Biomes of tall grasses and herbivores: Exploring grassland ecosystems
Grasslands are a unique biome on Earth, characterized by their vast expanses of grassland, abundant sunshine, seasonal rainfall, and thriving herbivores. Here, tall grasses not only provide food for herbivores but also constitute their habitat. Globally, there are various types of grassland ecosystems, such as tropical savannas (also known as savannas) and temperate grasslands, which together support rich biodiversity.
This article will explore tall grasses and herbivores in grassland ecosystems to understand their lifestyles and interdependent relationships in this environment.
1. What is a grassland ecosystem?
Grasslands are vast ecosystems dominated by grasses, covering approximately 25% of the world's land area. Based on geographical location and climatic conditions, grasslands are classified into the following categories:
Tropical grasslands , also known as savannas, are mainly distributed in Africa, South America, and Australia. They have a relatively warm climate and moderate rainfall.
Temperate grasslands : such as the Great Plains of North America, the steppes of Ukraine, and the Pampas of Argentina. These grasslands have relatively dry climates and large temperature variations.
The main characteristics of grassland ecosystems include: large areas of grassland, sparse trees, heavy seasonal rainfall, and abundant herbivore populations.
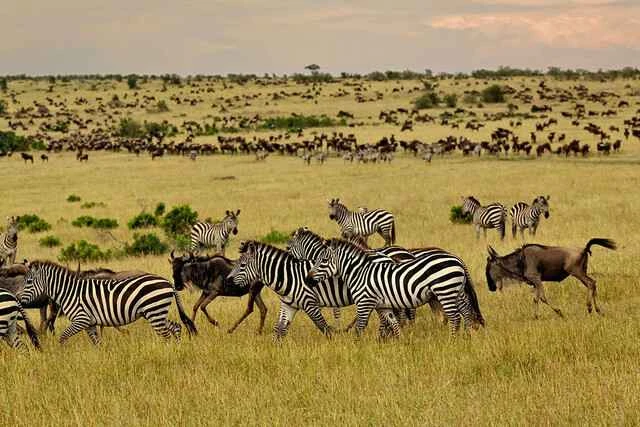

2. Tall grasses in grassland ecosystems
Grasses on grasslands are known for their height and diversity. Tall grasses are particularly important because they provide abundant food resources for herbivores and protect them from predators. Grasses play several key roles in grassland ecosystems:
Food provision : Herbivores mainly feed on grasses, and the leaves and seeds of tall grasses provide them with sufficient nutrition.
Habitat : Tall grasses not only provide hiding places for animals, but also help them avoid predators and extreme weather conditions.
Ecological balance : Grass plants form a symbiotic relationship with soil microorganisms, helping to maintain grassland health and soil fertility.
Common tall grasses include: Stipa gigantea, Andropogon gerardii, and Schizachyrium scoparium.
3. Herbivores living on grasslands
Grasslands are home to a large number of herbivores that feed on tall grasses and other grasses. Here are some common herbivores found in grassland ecosystems:
(1) Elephant
Distribution : African grasslands and savannas
Characteristics : Elephants are the largest land herbivores in the world, feeding on grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits. Their long trunks and enormous size allow them to consume vast amounts of vegetation, significantly impacting grassland plant communities.
(2) Giraffe
Distribution : African savanna
Characteristics : Giraffes are the tallest animals in the world. They primarily feed on the leaves of tall trees in savannas, but also eat grasses. Their long necks allow them to access food sources inaccessible to other animals.
(3) Antelope
Distribution : Grasslands of Africa, Asia, and North America
Characteristics : There are many species of antelope, such as gazelles, wildebeests, and blackhorns. They are all typical herbivores, feeding on grasses, shrubs, and other low-lying vegetation. Antelope herds usually migrate in groups to find abundant forage.
(4) Bison
Distribution : North American grasslands
Characteristics : Bison were once widely distributed across the Great Plains of North America. They were large herbivores that primarily fed on tall grasses. Bison herds migrated across the grasslands, grazing as they moved, helping to promote vegetation regeneration.
(5) Zebra
Distribution : African grasslands
Characteristics : Zebras primarily feed on grasses, especially tall grasses in grasslands. They are known for their distinctive black and white stripes, which help them camouflage themselves on the grasslands and avoid attacks from predators.
(6) Kangaroo
Distribution : Australian grasslands
Characteristics : Kangaroos are the most iconic herbivores of the Australian grasslands. They primarily feed on grasses, leaves, and shrubs. Their jumping ability allows them to move quickly and evade predators.
(7) Moose
Distribution : Temperate grasslands of North America and Northern Europe
Characteristics : Moose are large herbivores that live in temperate grasslands. They feed on grasses and shrubs and have shown a strong ability to survive, especially in cold regions.
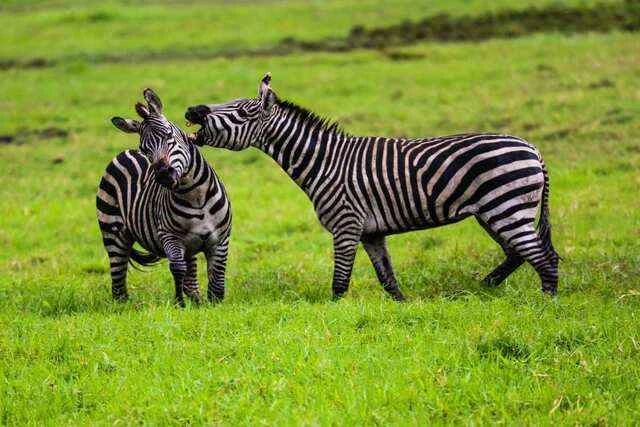

4. The relationship between predators and herbivores on the grasslands.
Herbivores on the grasslands not only live in close proximity to grasses but also face threats from predators. Lions, cheetahs, wolves, and other carnivores depend on these herbivores for food, forming a predator-prey chain within the grassland ecosystem. The presence of predators, to some extent, maintains a balance in herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing from causing ecological imbalance.
In addition, some herbivores, such as antelopes and zebras, form cooperative defense mechanisms, acting collectively to reduce the probability of being preyed upon.
5. The Importance of Grassland Ecosystems
Grasslands not only provide habitat for a large number of animals, but also play a vital role in the global ecosystem. They have the following functions:
Carbon storage : Grassland plants can store large amounts of carbon, which helps mitigate climate change.
Soil protection : The root systems of grasses help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil fertility.
Biodiversity : Grassland ecosystems possess rich flora and fauna diversity, supporting the survival and reproduction of a variety of species.
Grassland ecosystems are among the world's most important biomes, with tall grasses and herbivores forming the core ecological relationship. Herbivores such as elephants, antelopes, and zebras maintain the dynamic balance of grasslands by consuming grasses. At the same time, grasslands provide abundant food sources for predators, creating a complete ecological chain. Grassland protection is particularly important in efforts to protect global ecosystems.