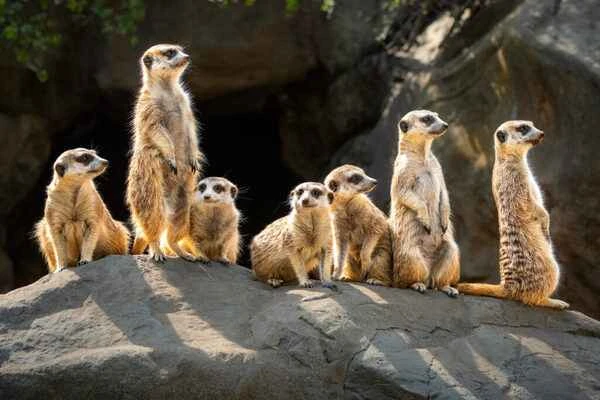
If you've ever watched a nature documentary or visited a zoo, you've probably seen adorable meerkats. These social animals are known for their upright posture, curious nature, and strong family bonds. This article will explore everything about meerkats, including their habitat, behavior, diet, and role in the ecosystem.

What is a meerkat?
Meerkats are small mammals belonging to the family Mustelidae, with the scientific name * Suricata suricatta *. They are native to arid regions of South Africa, particularly Botswana, Namibia, and other South African countries. With their distinctive facial markings and lively personalities, meerkats have won the hearts of many.
Physical characteristics
Size : Adult meerkats typically weigh between 1.5 and 2.5 pounds and are about 12 to 14 inches long (excluding the tail).
Appearance : They have slender bodies, long tails, short limbs, and pointed snouts. Their fur is mainly light brown with dark stripes on their backs, helping them blend into their environment.
Eyes : Meerkats have large, expressive eyes that enhance their keen vision, enabling them to spot predators from a distance.
Meerkats are known for several distinctive features:
Social structure : They live in large family groups called groups or clans, usually consisting of 20 to 50 individuals, exhibiting strong social connections and cooperative behavior.
Upright posture : Meerkats are known for their ability to observe their surroundings while standing upright on both legs, which helps them spot predators.
Communication skills : They have complex vocalizations, body language, and scent marking systems for communicating with each other, especially for issuing danger alerts to the group.
Digging behavior : Meerkats dig extensive burrow systems to provide themselves with refuge and protection against predators and extreme weather.
Foraging ability : They are efficient foragers, mainly feeding on insects, but also eating small vertebrates and plants.
Cooperation in raising offspring : In addition to the mother, other members of the group also help care for the young, demonstrating their cooperative nature.
These characteristics make meerkats fascinating and adorable animals in both the wild and in captivity.
Habitat and Distribution
Meerkats are adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, typically inhabiting grasslands, meadows, and deserts. They prefer areas with sparse vegetation, allowing them to better observe potential threats. Meerkats dig extensive burrowing systems to provide themselves with refuge from extreme temperatures and predators.

social structure
One of the most striking characteristics of meerkats is their social behavior. They live in groups called packs or colonies , typically consisting of 20 to 50 individuals. These groups usually consist of associated females and their offspring, with the dominant breeding pair serving as the group leader.
Cooperation and Communication
Meerkats are known for their cooperative behavior, working together to raise their young and protect their territory. They have complex vocalizations, body language, and scent marking systems for communication. Alarm calls are particularly important, alerting the group to the presence of predators.
Are meerkats friendly?
Meerkats are typically highly social animals, exhibiting friendly behavior towards members of their group. They live in close-knit family units, forming strong bonds with each other. Meerkats play, groom each other, and cooperate in caring for their young.
However, meerkats are wild animals, and their behavior can be unpredictable, especially when interacting with humans. In captivity, some meerkats may become accustomed to human interaction and appear friendly, but they still retain their wild instincts. It is important to remember that meerkats are not domesticated animals, and interactions with them should be conducted with caution and respect for their natural behavior.
Do meerkats bite? Analysis of their aggression and natural enemies.
Meerkats are not typically known for their aggressive behavior towards humans. However, like any wild animal, they may bite when they feel threatened or cornered. It is important to remember that they have natural instincts that may trigger a defensive response when they perceive danger.
The aggressiveness of meerkats
Social animals : Meerkats are highly social creatures that live in groups. They exhibit cooperative behavior and strong family bonds, which usually makes them display friendly behavior among their companions.
Defense mechanisms : While not inherently aggressive, meerkats protect their territory and cubs from perceived threats. If they feel their group is in danger, they may exhibit aggressive behavior towards intruders, including humans.
Coping with stress : In captivity, meerkats may bite if they feel stressed or fearful. Proper handling and stress reduction are crucial to preventing this reaction.

The natural enemies of the meerkat
In the wild, meerkats face a variety of natural threats:
Birds of prey : Eagles and hawks are among the biggest threats to meerkats. They often hunt meerkats from the air, so groups need to be vigilant to spot aerial predators.
Snakes : Certain snakes, such as cobras, can also pose a danger to meerkats. Meerkats are known for their wariness of snakes and usually avoid approaching them.
Carnivores : Larger carnivores, such as jackals and wildcats, also prey on mongooses. They rely on burrowing systems to protect themselves from these predators.
While meerkats are generally not aggressive towards humans, they may bite when threatened. Understanding their social structure and natural instincts is crucial for interacting with them safely. In the wild, they face threats from a variety of predators, so alertness and cooperative behavior are essential for survival.
Diet and foraging
Meerkats are primarily insectivorous, and their diet includes:
Insects : such as beetles, grasshoppers and termites.
Small vertebrates : Occasionally catches small lizards or rodents.
Plants : During the dry season, when insects are scarce, they also eat roots, fruits, and seeds.
Meerkats are efficient foragers, using their sharp claws to dig for food buried in the sand. They typically take turns foraging, leaving some members behind to monitor predators.
Reproduction and lifespan
Meerkats can breed year-round, with the dominant pair in the pack usually responsible for most reproduction. After a gestation period of about 11 weeks, females give birth to 2 to 5 cubs. The cubs are born blind and helpless, relying on their mothers and other pack members for care and protection.
life
In the wild, meerkats have a lifespan of about 6 to 10 years. However, in captivity, they can live much longer, sometimes up to 12 years, because they are free from predators and can receive regular veterinary care.
Role in the ecosystem
Meerkats play a vital role in their ecosystems. By controlling insect populations and becoming prey for large predators, they help maintain the balance of the food chain. Their digging activities also loosen the soil and promote plant growth.
Which countries use meerkats for food and what are their conservation status?
Meerkats are known for their fascinating behavior and social structure, but in some areas, they are also used as food, particularly in parts of Africa. Below is information on countries where meerkats are eaten and their conservation status.
Countries that eat meerkats
South Africa : In some rural communities, meerkats are hunted and eaten. Although this is not a common practice, it still occurs in specific cultural contexts.
Botswana : Similar to South Africa, residents in some areas may eat meerkats, but this is not a common food source.
Namibia : In Namibia, meerkats are occasionally hunted for food, especially in more traditional communities.
Protection status
Meerkats are classified as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means they are not currently considered to be at risk of extinction. However, their populations may be affected by habitat loss and illegal hunting in some areas.
Conservation measures : Although there are no specific protections for meerkats, they benefit from general wildlife protection laws in many countries. Conservation efforts primarily focus on habitat protection and raising awareness of the species' ecological role.
Education and advocacy : Raising awareness of the ecological importance of meerkats and their role in the ecosystem can help reduce hunting pressure and encourage conservation efforts.
Although meerkats are used as food in some parts of Africa, their overall conservation status is stable. Continued habitat conservation and community education efforts can help ensure these fascinating animals continue to exist in the ecosystem.
Meerkats are fascinating creatures with complex social structures and behaviors. Their adaptability to harsh environments and cooperative nature set them apart from other mammals. Whether observed from afar in the wild or watched in zoos, meerkats continue to captivate animal lovers worldwide. Understanding their role in the ecosystem and their unique behaviors allows us to appreciate these extraordinary animals more deeply.
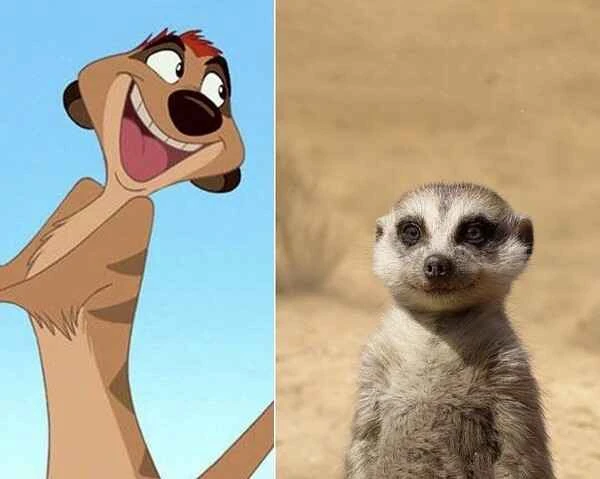

Exploring the allure of meerkats in culture and film
Meerkats have captivated audiences worldwide with their charming appearance and social behaviors, and have secured a place in various cultural contexts and media portrayals. Below is an overview of meerkats' representation in culture and film.
Cultural significance
Symbol of Family and Community : In many cultures, meerkats are celebrated for their strong social bonds and cooperative behavior. They are often seen as symbols of family and community, demonstrating the importance of teamwork and mutual support.
Folklore and Mythology : In some African cultures, meerkats appear in folklore and legends, often highlighting their intelligence and protectiveness. These stories may be used to teach lessons about cooperation and vigilance.
Conservation Awareness : With increasing awareness of wildlife conservation, meerkats have become a symbol of broader efforts to protect their natural habitats. Their social structure and ecological role make them more relevant in discussions of biodiversity.
The portrayal of meerkats in film and television
The Lion King : One of the most famous portrayals of the meerkat is Timon, the character in Disney's animated film The Lion King. Timon, along with his friend Pumbaa, provides comedic relief and embodies the carefree spirit of the meerkat. This film significantly boosted the meerkat's popularity in popular culture.
*Meerkat Estate* : This nature documentary series, broadcast on Animal Planet, follows a group of meerkats living in the Kalahari Desert. The series delves into their social dynamics, highlighting their daily lives, challenges, and interactions, and is beloved by audiences for its educational value regarding meerkat behavior.
Documentaries and wildlife programs : Meerkats frequently appear in various wildlife documentaries, showcasing their behavior, habitats, and interactions with other species. These programs help raise awareness of the importance of conservation and the challenges meerkats face in the wild.
Products and popularity
The popularity of meerkats has led to a range of products, including toys, clothing, and plush toys. Their adorable appearance and social behavior make them a favorite among both children and adults.
Meerkats occupy a unique place in culture and media, serving as symbols of family, cooperation, and conservation. Through films, documentaries, and merchandise, they continue to capture audiences' attention, raising awareness of their ecological importance and the need for wildlife conservation. Whether through the lens of film or in the pages of stories, meerkats remind us of the beauty of nature and the bonds that connect us all.