Hummingbirds are the smallest known and extant birds, belonging to the family Hummingbirdidae in the order Apodiformes. Modern hummingbirds are mainly distributed in Central and South America, with a few species found in North America. Their habitats are very diverse, ranging from arid deserts to dense tropical rainforests. About 24-28 species of hummingbirds are listed as endangered or critically endangered, and the numbers of many other hummingbird species are also declining.
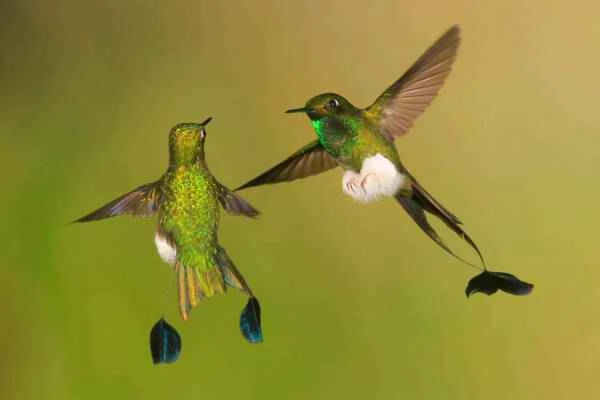

Hummingbirds are typically brightly colored and are charming and beautiful birds. They get their name from the buzzing sound their wings make during flight and are the only birds capable of flying backwards, which is useful for catching nectar from plants and insects. Of course, hummingbirds have many other impressive abilities. Let's take a look at this smallest migratory bird in the world.

1. How many kinds of hummingbirds are there?
There are over 350 known species of hummingbirds, with new species being described every year. Two other hummingbird species have gone extinct since their initial discovery in the 19th century. The Brae's kingfisher and the Central American kingfisher have become extinct within the last 150 years. Hummingbirds have their own family, called Trochilidae.

2. Where do hummingbirds live?
All hummingbird species can be found in the Americas. Of the remaining hummingbird species, only eight breed regularly in the United States—the vast majority live in tropical regions of Central and South America and the Caribbean.
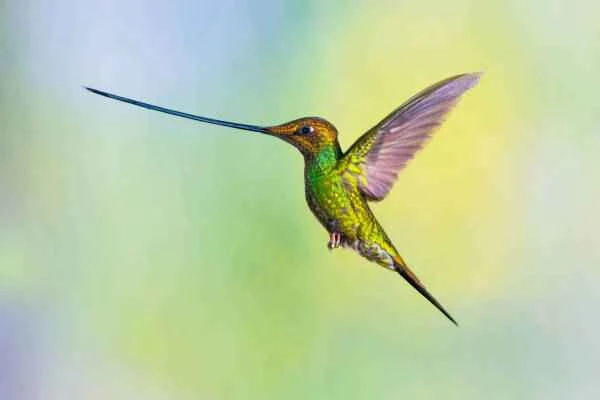

3. Where does the word "hummingbird" come from?
The hummingbird family name Trochilidae comes from Greek, which Aristotle used to describe a small bird (possibly the European wren we know today).
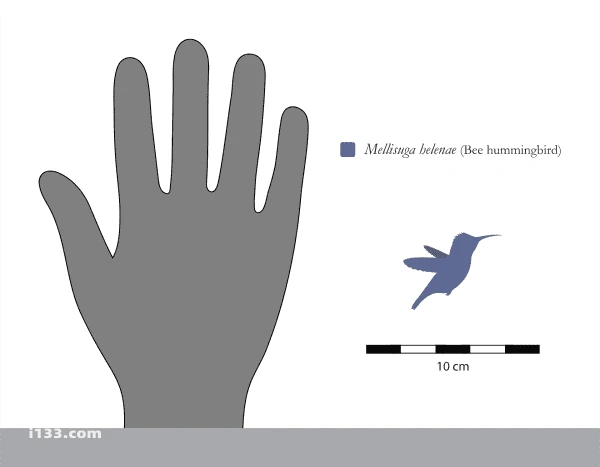
Humming bird size comparison with human hand
Even that tiny creature, a shuttlecock weighing 8-12 grams, looks like a behemoth in this company. Most hummingbirds weigh between 2.5 and 6.5 grams, with the smallest Cuban hummingbird weighing only 1.6-1.9 grams (just a little heavier than a standard paperclip).
It pales in comparison to many insects, with half of its 5.5-centimeter length consisting of its beak and tail. Its delicate nest is only 2.5 centimeters in diameter; its eggs are smaller than coffee beans.

4. What do hummingbirds eat?
Hummingbirds feed on nutrient-rich plant nectar, sap, and insects. Their insect diet includes spiders, insect eggs, and other small insect species, all of which provide essential protein and energy.
5. How much does a hummingbird weigh?
Hummingbirds come in various shapes and sizes, but none are heavy. The average hummingbird might weigh around 4 grams, but it can fatten up to a relatively impressive 8 grams before migration. The smallest hummingbird is the honey bee hummingbird, which is actually the smallest bird of all species. The male hummingbird is only a little over 5 centimeters long and weighs less than 2 grams, less than half the weight of a nickel.
At the other extreme is the giant hummingbird, which is about 23 centimeters long and weighs about 20 grams, ten times the size of a bee or hummingbird.
There are many hummingbirds in between, some of which are quite peculiar. The sword-billed hummingbird's beak is even longer than its body!
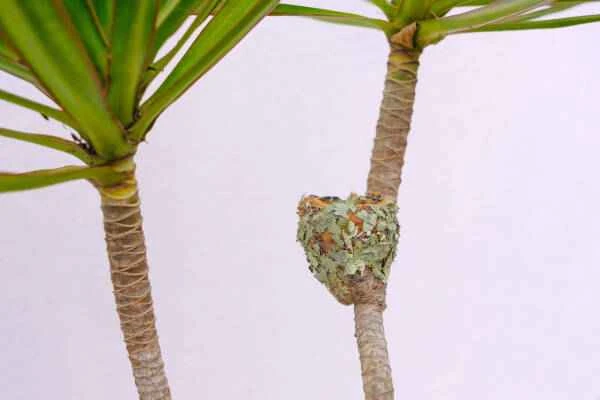

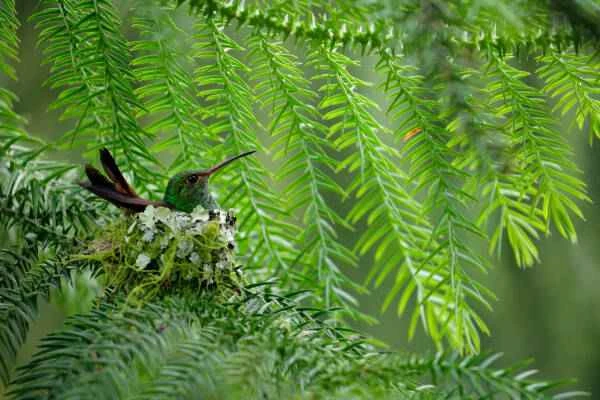
6. What does a hummingbird's nest look like?
Hummingbirds' nests are small, which is not surprising, but it is incredible how small they are—the nests of smaller species are no bigger than half a walnut shell!
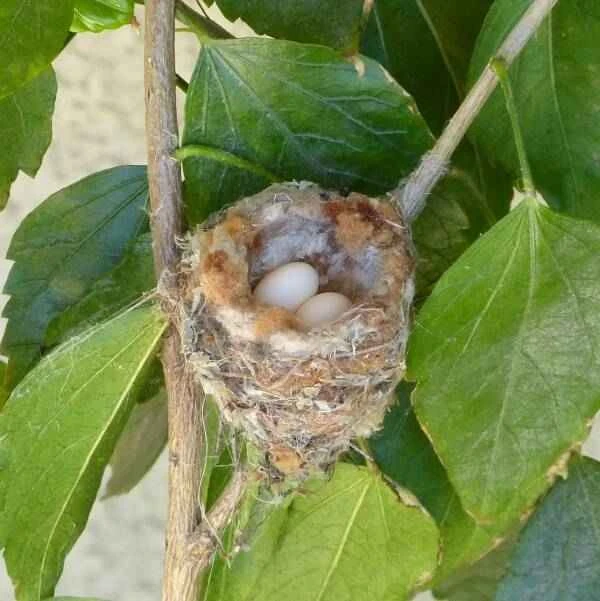

Hummingbird nests are often hidden in the forks of branches, along twigs, or deep within protective bushes, and are not always easy to find. But these miniature architectural wonders made of lichen, moss, and spider silk are well worth seeing.
Sometimes hummingbirds nest in more unusual places, such as on top of wind chimes or even on clotheslines!

7. How fast does a hummingbird flap its wings?
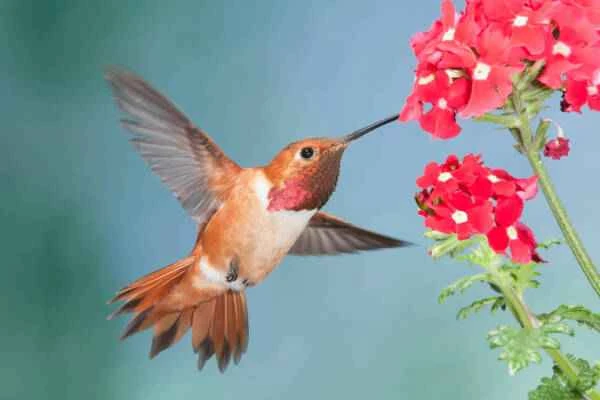
Hummingbird species flap their wings at different speeds; giant hummingbirds flap their wings 12 times per second. Many species flap their wings 50 to 80 times per second, which is barely visible to the naked eye. But this is actually quite slow for hummingbirds! When they are diving, they can flap their wings 200 times per second.
Hummingbirds' unique wings make them the most mobile birds on Earth—they are the only birds that can fly backwards and the only birds that can hover for such a long time because they can move their wings in a graphic pattern—eight modes.
8. How fast is a hummingbird's heart rate?
Hummingbirds can have a heart rate of over 1200 beats per minute – more than 20 beats per second! Their hearts are so small that we can’t hear them, but if we could, they would be beating so fast that it would just sound like a high-pitched hum to us.

9. Do hummingbirds have natural enemies?
They may be the most agile birds in the world, but that doesn't mean hummingbirds are immune to predators. Because of their small size, the list of predators for hummingbirds is actually quite long.
Reptiles like snakes and lizards will gladly attack and eat hummingbirds, and large frogs and even fish will leap out of the water to catch their prey.
Other birds also eat hummingbirds—small birds of prey like kestrels kill them, as do shrikes, crows, and roadrunners.
And let’s not forget invertebrates, because large praying mantises will snatch passing hummingbirds, and hummingbirds may even get trapped in the sticky webs of orb-weaver spiders.
Hummingbirds aren't even safe at night, because bats and owls will eat anything they roost in the dark.

10. How long do hummingbirds live?
Wild hummingbirds typically live for 3 to 5 years, but the oldest known hummingbirds have lived up to 12 years, and some have been recorded to live up to 14 years in captivity.
Hummingbirds have a very fast metabolism, so they are always hungry! They need to consume about half their body weight in food every day, most of which is nectar, but also small insects and spiders.
In fact, hummingbirds need so much food that they would go hungry all night if they slept normally. Instead, they enter a deeper sleep, more like a mini-hibernation called "dormancy," during which their metabolism slows down so they can get through the night.
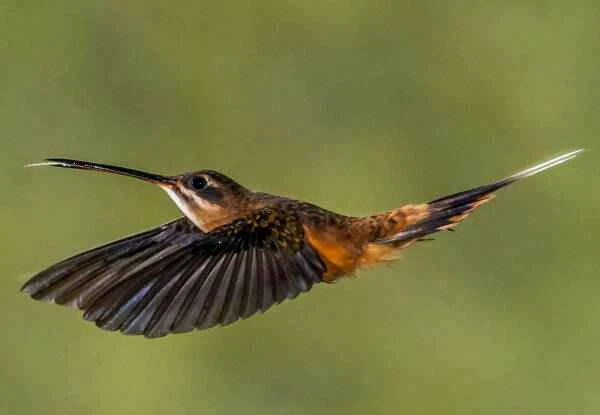

11. How far do hummingbirds migrate?
Many hummingbirds winter in Central America and then migrate north to their breeding season in the spring. Their migration appears to be triggered by the sun's position in the sky and the length of the day, with individual birds typically leaving or arriving at their breeding grounds on almost exactly the same day each year.
The reddish-brown hummingbird has the longest migration time, flying more than 6,000 kilometers between Mexico and Alaska.
But perhaps even more impressive is the Ruby-throated Hummingbird, which flies 800 kilometers across the Gulf of Mexico without stopping. While that may not seem like much to many birds, it takes these hummingbirds more than 20 hours to complete the crossing—a remarkable feat for birds that typically have to feed 5-8 times an hour to avoid starvation.

12. How fast is a hummingbird's tongue?
The hummingbird's tongue is a true evolutionary marvel. We have only recently come to understand how it works using a specially designed transparent feeding tube and a high-speed camera.
It turns out that hummingbirds use their tongues as flexible "miniature pumps," working in a way similar to how we drink water with a straw. However, instead of creating a vacuum in a straw, they use elastic energy stored at the base of their tongues to draw out nectar. This is more akin to how we use a squeeze pipette to draw liquids.
And this is happening at a very high speed—a hummingbird's tongue can go in and out of a flower up to twenty times per second!

13. Are hummingbirds endangered?
Currently, approximately 10 percent of hummingbird species are listed as critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
In all cases, a significant factor in their status is habitat loss and destruction. Another major concern for hummingbird conservationists is the potential impact of climate change on bird food supplies and migration routes.


