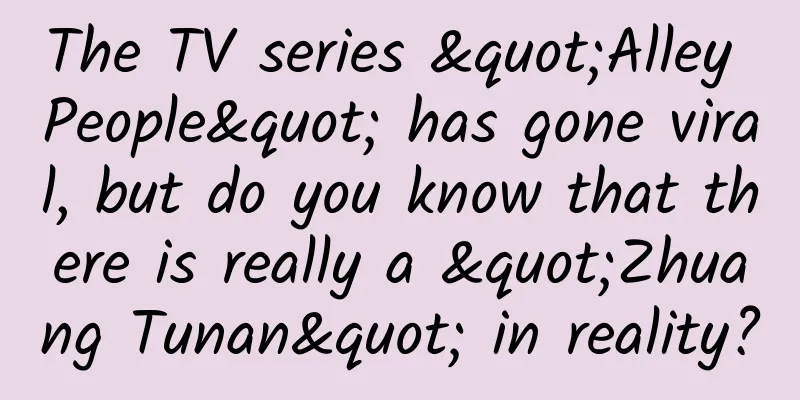China Semiconductor Industry Association: China's integrated circuit industry's total revenue reached 1,045.83 billion yuan in 2021, an increase of 18.2% year-on-year

|
Since the release of the Integrated Circuit Development Outline in 2014, the domestic chip industry has developed rapidly. According to statistics released by the China Semiconductor Industry Association, the domestic integrated circuit industry has continued its rapid and steady growth in the past few years, and the industry's total revenue exceeded one trillion yuan for the first time in 2021, reaching 1,045.83 billion yuan, an increase of 18.2% year-on-year. Among them, the design industry's sales were 451.9 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 19.6%; the manufacturing industry's sales were 317.63 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 24.1%; and the packaging and testing industry's sales were 276.3 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.1%. As can be seen from the above figure, although the growth rate of domestic integrated circuits has declined slightly, it has maintained a year-on-year growth rate of more than 15%, and the overall market is steadily rising. However, for the domestic chip industry, it is far from time to celebrate. As many experts have said, the development of domestic chips in the past few decades has been mainly based on simple chips and direct "me too" domestic substitution. However, with the changes in global demand, the update of upstream technology and the changing international situation, this can no longer meet our huge domestic demand, which has forced the domestic chip industry to enter the deep water zone. "Big chips" is one of the important directions. But unlike the arduous journey at the beginning of this century, domestically produced large chips are now at a new starting line. Twenty years of hard work: From mobile phones to data centers There is no fixed definition of "big chips" in the industry, but everyone generally refers to CPUs, GPUs, DSPs, and the DPU and AI chips that have become popular in recent years in mobile phones and devices as big chips. Global leading chip companies such as Intel, Nvidia, AMD, Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Marvell, which are well-known to everyone, are typical big chip leaders. The world's top 10 chip design companies in the first quarter of 2021 (source: TrendForce) In the past few decades of development of the chip industry, these large chip leaders in different fields have survived many rounds of competition. Especially after TSMC was established in 1987 and promoted the prosperity of the fabless industry, the competition among chip (including large chip) design companies has been particularly fierce. Take the Internet boom around 2000 as an example. At that time, the soaring Internet bubble attracted American venture capital and high-tech companies to compete to build the next generation of infrastructure equipment. In order to cope with the expected explosion of Internet traffic, they set their sights on network processors that can handle more network services and growing data rates. According to incomplete estimates, dozens of start-ups were born around such processors at that time. However, as of 2007, only Cisco Systems, Marvell, Freescale, Cavium Networks, AMCC, Intel and Ezchip were still selling network processors in large quantities. This is enough to prove the cruelty of the big chip competition, but the high returns of the winners have been driving companies to invest in the big chip competition in response to market demand in the past few decades. For example, in China, in the past decade or so, the wave of mobile devices has produced many big chip "winners". Around 2000, China's Ministry of Information Industry (the predecessor of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) issued "Document No. 18" to encourage the development of the software and integrated circuit industries. This attracted a group of overseas people to return to China to start businesses. China's mobile phone chip giant Spreadtrum (now Spreadtrum) was established at this stage, which is also a successful attempt worthy of a strong mark in the development of domestic large chips. At the same time, Rockchip and Actions were established one after another. They, together with Huawei HiSilicon and Allwinner, which were established a few years later, became pioneers of domestic large chips in the mobile era. In a sense, this is also the first time that domestic large chips have made a "Chinese voice" in the new wave of terminal devices. While domestic large-scale chips are making steady progress in the mobile terminal, they are also sprouting in another huge electronic terminal market - PC. Several current domestic PC chip manufacturers: Loongson can be traced back to the "Loongson Research Group" established in 2001, which entered the processor industry from MIPS; the Feiteng team has been engaged in Arm CPU research and development since 1999. In the second decade of the 21st century, China welcomed two X86 processor manufacturers, Zhaoxin and Hygon. They obtained X86 architecture licenses through cooperation with VIA and AMD respectively, and embarked on different new paths for domestic CPUs - the former took computers as the first foothold, while the latter focused on data centers first. That is, starting from the year when Haiguang was founded, domestic large chips entered the data center stage, and it all started in 2012. Four waves: from AI chips to CPUs In the article "Nvidia's Road to Dominance in AI Chips" published by Semiconductor Industry Observer, it is described that "In 2012, Alex Krizhevsky, a student of Geoff Hinton, one of the founders of deep learning, successfully trained the deep convolutional neural network AlexNet, and used this network to significantly improve the performance in the field of image classification and recognition (15% error rate, 10 absolute percentage points higher than the second place), thus becoming a landmark event in artificial intelligence. And this pioneering work was achieved by him using Nvidia's GPU." NVIDIA has the GPU and its ecosystem CUDA, but the market is infinite. Seeing the potential of dedicated AI chips in training and reasoning, the world has set off a vigorous AI chip startup wave, such as Graphcore, Cerebras Systems, Habana Labs (already acquired by Intel) and Hailo. This is also the first wave of domestically produced large chips in recent years. Giants including Baidu Kunlun, Suiyuan Technology, Horizon Robotics and Cambrian have grown up in this wave, and more new companies are also flourishing in the AI craze. During this period, another type of challenger to Nvidia emerged - GPU start-ups, which is also the second wave of domestic large-scale chip start-ups that I have seen. Readers familiar with NVIDIA should know that this GPU giant has two product lines, namely graphics GPUs for graphics applications and GPUs for AI applications, which are also known as GPGPUs. Overseas, Intel and AMD are attacking NVIDIA from these two product lines. In China, most GPU startups choose to enter the market from the GPGPU direction. According to incomplete statistics from the author, in addition to the old-line manufacturers such as Jingjiawei, Loongson, Zhaoxin and Feiteng, there are also new domestic GPU companies such as Tianshu Zhixin, Biren, Muxi, Moore Thread, Denglin and Xindong. As for why there is still an opportunity for GPUs, Li Xinrong, co-CEO of BiRen Technology, said in an interview with Titanium Media: "In the digital economy era, the demand for computing power from artificial intelligence and high-performance computing is growing rapidly. General-purpose GPUs are born to meet the demand for fast-iterating artificial intelligence computing power. So if the market has this demand, the large-scale implementation of general-purpose GPUs will definitely be realized." As AI chips and GPUs are gaining popularity, another "big chip" DPU has also emerged. According to the dedicated data processor (DPU) technology white paper, DPU (Data Processing Unit) is a dedicated processor constructed with data as the center, using software-defined technology to support infrastructure layer resource virtualization, and supporting infrastructure layer services such as storage, security, and service quality management. Its most direct role is to serve as a CPU offload engine, taking over infrastructure layer services such as network virtualization and hardware resource pooling, and releasing the CPU's computing power to upper-layer applications. In the past few years, international chip giants such as Amazon AWS, Nvidia, Intel and Marvell have all made efforts in this product form. Domestic Huawei, Alibaba, Tencent and Baidu have also followed suit. In addition, Zhongke Yusu, Yunbao Intelligence, Yunmai Xinlian, Xinqiyuan, Dayu Zhixin, Yisixin and Shanghai Juxiang Technology have also become new gold diggers in this market. With the continuous development of the above three chips, the changes in data center architecture, and the ever-changing international situation, in the past two years, Arm CPU, with the new direction of PC chips and server chips, has stepped into the center of the domestic large chip stage. The former, represented by this chip, is eyeing the Arm opportunities in the PC market; the latter is fiercely competitive and is targeting the hot data center market. Ten years of ups and downs: Arm server chips finally become mainstream In fact, Arm server chips are nothing new. Since 2008, everyone from Arm to chip companies have begun to have ideas about this market. Then many companies have made a lot of attempts in the past few years. But until the launch of Huawei Kunpeng and Amazon Graviton in recent years, the entire Arm server chip market was basically in a stage of moving forward with twists and turns. But after Huawei and Amazon, Microsoft, Tencent, Alibaba, ByteDance and Google have also set their sights on Arm server chips, and there are some factors behind this. First of all, Arm server chips have entered a new stage with the release of Arm Neoverse, which focuses on infrastructure, in October 2018. According to Arm, the global infrastructure is changing with each passing day in order to cope with the growing workloads and increasing performance requirements. Arm Neoverse can be optimized for cloud, edge and 5G networks, providing excellent speed, energy saving, performance power consumption and performance cost ratio to meet the needs of future infrastructure and its customers. Arm Neoverse Roadmap (Published in September 2020) In addition, Arm has switched to 64-bit and launched the new Armv9 architecture. In addition, Arm has unified the mobile phone market with an absolute share, generating huge traffic in data centers. At the same time, it is gradually penetrating into the PC market, which has created a good environment for Arm server chips in terms of time, location and people. Since Apple released the first generation of iPhone in 2007, the mobile phone industry has undergone tremendous changes, and Arm, an expert in low-power processor technology, has also become famous. Due to the characteristics of its architecture and its unique business model, mobile phone chips built on the Arm architecture have monopolized the smartphone SoC market. At the same time, the network has also moved from 3G to 5G, which has also made smartphone terminal applications have unlimited possibilities. The rise of "cloud-native" applications such as games and short videos has posed new challenges to data centers. Coupled with the impact of the booming development of applications such as the Internet of Things and cloud computing, the cost and power consumption pressure brought by the surge in data centers has suddenly increased. The above factors have driven some subtle changes in data centers that have been dominated by the X86 architecture for more than a decade, which has brought opportunities to Arm. Looking back at the development of servers and data centers over the past few decades, it has gone from being independent to the current situation where there are only a handful of oligopolies. The same is true in the chip field, from the early days of a hundred schools of thought to the final dominance of Intel's X86 architecture chips. There are many factors behind this result. But in the view of Dr. Luo Yong, CEO of Yuxianwei, a domestic server chip startup, the domination of the PC market by X86 processors is one of the key factors. Dr. Luo Yong pointed out that Intel proved its success in the PC field after proving the success of the generalization strategy, and then proved itself in terms of efficiency, stability, and mass shipments. It also achieved great success in network chips, which gave them the opportunity to optimize CPU performance and made servers a success. Of course, the "system company + CPU company" model has also been verified in the PC field, so it is considered feasible in servers. And Intel replaced IBM, a company that fully integrated software and hardware chips, in the server market, so the software companies and system companies cooperated with Intel, and everyone got a share of this change. From Dr. Luo's introduction, we learned that in the past few years, Arm has collaborated with chip and ecosystem companies to solve ecosystem problems and shipped them in large quantities in mobile terminals, which makes it easier for them to enter the server market. Under this premise, it is natural for chip solutions with more cores (just right for cloud native needs) and better TCO to become the choice of server chips in the cloud computing era. Coupled with the successful experience of Huawei and Amazon, Arm server chips have finally reached their critical moment, which has also spawned a number of Arm server chip companies. In addition to the birth of Ampere Computing, Huawei and Fujitsu continue to delve into it. Nvidia has also made a comeback in recent years with its Grace series. Cloud vendors such as AWS and Alibaba have also become important players in the Arm server chip market. Coming to the domestic market, the market demand and the impact of international competition have made it urgent to develop local Arm server chips. This has also driven the birth of many start-ups such as Yuxianwei, Hongxinwei, and Qilingxin to enter the market. In addition, Huawei, ZTE, Feiteng and other companies that have already been deeply involved in this market. It can be seen that a new chapter has officially begun for Arm server CPUs in China and even the world. Observations from the semiconductor industry |
Recommend
Have you ever seen a golden mosquito?
Some time ago, Dalian Customs in Liaoning capture...
New media operation title guide: 5 methods and 3 practical skills
“A good title is half the work.” If you can choos...
Zhihu algorithm, ranking, increasing followers, traffic generation and practical skills
OK, before we talk about Zhihu algorithm , Q&...
Developers' Notes: Hot Topics in Mobile Development in 2015
It has been 8 years since Steve Jobs launched the...
Traffic War: How do I operate e-commerce on JD.com (Part 1)
Beijing has been sunny in recent days, and people...
Case | oCPC advertising optimization strategy effectively reduces conversion costs
In this case, an advertiser in the education and ...
How to do marketing promotion? Master these 14 methods!
Marketing promotion is never just about making pe...
It’s 2020 now. Which is better, fingerprint recognition or facial recognition?
Eight years ago, mobile fingerprint recognition w...
Bad breath, is it all caused by Helicobacter pylori?
In the eyes of some people, Helicobacter pylori i...
iPhone 6 teardown revealed: Don't worry about the protruding camera
We are all familiar with the appearance of iPhone...
Don't eat fruit like this anymore, or you may get mentally disturbed...
As soon as spring comes, all kinds of fruits begi...
Detailed official interpretation of TikTok operations, policies, etc.!
After TikTok became popular, a large number of so...
【Huang Xiaoqing】The first Chinese business leader won the IEEE CQR Chairman Award
On the morning of May 11th, Beijing time, the Ins...
The super weapon of element synthesis! See what is the key to artificially synthesizing elements →
Welcome to Science Popularization China’s special...
Postpartum care center-Tencent advertising customer acquisition strategy
Industry dynamics overview The market size has a ...