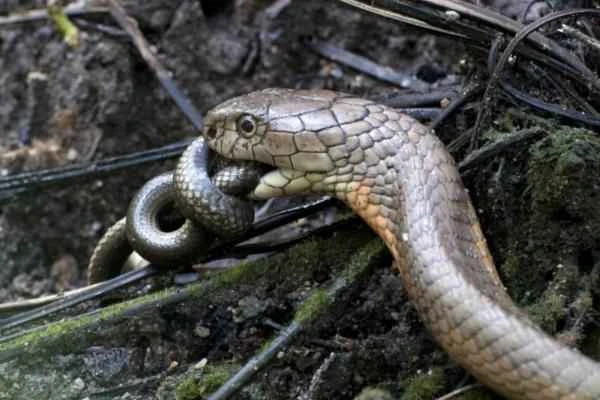
Snakes are considered by many to be the most powerful and deadly creatures in the animal kingdom, but in reality, they also have many natural enemies. Besides their fearsome appearance, snakes, as limbless reptiles, crawl on the ground, and some species possess venom to defend themselves against predators. This article will introduce you to 20 of the snake's major enemies, telling you which animals are its primary adversaries, and will also reveal common snake-eating birds of prey.

1. King Cobra (Ophiophagus hannah)
King cobras are one of the natural predators of snakes. They prey on other snakes, hence their name "snake-eating snake." King cobras are among the most venomous and largest snakes in the world, capable of injecting approximately 500 ml of venom to rapidly paralyze the respiratory and cardiac functions of their prey. Some king cobras even exclusively feed on specific snake species, such as large pythons and Asian rat snakes (Ptyas). They play a crucial role in controlling snake populations.

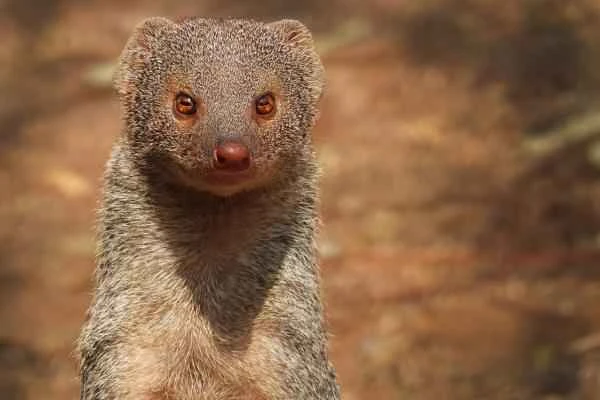
2. Meerkat or grey mongoose (Herpestes edwardsii)
Meerkats are fierce carnivorous mammals that show no fear of snakes. They particularly favor king cobras, as they are immune to their venom. Meerkats capture their prey by feigning harmlessness, approaching the snake, and then striking swiftly. The struggle between meerkats and snakes is a constant one, and snakes also threaten meerkat pups. Despite their resistance to venom, the fangs of large snakes can still pierce the stomach wall of a meerkat, leading to death.

3. Snake-eating hawk (Spilornis spp.)
Snake-eating hawks are birds of prey that primarily feed on snakes. They use their altitude advantage to locate prey, then swiftly swoop down to seize the snake's head, preventing any counterattack. Their legs are covered in thick scales to protect against snake bites, allowing them to capture and carry snakes away from the air or feed directly on the ground.
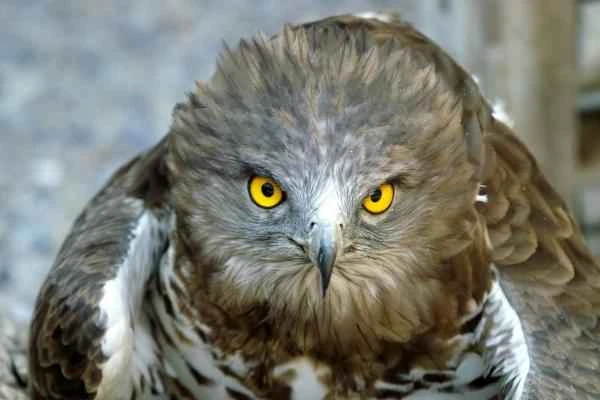

4. Raccoon (Procyon lotor)
Raccoons are one of the natural predators of snakes, with a wide diet consisting of both herbivores and animals. They prefer to attack injured or slow-moving snakes and avoid venomous snakes. Raccoons occasionally hunt snakes, but generally avoid direct confrontation with venomous snakes.
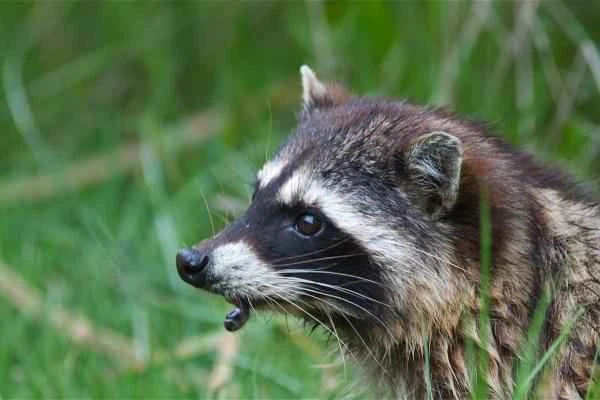

5. Fox (Vulpes vulpes)
Foxes are omnivores, and although they are not exclusively snake predators, they will hunt snakes when they encounter them. With their keen sense of smell and skillful hunting techniques, they can catch various creatures, including snakes, but they are not immune to venomous snakes and may die from a snake bite.
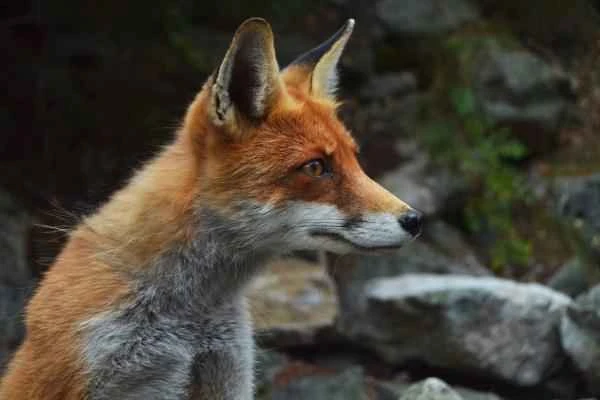

6. Hedgehog (Erinaceidae family)
Hedgehogs are unexpected natural enemies of snakes. They are immune to many snake venoms and primarily prey on venomous snakes such as vipers. Hedgehogs can resist bleeding reactions caused by venom, and fierce confrontations between hedgehogs and snakes are common.
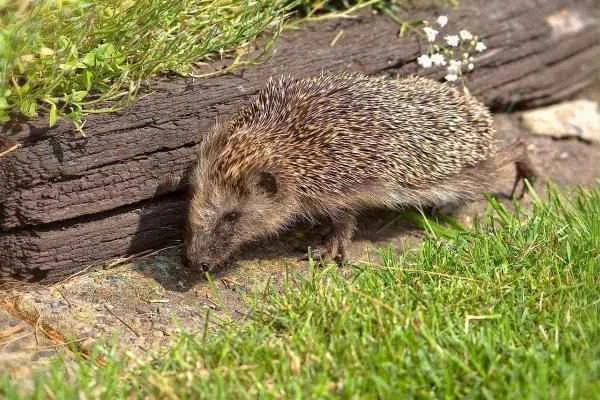

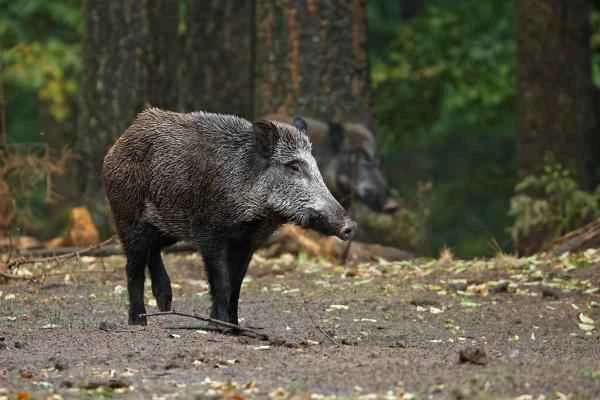
7. Wild boar (Sus scrofa)
Wild boars are omnivorous, with a diverse diet including snakes. They possess a receptor that blocks the neurotoxins of snake venom, thus providing them with strong immunity to venomous snakes.

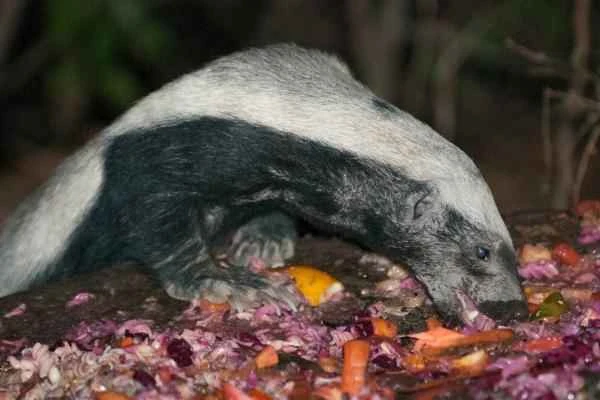
8. Honey Badger (Mellivora capensis)
Honey badgers are among the few mammals immune to snake venom. They are dexterous and agile, capable of hunting various snakes, from king cobras to pythons, and completely eliminating their prey, leaving not even bones or skin behind.

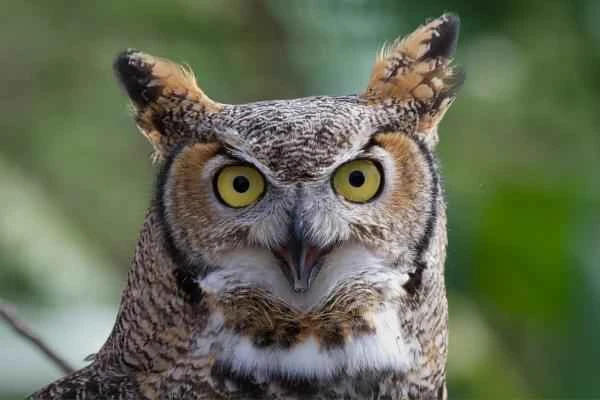
9. American owl (Bubo virginianus)
American owls are nocturnal animals. Although snakes are not their primary food source, they do prey on snakes smaller than themselves and are common snake-eating birds.

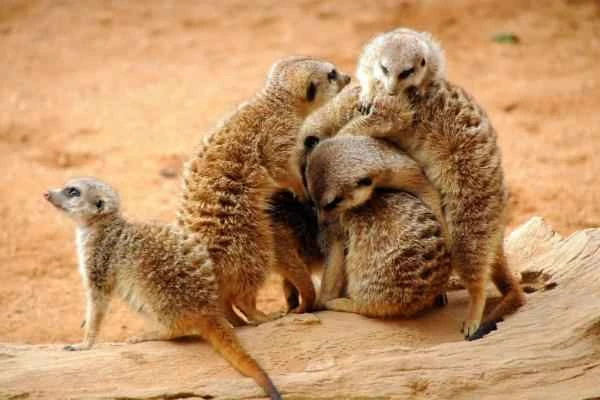
10. Meerkat (Suricata suricata)
Meerkats and mongooses belong to the order Carnivora and primarily feed on insects, but they also prey on snakes and scorpions. They are immune to some snake venoms, including king cobra venom. When faced with a snake, they will surround it, forming a massive enclosure to intimidate the predator.

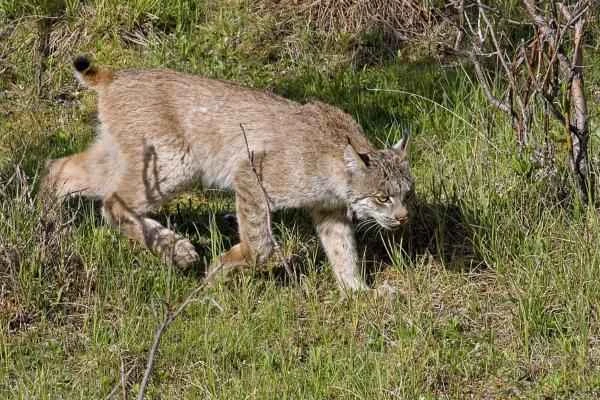
11. Lynx (Lynx spp.)
Lynxes can hunt and kill venomous snakes such as rattlesnakes. Usually, the snake attacks first, and the lynx swiftly retaliates with its agile claws, biting the snake's head and killing it. Other felines similar to the lynx (such as lions) have also been recorded hunting snakes, but this is less common.

12. Human beings (Homo sapiens sapiens)
Humans are also the "ultimate enemy" of snakes. Many snake species are hunted out of fear of humans, and many species, including the king cobra, are endangered. Human activities have led to the massive loss of snake habitats, threatening their survival.
Other snake predators
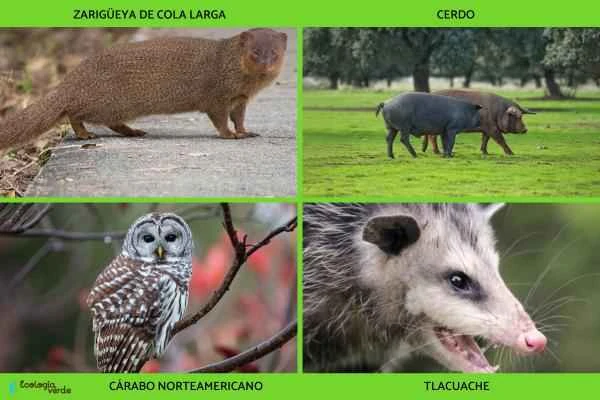
Thick-tailed opossum (Lutreolina spp.)
Domestic pig (Sus scrofa domestica)
North American Spotted Owl (Strix varia)
South American opossum (Didelphis marsupialis)
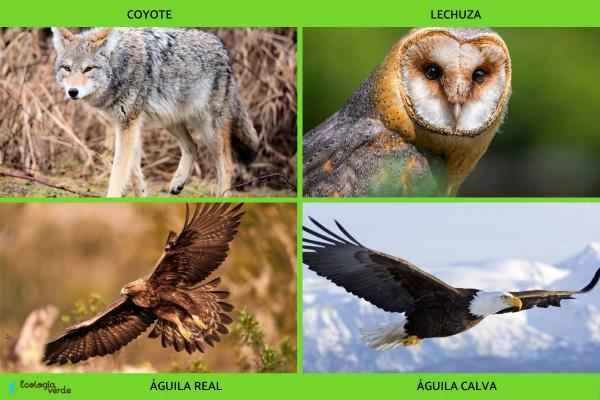
Coyotes (Canis latrans)
Strigiformes (owls)
Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos)
Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus)


If you would like to learn more about snakes and other animals, please visit our "Wildlife" category.
bibliography
Beatty, R., Beer, A., and Deeming, C. (2010). The Book of Nature. Dorling Kindersley, UK.
Young, D. (1999). "Ophiophagus hannah" is available at: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Ophiophagus_hannah/
Featherstone, D. (2021). Why are mongooses and snakes enemies? (See: https://www.forestwildlife.org/why-are-mongooses-and-snakes-enemies/)
Global Biodiversity Information (GF) Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Linnaeus, 1758. Accessible at: https://www.gbif.org/species/113274582