On the first day of the new year, beautiful images came from Mars
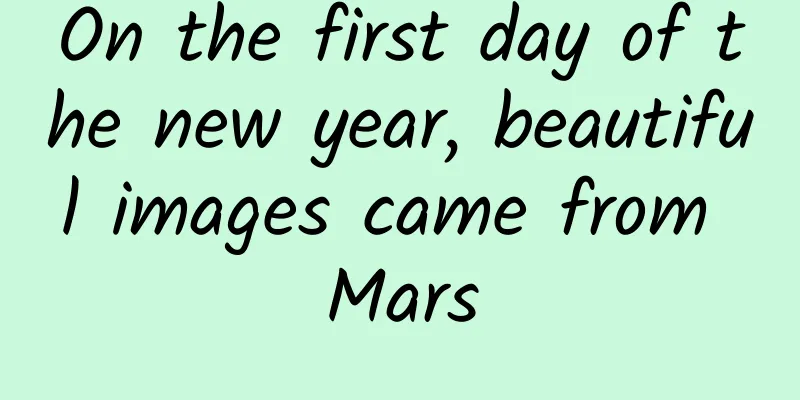
|
On New Year's Day 2022, the National Space Administration released a set of beautiful images sent back from the distant Mars by the Tianwen-1 probe, my country's first Mars exploration mission, to report the safety of Tianwen-1 to the people of the whole country and to extend holiday greetings. This set of images includes photos of the orbiter and Mars, a close-up of the orbiter, the Martian Arctic ice cap, and the Zhurong Mars rover photographing the Martian surface topography, etc., showing the working status of the orbiter and the Zhurong Mars rover and the acquired Martian surface morphology. Currently, the Tianwen-1 mission is carrying out exploration and related tests as planned, and is in good condition and operating normally. The orbiter takes a photo with Mars. (Photo courtesy of the National Space Administration) Figure 1: Orbiter and Mars photo In the image, the orbiter is flying over the north pole of Mars. The orbiter itself is golden, the directional antenna for high-speed data communication with the ground is silver, and the solar panels and radar antenna are in good condition. The white area on Mars is the "ice" field covering the North Pole. Unlike the ice at the Earth's poles, the "ice" on Mars is composed of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) and water ice. The dark area below Mars is Olympia Shap, the bright crater in the upper left corner is called Korolev Crater, and the rest of the red and dark areas are exposed surfaces. A partial close-up of the orbiter. (Photo provided by the National Space Administration) Figure 2: A close-up of the surround In the image, the solar panels on one side of the orbiter are fully deployed and in a stable position. A deployed subsurface detection radar antenna is parallel to the solar panels, and the magnetometer extension rod extends to the upper left of the orbiter. Mars's northern polar ice cap. (Photo courtesy of the National Space Administration) Figure 3: Mars’ North Pole Ice Cap The image shows the Martian north pole ice cap, with clear layers. After years of deposition and melting, it presents a circular spiral landform composed of white ice layers and exposed surface centered on the pole. The Martian surface features photographed by the Zhurong Mars rover. (Photo courtesy of the National Space Administration) Figure 4: Martian landforms photographed by the Zhurong Mars rover The image is composed of three images recently acquired by the Zhurong Mars rover using its navigation terrain camera. Typical Martian landforms such as craters and rocks can be seen in the image. Source: Xinhua Viewpoint (ID:XHSXHSD) Reporter: Hu Zhe |
<<: December 2021 "Science" Rumor List: Does nuclear heating have radiation?
>>: Come and see which new animals are going to be made into emoticons!
Recommend
After the college entrance examination, be careful of the hidden things in seafood
After the college entrance examination, you can r...
Google phone exposed to have a defect: it bends when you bend it
The Nexus 6P mobile phone, which is commonly know...
First confirmed! This part of the human body evolved from fish gills
The international academic journal "Frontier...
Where the Heart “Sounds” – Exploring the Beautiful Sounds of the Heart
Author: Chen Bingwei, deputy chief physician of T...
Entrepreneurship Yeast·Management Fermentation Card, a compulsory course for 100 million managers
Entrepreneurship Yeast·Management Fermentation Ca...
Observation on Vietnam's electric vehicle market: weak in strength but big in ambition, always wary of Chinese brands
In recent years, have you often heard that "...
Gentleman is not white_Taobao Internet celebrity store 100% store opening method
Hello everyone, I am Shen Bai. Friends and studen...
JD Power: 2024 China New Energy Vehicle Customer Experience Value Research
The study uses the Customer Experience Value Inde...
Eating colleagues with big mouths? Pelican, why do you stuff everything into your mouth?
Recently, a pelican in a theme park in Xi'an ...
Practical case: 3 major marketing scenarios to explain the precise delivery of APP
There are many channels for APP promotion . Today...
Will eating persimmons on an empty stomach cause kidney stones? Will eating persimmons make anemia patients' condition worse? Pay attention to these 3 points and eat persimmons without worry →
gossip Autumn is a time for abundant harvests. Th...
Growth hacking in action: a complete case study to explain the core operation methods
The concept of growth hacking has been very popul...
Soft and light... these shoes are comfortable but hurt your feet! Are the "shit-like" shoes really good?
This article was reviewed by Dr. Tao Ning, Associ...
80% of people have experienced flashing eyes. Is this actually a disease?
Have you ever experienced something similar to th...









