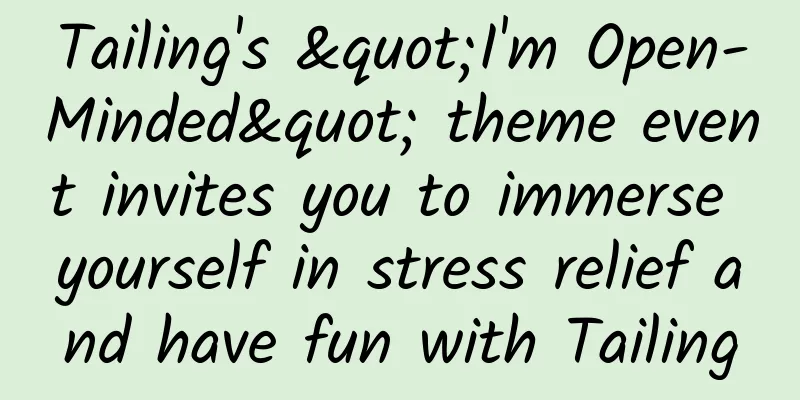Shaluli Mountains, the central mountain range of Hengduan Mountains

|
Shaluli Mountain, located in the eastern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is one of the "Seven Veins and Six Rivers" of the Hengduan Mountains. Among the series of mountain ranges that make up the Hengduan Mountains, the Shaluli Mountains are quite low-key, so low-key that many people have never heard of its name. But when it comes to the many landscapes of the Shaluli Mountains, they are well-known, such as the Aden Snow Mountain, the Genyen Sacred Mountain, the Queer Mountain, and the Cuopu Valley. What kind of mountain is it that gave birth to such a stunning Shaluli Mountains, and how many magical secrets does it hide? ▲Aerial photography of Hengduan Mountains, photo by Li Zhongdong Central Range of Hengduan Mountains The Hengduan Mountains are composed of "seven veins and six rivers". They run alternately in the north-south direction and cross the east and west, making them the most peculiar mountains in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Chinese mainland. The seven mountains from east to west are: Minshan, Qionglai, Daxue, Shalu, Mangkam-Yunling, Tanianthaweng-Nu, Boshula-Gaoligong, collectively known as the "Seven Ranges of Hengduan". The Shaluli Mountains are the fourth range, stretching across the middle and forming the central range of the Hengduan Mountains. The Shaluli Mountains start from the south of Queer Mountain in the north and end at Yulong Snow Mountain in Yunnan. It is 450 kilometers long from north to south and 150-200 kilometers wide from east to west, covering an area of about 80,000 square kilometers. It is the watershed between the Jinsha River and the Yalong River. These two most important water systems in Sichuan are separated by it on the east and west sides, and finally meet at Sanduizi in Panzhihua City thousands of miles away. ▲Shaluli Mountains is the central mountain range of Hengduan. The Shaluli Mountains are also composed of a series of mountains running from north to south. From north to south, there are Queer Mountain, Sulong Mountain, Genie Mountain, Haizi Mountain, Mula Mountain, and Nianqing Gonggar Risong Gongbu (Yading Snow Mountain). The Shaluli Mountains are the longest and widest mountain range in Sichuan Province, and the widest mountain range in the Hengduan Mountains. The main part of the mountain range is composed of a 4,500-4,700-meter-high planation surface and the remaining mountains standing on it, with a few fault basins and tributary valleys in between. The overall terrain of the mountain range is high, with long remaining mountains, undulating hilly plains, open valleys between the plains, and winding rivers. ▲ Mount Genyen in the middle of the Shaluli Mountains. Photo by Yang Tao. The most beautiful hilly plains in Hengduan Mountains Affected by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian continents, the Shaluli Mountains formed a secondary planation surface during the Paleogene and Neogene periods as the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau continued to rise. About 3 million years ago, the uplift intensified, and the planation surface was cut and fragmented, forming a hilly plateau with alternating hills and valleys, wide valleys and round hills, and undulating hills. The Jianziwan Mountain, Kazila Mountain and Haizi Mountain we saw along the way are all hill-like plateaus formed by the cutting and fragmentation of the planation surface. These hill-like plateaus are generally 4,000-4,500 meters above sea level, forming a three-dimensional grassland similar to the Kalajun of the Tianshan Mountains. On the plateau, there are many remnant mountains, some of which are independent and some are connected into groups. They are the places where ancient mountain glaciers raged and the last territory of modern glaciers. Snow-capped mountains stand in the distance, and the undulating hilly ridges are graceful, with green grass and wild flowers on top. Below are the indigo primeval forests and long and deep river valleys, which subvert the aesthetic "fatigue" of the monotonous colors and single landscapes of ordinary grasslands and show the unique aesthetic value of alpine grasslands. ▲Hump-shaped plateau - Kazila Mountain. Photo by Li Zhongdong. Ancient ice cap remains The vast planation surface of the Shaluli Mountains was covered by thick ice and snow during the Quaternary Ice Age, which began 2.6-3 million years ago, forming multiple ice caps, like miniature Antarctica. Later, as global temperatures rose and the Ice Age ended, the ice caps gradually melted and disappeared, but the remains of the ice caps are scattered throughout the mountains, forming magnificent and precious ancient ice cap relics. Haizi Mountain in the south-central part of the Shaluli Mountains is the largest ancient ice cap relic on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The distribution range of the ancient ice cap relic area spans the two counties of Litang and Daocheng, with a total area of 6,965 square kilometers. Here, various glacial erosion and glacial accumulation landforms can be seen everywhere. Among them, hundreds of millions of granite boulders (stone seas) and thousands of glacial rock basins (lakes) cover the entire mountain area, forming the breathtaking "Thousand Lakes and Stone Mountains" strange landscape, like the border of the world or the surface of another planet. ▲Haizi Mountain ancient ice cap. Photo by Wen Junhao. In addition to Haizi Mountain, small ancient ice cap remains can also be seen in other places in the Shaluli Mountains, such as Xinlong Zanduocuolama, Daocheng Bangretang, and Litang Xiawogeza. Of all the areas where ancient ice caps have been found on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the Shaluli Mountains are undoubtedly the most prominent. What is strange is that to the east of the Shaluli Mountains is the Daxue Mountains, where the main peak of the Hengduan Mountains, Gongga Mountain, with an altitude of 7,556 meters, is located. But why can ice caps develop in the Shaluli Mountains, while only mountain glaciers can develop in Gongga Mountains? This is actually due to the continuous Yanshanian granite in the core area of Shaluli Mountain. Due to the hardness of this rock, the ancient planation surface formed is more easily preserved intact, thus providing a geomorphological basis for the development of ice cap glaciers. ▲Ancient ice cap at Tiejiang Mountain in Litang. Photo by Wang Hong. In addition to the remains of ancient ice caps, the remains of ancient mountain glaciers are also widely distributed in the Sharuli Mountains, mainly in the high mountain areas above 4,000 meters above sea level. The high-hanging cirques, the glacial polished surfaces worn smooth by glaciers, the wide and gentle river valleys transformed by glaciers, the ridge-like landforms formed by the accumulation of glacial materials from different periods, the bead-like glacial lakes, and the glacial boulders scattered in the grasslands and forests all tell the story of the Ice Age. This is the area with the highest density of glacial lakes in Sichuan. They are green like emerald, sapphire, delicate and exquisite, with an otherworldly beauty. ▲The Pearl Lake in Mount Genyen. Photo by Wang Hong Glacial troughs, also known as glacial U-shaped valleys or secluded valleys, are valleys formed by erosion of the bottom of the glacier and the mountains and rocks on both sides during the movement of the glacier. They are named because of their U-shaped cross section. Such valleys are often the gathering place of beautiful scenery, such as Gongga Yingou in Yading, Lenggugou and Cuopugou in Genyen, which are all glacial U-shaped valleys. In addition to the remains of ancient glaciers, a small number of modern glaciers are still preserved in the extremely high mountain areas of the Sharu Mountains, such as Mount Queer, Mount Genyen, and Mount Nyainqen Risong Gumpo. These glaciers are gradually retreating and are facing the risk of eventually disappearing every day. ▲The hanging valley glacier of Mount Genyen. Photo by Li Zhongdong. A diverse, complex, ancient biological landscape Like other mountain ranges in the Hengduan Mountains, the complex natural conditions of the Shaluli Mountains have also nurtured a rich variety of vegetation types and animal and plant populations. The north-south mountain ranges and rivers have also brought many interesting changes to the creatures here. For example, heat-loving creatures in the south can spread northward along the dry and hot river valleys, while cold-resistant creatures in the north can also find habitats in the high-altitude areas here. The fauna here is also a mixture of southern and northern animals, such as the representative monkeys from the south and the representative families from the north, such as the ochotonidae and mole families, which can be seen everywhere. This is the distribution center of white-lipped deer, and the forest musk deer, red musk deer, white-eared chicken, and blue sheep are one of the highest density areas in Sichuan Province. ▲The sea of flowers on the southern slope of Haizi Mountain. Photo by Li Zhongdong. This is also a rare biological refuge during the Ice Age. When the Quaternary Ice Age came, most of the creatures in the area became extinct, but many ancient plants survived here and became living fossils, such as spruce, fir, hemlock, larch and other gymnosperms. In addition, a large number of ancient Mediterranean relict plants are preserved here, such as the Alpine Oak, which is a direct derivative of the ancient Mediterranean vegetation. It is not only widely distributed here, but also the distribution center. Almost all Alpine Oak species are concentrated here, and they are in the form of trees. ▲Litang Zhongnagou, Taoerqi. Photo by Li Zhongdong The beauty of snow-capped mountains There are three extremely high mountains of 6,000 meters in the Shaluli Mountains, namely, Queer Mountain, Genie Mountain and Yading Snow Mountain, which are located in the north, middle and south of Shaluli. Queer Mountain is called Zhuola Mountain in Tibetan, which means a mountain that birds cannot fly over. It is located in the north of Shaluli Mountain. The main peak in Derge County is Rongmai Oza, which is 6,168 meters above sea level. It has always been a natural barrier in northern Kang. Queer Mountain is a sea of mountains, with 28 peaks over 5,000 meters and 1,666 peaks over 4,000 meters. This is the distribution area of modern glaciers in the Shaluli Mountains, with more than 30 glaciers of various sizes and a glacier area of 80 square kilometers. The two largest glaciers are distributed in the northwest and northeast, with a length of about 6 kilometers. ▲At an altitude of 9,000 meters, overlooking the mountains in the Queershan area of the Shaluli Mountains. Photography|@7556 Wen Junhao Genyen Sacred Mountain is located in the middle of the Shaluli Mountains, with a maximum altitude of 6,204 meters. It is the highest peak of the Shaluli Mountains, the third highest peak in Sichuan Province, and the fifth highest peak in the Hengduan Mountains. This area is called "Gangbo Ridge" in Tibetan. It consists of a series of snow-capped mountains. Looking down from the air, numerous mountains, snow-capped peaks and valleys surround a place called "Heart of Genyen" like a blooming lotus. Mount Genyen is a place where modern glaciers and ancient glacial landforms coexist. In addition to the highest peak, Mount Genyen, there are also extremely high mountains such as Mount Xiangba and Mount Xiaozha, all of which have a large number of hanging valley glaciers and cirque glaciers distributed on them. Under the glacier, there are a large number of ancient glacier relics in Lenggugou, Xiaozagou and Zhongnagou, and three-dimensional grasslands on the hilly plateau, with ridges and slopes undulating like lines and green grass. There are diverse river valley landforms, wild flowers like brocade, and rivers like snakes. They have a quiet beauty that is isolated from the world, set against the backdrop of snow-capped mountains in the distance and forests nearby. ▲Mount Genyen. Photo by Tuchong Creative. On the ridge slopes of the hilly plateau, bead-like alpine meadow-type lakes often develop. Affected by the rise and fall of lake water, the lakeside vegetation is divided into circular zones with the center of the lake as the center, showing circular color changes. Looking down from the air, it looks like the pupil of a beautiful girl's eye, so it is called the "Eye of Genyen". Genyen is also a snow mountain full of "divinity". It is the 13th goddess among the 24 sacred mountains of Tibetan Buddhism in my country, and one of the eight sacred places of Heruka. In Tibet, the only sacred places of Heruka are the Himalayas and Genyen. ▲The Eye of Genyen under the Genyen Peaks. Photo by Tuchong Creative. Yading Snow Mountain, also known as Nyainqen Gonggarisong Gongbu Snow Mountain, is located at the southern end of the Shaluli Mountains, in the south of Daocheng County, at the junction of Muli County and Yunnan. Its highest peak is Xiannairi Snow Mountain with an altitude of 6,032 meters. There is one 6,000-meter snow-capped mountain and 10 5,000-meter snow-capped mountains here. Xiannairi, Xianuoduoji and Yangmaiyong are the most famous snow-capped peaks. They are independent of each other and arranged in a "品" shape, and are called the "Three Sacred Mountains of Aden". With Nyainqen Gonggar Risong Gongbu Snow Mountain as the center, there are 26.73 square kilometers of hanging glaciers. The glaciers are small, delicate, sensitive and fragile. ▲Yangmaiyong Snow Mountain in Yading. Photo by Mingtian Z (TuChong Creative) The alpine ecosystem here has been preserved in its most primitive and perfect state. Subalpine coniferous forests are distributed in patches, and alpine oak forests grow in the form of tall trees. Here you can see the lamas of the temple feeding wild white-eared chickens and wild river fish. Every blade of grass, every mountain and every stone here are regarded as "sacred objects" by the local residents and are consciously protected. In 1928, Joseph Locke, an American from Austria, came here and introduced it to the world. In 1933, British writer James Hilton wrote and published the novel "Lost Horizon" based on Locke's legendary experience. Later, the novel was made into a movie, and the place described in the book was called "Shangri-La". From then on, this word became a paradise in the hearts of people all over the world... ▲Xiannairi and Yading Village. Photo by Vegetable Candy Party (TuChong Creative) -END- References: 1. Li Zhongdong, "The masterpiece of the 700,000-year-old ice cap of Mount Haizi", National Geographic China, Issue 09, 2020; 2. Li Zhongdong and Tan Yibo, The Soul of Shambhala: Secret Daocheng, China Tourism Press, second edition, 2012; |
<<: Toona sinensis, Houttuynia cordata, and Durian, which one has the top 1 stink?
Recommend
Digging a pit is the first step, a big step for civilization? Let’s talk about the ancient toilets~
What is unexpected is that in the peak tourist se...
A brief talk about user operations, my AARRR model!
1. Start by reconstructing the AARRR model After ...
Online education app buying trends and delivery insights!
According to Adinsight product monitoring by Reyu...
After negotiations with Mercedes-Benz and BMW failed, Apple reportedly reached an agreement with Volkswagen on autonomous driving transformation
Apple has continued to advance its self-driving c...
Why is it said that home appliance companies investing in sports is equivalent to investing in real estate?
On January 14, Hisense announced that it would be...
Can Douyin’s yellow V certification increase push notifications? How to increase fans?
There was no sign of Tik Tok's rise to fame; ...
How can brands leverage internet celebrities and big Vs to do "influencer marketing"?
Alibaba released the first " Internet Celebr...
Health protection tips during sandstorms
Health protection tips during sandstorms In dusty...
What preparations should be made before launching an App or Web product?
This is a question that has been delayed for quit...
Why do bicycles also love "magnesium"?
What? Bicycles love magnesium too? It turns out t...
There are so many advertising channels, how do you choose?
Faced with the intensified competition of product...
94.1% of people have experienced “forgetting words when writing”, and now we finally know the reason!
How long has it been since you last wrote with a ...
In 2020, beware of suffering from "traffic anxiety"!
With the disappearance of traffic dividends, the ...
How to write the copy for Women’s Day? 11 industries for your reference!
The copywriting for Women's Day can choose to...
Theory + practice comprehensive live streaming technology
Theory + practice Comprehensive practical live st...