The highest-flying animal on Earth is the African vulture, a large African vulture belonging to the family Accipitridae and the genus Vulture. It can fly at an altitude of 11,000 meters, making it the highest-flying bird species known to humankind. This giant bird, which lives in south-central Africa, typically hovers at around 6,000 meters to forage, aided by thermals from the ground. The African vulture broke the flight altitude record in 1973 when a plane flying at 11,000 meters collided with one.

The Himalayan vulture can fly extremely high, approximately 11,000 meters, making it the highest-flying bird on Earth. While typically flying at altitudes of 6,000 meters, it is the highest-flying bird known, capable of reaching altitudes of 11,000 meters. Their hemoglobin α-D subunit has a high affinity for oxygen, allowing them to more efficiently inhale oxygen in the low-pressure areas of the upper troposphere.
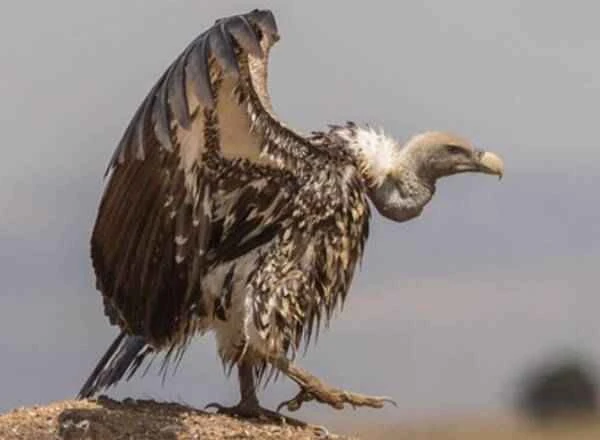

The black-and-white vulture is a carnivore that feeds on carrion. It typically eats African ungulates such as blue wildebeest, plains zebras, and Thomson's gazelles, and occasionally livestock when it comes close to humans.
Black-and-white vultures can fly at speeds up to 35 kilometers per hour, traveling 150 kilometers from their nests to forage. They build their nests on rocky reefs or in acacia trees. Two hours after sunrise, when thermals rise, they leave their nests to forage on the plains. They can wait for several days until predators have removed their carcasses.

The highest-flying bird on Earth: the black-and-white vulture, a species of vulture. The highest known bird to fly is the griffon vulture, capable of soaring at an altitude of 11,000 meters. (Guinness World Records)