather than attack humans.
Final thoughts on the Southern Hognose Snake
The southern hognose snake is a fascinating and unique creature with a variety of interesting adaptations. From its pig-like upturned snout to its dramatic defensive behaviors, these snakes are truly a marvel of nature. While they can be intimidating when threatened, they pose no threat to humans and are an integral part of the ecosystem.
As conservation efforts continue, it is hoped that these snakes can continue to thrive in the wild. By understanding species like the southern hognose snake, we can help reduce misunderstandings and contribute to protecting their natural habitats.
If you are interested in wildlife or planning a trip to the southeastern United States, keep an eye out for this unique snake—you might have a chance to encounter it in its natural habitat!

Eastern and Southern Hognose Snakes: A Detailed Comparison
The eastern and southern hognose snakes both belong to the genus *Heterodon* and are known for their distinctive upturned snouts. While they share some similarities, they are distinct species with different physical characteristics, habitats, and behaviors. Below is a detailed comparison of these two snakes, highlighting their key differences and similarities:
| feature | Eastern hognose snake (Heterodon platirhinos) | Southern hognose snake (Heterodon simus) |
|---|---|---|
| scientific name | Heterodon platirhinos | Heterodon simus |
| Distribution area | It is distributed in the eastern United States, from southern Canada to northern Florida, and west to eastern Texas. | They are mainly distributed in the southeastern United States, especially in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, and Alabama. |
| Habitat | They inhabit forests, grasslands, and meadows, and prefer well-drained sandy or loamy soils. | They like sandy pine forests, shrublands, and coastal dunes, and also prefer soft sandy soil. |
| body shape | It is typically 14 to 18 inches long, but can reach up to 30 inches in length. | Smaller than the Eastern Hognose Snake, it typically measures 14 to 24 inches in length. |
| Appearance features | The back is brown, gray, or tan with darker markings, while the belly is usually lighter in color. | They look similar, but their belly color is usually more even and lighter than that of the Eastern Hognose Snake. |
| nose | Its upturned, pig-like snout was used for digging and foraging. | They also have upturned noses, used for digging in sand. |
| diet | They mainly feed on frogs and toads, and sometimes also eat small reptiles. | They mainly eat frogs and toads, and are especially adapted to eating toads with toxic secretions. |
| Behavior | It is known for its defensive behavior of "playing dead"; it will also hiss and spread its body out. | They will also feign death when threatened, but are more likely to frighten enemies by inflating their bodies and hissing. |
| toxicity | It is non-toxic and uses intimidation to scare away predators. | It is non-toxic and relies on intimidation and defensive postures to scare away enemies. |
| Defense mechanism | It will flip its body, make a hissing sound, and open its mouth to display itself. | Similar defensive displays, but with a greater tendency to inflate the body and flatten the shape to make itself look bigger. |
| Protection status | It is listed as a "Least Concern" species, but is affected by habitat destruction. | Listed as a "vulnerable" species due to habitat loss and population decline. |
| life | Their lifespan in the wild is 9 to 12 years. | Lifespan is similar to that of the eastern hognose snake, although specific data on the southern hognose snake is less available. |
| Activity period | They are active mainly from spring to autumn, especially during the warmer months. | They are also active from spring to autumn, especially in warm sandy environments. |
Main differences:
Distribution : The eastern hognose snake has a wider distribution, from southern Canada to Florida, while the southern hognose snake is only found in the southeastern United States.
Size : Eastern hognose snakes are typically larger, reaching up to 30 inches, while southern hognose snakes are smaller, usually between 14 and 24 inches.
Conservation status : The population of the Eastern Hognose Snake is relatively stable, but it is also affected by habitat destruction, while the Southern Hognose Snake is considered a vulnerable species and faces greater conservation challenges.
Key similarities:
Both types of snakes have a distinctive upturned nose, which they use for digging and foraging.
They are all non-venomous snakes that rely on intimidation and defensive behaviors, such as playing dead, hissing, and inflating their bodies, to scare away enemies.
Their diet consists mainly of frogs and toads, and they are highly adaptable and can process toad toxins.
Although the eastern and southern hognose snakes share many behavioral similarities, such as their defense strategies and diets, they differ significantly in geographical distribution, size, and conservation status. The eastern hognose snake has a wider distribution and larger population, while the southern hognose snake has a smaller distribution and faces more severe conservation challenges. Both are remarkable creatures in nature, especially known for their unique snouts and their adaptability to sandy environments.

Research and Medicine on Hognose Snakes: An Overview
Hognose snakes are extensively studied scientifically for their distinctive upturned snouts and unique defensive behaviors. These snakes, belonging to the genus *Heterodon* , are frequently investigated for their biology, behavior, toxicity (or non-toxicity), and ecological role. Although hognose snakes are non-venomous to humans, their biology and behavior provide valuable research material for researchers in areas such as evolutionary biology and medical applications.
1. Biology and Behavior of the Hognose Snake
Studies of hognose snakes typically focus on their unique characteristics, such as their distinctive upturned snouts, which help them dig in sandy soil. This adaptation allows them to burrow into the sand in search of food, primarily amphibians such as frogs and toads. Their defense strategies, including the well-known "playing dead" behavior, are also a focus of research. Playing dead involves the snake rolling over onto its back, opening its mouth, and releasing a foul odor to make itself appear unattractive to predators.
Scientists are keenly interested in the evolution of these behaviors and how they help hognose snakes avoid predators in their habitats. The hognose snake's ability to tolerate the toxins of certain toads, such as the Colorado River toad, is also a research area, providing valuable clues to the resistance of animals to venom and poisons.
2. Hognose Snake and Venom Research
Although hognose snakes are not venomous to humans, they do possess a mild venom primarily used to subdue their prey. The venom is injected through grooved fangs, which are not as potent as the hollow fangs of venomous snakes. The venom is used to paralyze smaller prey, such as amphibians. Researchers are studying the composition of hognose snake venom to understand its components, including enzymes or proteins that may have medical applications.
Interestingly, researchers have also investigated the potential medical uses of hognose venom, particularly in developing treatments for blood pressure regulation and even pain management. While there are currently no commercial applications, venom research has provided new insights into how snakes, including hognose snakes, produce and utilize these toxic compounds.

3. The role of hognose snake in ecological research
Hognose snakes play a vital role in their habitat. They prey on amphibians, particularly toads, which are often venomous. Understanding how hognose snakes consume these venomous animals has sparked interest in pharmacology. Studying the relationship between hognose snakes and their prey can provide clues to resistance to natural toxins and could have implications for the medical field, especially in understanding how the body develops resistance to certain poisons.
Furthermore, hognose snakes serve as a model for behavioral and evolutionary studies. Their unique defensive behaviors and adaptations to burrowing provide important clues for understanding animal evolution, survival strategies, and the development of traits.
4. Hognose Snake and Human Medicine
Although hognose snakes are not directly used in human medicine, their venom and physiological adaptations provide useful clues for pain management and pharmacological research. Researchers are particularly interested in how hognose snake venom affects small prey, as it can influence blood flow and muscle contraction. This may be relevant to the treatment of certain diseases in humans, especially vascular or muscular disorders.
Research into snake venom has paved the way for medical breakthroughs, and the venom of other snake species has also facilitated the development of anticoagulant and blood pressure medications. Although hognose venom is not yet widely used for these purposes, continued research may lead to new discoveries and open up new possibilities for medical treatments.
5. Conservation and Medical Uses of the Hognose Snake
Some hognose snake species, such as the eastern hognose snake, face population decline due to habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Conservation measures aim to protect these fascinating creatures, as they play a crucial role in controlling amphibian populations and maintaining ecological balance. Protecting these species becomes even more important as scientists continue to explore the biological and medical potential of hognose snakes. Research in wildlife biology and conservation medicine highlights the interrelationships between species and ecosystems, demonstrating how the loss of one species can lead to broader ecological and even medical consequences.
Hognose snakes are not only fascinating creatures with unique behaviors, but they are also valuable subjects of scientific research, particularly in animal biology, venom studies, and antitoxin research. Although they currently do not have a direct commercial impact on human medicine, research on their venom may have profound implications for pharmacological research. Furthermore, their role in the ecosystem and their surprising survival strategies continue to inspire and motivate researchers across various fields, from evolutionary biology to conservation efforts.