In early biological taxonomy, scientists typically classified animals into so-called "lower" and "higher" animals based on the complexity of their body structures, particularly the development of their nervous and organ systems. Simpler organisms, especially those lacking complex organs or nervous systems, were generally considered "lower." However, modern biology has gradually abandoned this overly linear classification method, instead viewing all organisms from an evolutionary perspective, believing that each species is a product of long-term natural selection and adaptation to its environment, without inherent hierarchy.
In this context, we can start from simplicity and primitiveness to discuss some animal types that are relatively simple in morphology and function.
II. Sponges: The simplest multicellular animals
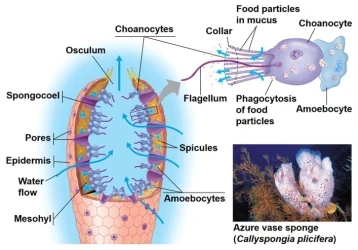
Sponges (Porifera) are widely recognized as among the simplest multicellular organisms in the animal kingdom. They are among the oldest and most primitive groups of multicellular animals, and scientists believe they may have appeared on Earth 500 to 700 million years ago.
1. Structural characteristics of sponges
Sponges have an extremely simple body structure, lacking true organs, tissues, or a nervous system. They consist of a porous structure made up of a gelatinous matrix, containing countless tiny pores (called pore cells) and a small number of cell types. Despite lacking complex organ systems, sponges are able to effectively filter nutrients and remove waste from water.
Sponges have a simple lifestyle. They typically attach to the seabed or other solid surfaces, relying on water currents for filtration and feeding. Water flows through pores in their bodies, capturing and digesting tiny food particles. This simple structure allows sponges to survive in complex ecosystems.
2. The evolutionary significance of sponges
Despite their remarkably simple structure, sponges hold a significant place in animal evolutionary history. As among the earliest differentiated multicellular animals, their existence demonstrates that multicellular structures in animals may have evolved through the synergistic interaction of simple cell clusters. The simplicity of sponges also provides crucial clues for understanding how animal complexity gradually evolved.
3. The regenerative capacity of sponges
Another amazing characteristic of sponges is their regenerative ability. Even when cut or broken, a sponge's cells can reassemble and form a complete individual. This regenerative ability is extremely rare in the animal kingdom, highlighting the unique biology of sponges.
III. Single-celled organisms: the link between animals and protozoa
Single-celled animals, also known as protozoa, are tiny organisms composed of a single cell. Although they lack the complex structure of multicellular animals, they are traditionally included in discussions of the animal kingdom because of their many similarities to animals in terms of life form.
Amoeba: A representative of single-celled life
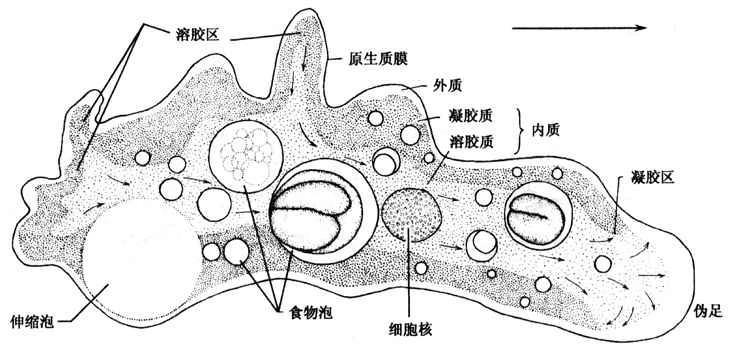
Amoeba is a representative of protozoa, often considered one of the lowest animals. An amoeba's body consists of a single cell, has no fixed shape, and is able to move using pseudopodia. They use pseudopodia on their cell membranes to propel themselves toward food or escape threats.
Despite their remarkably simple structure, amoebas exhibit complex survival behaviors, such as feeding, locomotion, and responses to external stimuli. Amoebas can capture extracellular food particles through endocytosis and digest them within the cell, demonstrating that even single-celled organisms possess a degree of complexity.
2. Paramecium: Movement in the Microscopic World
Paramecium is also a common single-celled protozoan. Paramecia have a more regular morphology and an exterior covered with cilia, which help them move quickly in water. They possess a oral groove, which allows them to introduce tiny food particles into their bodies.
Compared to amoebas, paramecia, despite being single-celled organisms, exhibit more complex behavioral patterns and structural functions. Paramecia possess a contractile vacuole for excretion and a nucleus that controls cellular activity, demonstrating that even single-celled organisms can achieve significant functional changes.
3. Single-celled animals
Despite their extremely small size, single-celled organisms play a vital role in ecosystems. Protozoa are an indispensable part of the food chain, feeding on many animals that depend on aquatic environments. At the same time, some single-celled organisms, such as Plasmodium, also have significant health impacts on humans and other animals, further demonstrating their ecological importance.
IV. Discussing the simplicity of "lower" animals does not imply their evolutionary failure. On the contrary, they achieve a survival advantage in different ecological environments by maintaining low-complexity structures and functions. These animals may lack complex nervous systems or organs, but their biological characteristics enable them to survive stably in nature for extended periods.
V. The concept of the so-called "lowest animals" is no longer strictly applicable in modern biology. However, from the perspective of structural and functional simplicity, sponges and single-celled organisms such as amoebas and paramecia can be considered the simplest representatives in the animal kingdom. They demonstrate the ability of multicellular and single-celled organisms to survive, reproduce, and adapt to their environment in nature with minimal complexity.
These lower animals provide valuable clues for understanding the diversity of life and the process of evolution. Their existence not only demonstrates the diversity of life forms but also reminds us that every species, regardless of complexity, has its unique importance in the ecosystem. The simplicity of lower animals is a result of evolution, not a disadvantage; their ability to adapt to specific environments is the reason they have survived in nature. Therefore, all life forms deserve our attention.


