Among invertebrates, nematodes and nematodes are two easily confused concepts. They share many morphological similarities, both being elongated cylindrical in shape and widely distributed in various environments. However, these two groups of animals differ significantly in their biological classification, anatomical structure, physiological functions, and ecological roles. This article will analyze the differences between nematodes and nematodes in detail from multiple aspects, including taxonomy, morphological characteristics, lifestyle, and ecological roles.
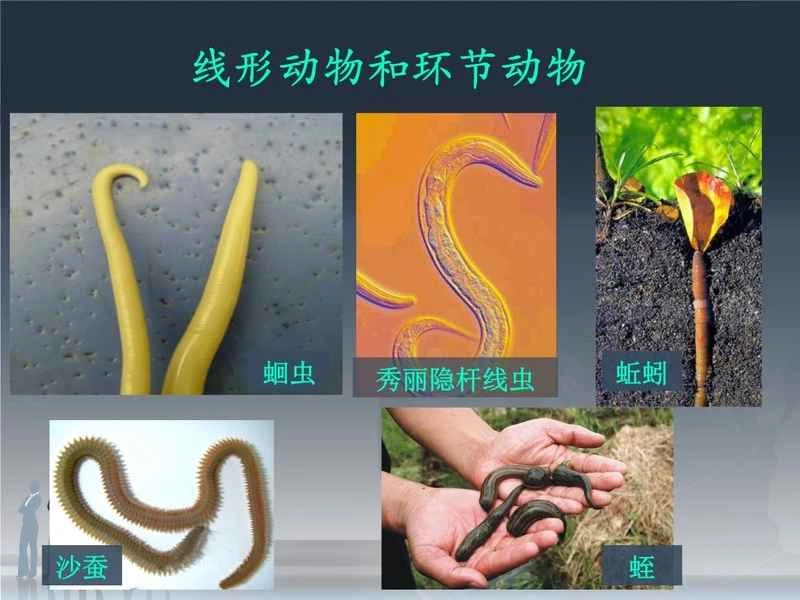

1. Basic concepts of nematodes and nematodes
1.1 Definition of Nematodes
Nemathelminthes was once a traditional phylum encompassing several similar groups of animals, including nematodes, kinorhyncha, and gastrotricha. However, with advancements in modern taxonomy, scientists have discovered that these animals are not closely related, and therefore the phylum Nemathelminthes has been split up and is no longer considered a formal taxonomic unit.
1.2 Definition of Nematodes
Nematodes are a still widely recognized phylum of animals. They are a group of true pseudocoelomates, characterized by their slender, cylindrical bodies covered with a cuticle to adapt to various environments. Nematodes are among the most abundant extant invertebrates, widely distributed in aquatic, soil, and parasitic environments.
Summarize :
Nematodes is an obsolete classification concept that once included multiple groups.
Nematodes are a clearly defined phylum and are still used in modern biological classification systems.
2. Taxonomic differences
2.1 Classification of Nematodes (Old Classification)
In early biological research, nematodes were considered to include the following groups of organisms:
Nematoda
Phylum Kinorhyncha
Phylum Gastrotricha
Phylum Acanthocephala
Because these groups differ significantly in morphology and ecology, modern taxonomy no longer uses the phylum "nematodes," but instead classifies them into different animal phyla.
2.2 Classification of Nematodes (Current Classification)
Nematodes belong to:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Nematoda
Class: Divided into free-living nematodes and parasitic nematodes.
The classification of nematodes is more stable, and this system is widely accepted by biologists.
Summarize :
Nematodes used to be an old classification that included multiple phyla, while nematodes are a distinct phylum.
Nematodes encompass a wide range of organisms, while nematodes specifically refer to organisms in the phylum Nematodes.
3. Differences in morphology and structure
3.1 Morphological characteristics of nematodes
The main morphological characteristics of nematodes include:
It has a slender, cylindrical body that tapers gradually at both ends.
Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity filled with fluid that provides some support.
The cuticle layer prevents moisture loss and provides protection for parasitic species.
It has no segmented structure and its internal structure is relatively simple.
A complete digestive system , with separate mouth, intestines, and anus.
3.2 Morphological characteristics of nematodes (including multiple different groups)
Because nematodes comprise many different groups, their morphological characteristics vary, for example:
Animals with segmented bodies and a retractable snout on their heads used for hunting.
Belly-haired animals : They are tiny, usually less than 1 mm in size, and their bodies are covered with cilia for locomotion.
Acanthocephalans : Parasitic organisms with retractable spiny structures on their heads for attaching to the host's intestines.
Summarize :
Nematodes have a relatively uniform morphology, with a long cylindrical body that is unsegmented.
Nematodes (old classification) comprise multiple groups with diverse forms, making it impossible to generalize.
4. Differences in lifestyle and ecological role
4.1 Lifestyle of Nematodes
Nematodes can be free-living or parasitic :
Free-living nematodes : widely distributed in freshwater, ocean and soil , participating in the decomposition of organic matter and ecological cycles.
Parasitic nematodes , such as roundworms, hookworms, and filarial worms, can parasitize plants, animals, and humans, causing diseases.
4.2 Lifestyle of Nematodes
Because nematodes comprise many different groups, their lifestyles also vary greatly, for example:
Animals : Free-living, feeding on small invertebrates.
Belly-haired animals : live in freshwater or seawater environments and feed on microorganisms.
Acanthocephalans : They are completely parasitic on their host and survive by absorbing nutrients from the host.
Summarize :
Nematodes have clearly defined ecological functions, including both free-living and parasitic species.
Nematodes comprise multiple phyla, and their ecological habits are complex and diverse, making it impossible to summarize them using a single model.
5. Summary of the main differences between nematodes and nematodes
| Comparison Dimensions | Nematodes (old classification) | Nematodes (current classification) |
|---|---|---|
| Taxonomy | Once classified as belonging to the phylum Animalia, this classification has now been abolished. | A separate phylum (Nematoda) |
| Scope | It includes multiple animal phyla, such as nematodes, kinorhynchophylla, and gastrochaetes. | Only nematodes |
| Morphology and Structure | They come in various forms, some with segmented structures. | Slender cylindrical shape, without segmentation |
| lifestyle | Including free-living and parasitic organisms | There are both free-living species and a large number of parasitic species. |
| Ecological role | Participating in aquatic and soil ecosystems, partially parasitic | Important soil organisms, some of which are agricultural and medical parasites. |
in conclusion
Based on the analysis in this article, we can conclude that:
Nemathelminthes is an old classification concept that is no longer used; it once included several different animal groups.
Nematoda is a separate phylum in modern biological classification. Its species are widely distributed in nature and play an important role in the ecosystem.
Nematodes have a relatively uniform morphology, while nematodes (old classification) include multiple groups with different morphological and physiological characteristics.
Hopefully, this article will help you understand the difference between nematodes and nematodes more clearly!