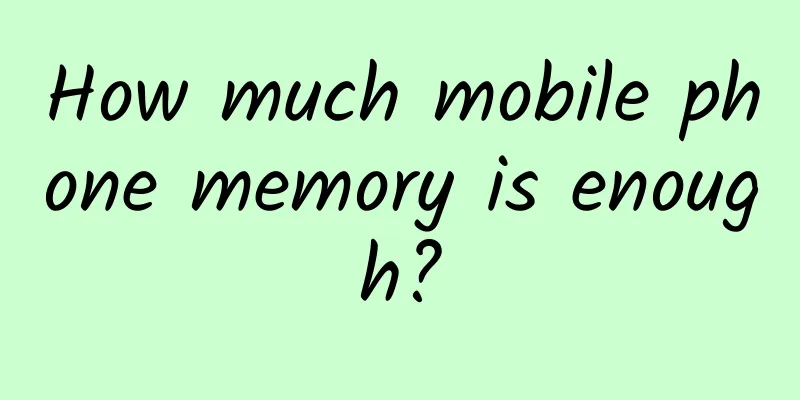
Antarctic glaciers are melting, and cities like New York will become oceans. Is it too late for scientists to save them?

|
Antarctica is known as the "cold source" of the earth. It has a significant impact on global climate change and the ecological environment, and is regarded as a sensitive "indicator" of climate change. Over the past 40 years, with breakthroughs time and time again, China has gradually moved from a "layman" in Antarctic topics to the forefront of Antarctic scientific research. This year marks the 40th anniversary of China's polar expedition. There are still too many unsolved mysteries on this frozen continent. Under the ice and snow, the secrets of the earth for millions of years are buried, and countless ecosystem treasures are nurtured. On the journey to Antarctica, there is not only the romance of the sea and the stars, but also more unknowns and hardships. Generations of Chinese scientific expedition team members have come here with curiosity and yearning, trying to uncover its mystery and continue to explore the ultimate mysteries of mankind and the earth. Xuelong 2 breaks the ice Another milestone in China's polar expedition On this year's World Antarctic Day (December 1), my country's Antarctic Zhongshan National Atmospheric Background Station (hereinafter referred to as "Antarctic Zhongshan Background Station") officially began operations. This important milestone marks another achievement of China's polar expedition, which is not only a positive contribution to global climate change research, but also an important demonstration of the country's scientific exploration capabilities. As my country's first meteorological observation station outside the country, the Antarctic Zhongshan Background Station will provide key scientific data for understanding climate change in the Antarctic region and its impact on the global environment. The Antarctic region is an important background area for global atmospheric environment observations. Its extreme climatic conditions and unique geographical location make meteorological observations in the region particularly important. The continuous and long-term atmospheric composition observations conducted at the Zhongshan Background Station in Antarctica will fully reflect the average state of the atmospheric composition and related characteristics in the Antarctic region. These data are not only crucial for the scientific community to understand the climate change mechanism in Antarctica, but will also provide a solid foundation for the global response to climate change. As an important part of the Antarctic Zhongshan Snow, Ice and Space Special Environment and Hazards National Field Scientific Observation and Research Station, the atmospheric composition observation data of Zhongshan Station have been included in the World Meteorological Organization's "Antarctic Ozone Hole Bulletin" and the China Meteorological Administration's "Polar Climate Change Annual Report", and have been used many times by scientists, effectively promoting scientific research in areas such as polar weather and climate change, and polar atmospheric chemistry. The opening of the Zhongshan Antarctic Background Station is not only the beginning of a scientific project, but also symbolizes my country's firm determination to address climate change and promote the construction of ecological civilization. In the days to come, the observation data of the station will provide precious scientific resources for the international community, help countries better understand the complexity of climate change, and promote global cooperation and exchanges. We hope that through this platform, scientists can reveal more mysteries of climate change in the Antarctic region and contribute wisdom and solutions to global sustainable development. Zhongshan National Atmospheric Background Station Observation Site, Antarctica Blowing the whistle on Antarctic warming Global warming is one of the major environmental challenges facing the Earth today, and its impact on Antarctica has become increasingly evident. According to numerous meteorological monitoring data and scientific research results, the temperature in Antarctica has shown a significant upward trend in the past few decades. This has caused the Antarctic glaciers to begin to melt faster, and a large amount of ice has melted into water and flowed into the ocean. Large areas of Antarctica that are rapidly warming are turning green at an alarming rate. Satellite images show that the vegetation coverage here has increased nearly 14 times in 35 years - a trend that will stimulate rapid changes in the Antarctic ecosystem. On the one hand, the edge of the glacier is constantly retreating, and the land originally covered by ice is gradually exposed. The soil, rocks and microorganisms contained in them that have been sealed under the glacier for a long time are beginning to be exposed to the outside environment and have the opportunity to interact with the external ecosystem. On the other hand, the water flow formed by the melting of glaciers is also changing the ecological environment of the oceans around Antarctica. For example, the temperature, salinity and distribution of nutrients in the sea water have changed, which further affects the survival of marine life and creates conditions for the "release" of those viruses and other microorganisms that were originally sealed. Moreover, as the melting speed of glaciers accelerates, some previously stable ice shelves will break and collapse, and huge ice blocks will fall into the ocean. According to a British website, the Thwaites Glacier, known as the "Doomsday Glacier" in western Antarctica, may collapse in the near future, which will have a catastrophic impact on the world. The "Doomsday Glacier" is not undeservedly named. The Thwaites Glacier has a total of about 480,000 cubic kilometers of ice reserves. If all of it melts into the ocean, it will cause the global average sea level to rise by 65 centimeters. It should be noted that in the past 100 years, the total global sea level rise has only been about 20 centimeters, and the potential "contribution" of the Thwaites Glacier is three times that. Worse still, this will also lead to the disappearance of a large area of the West Antarctic ice sheet, resulting in the catastrophic consequence of a 3.3-meter rise in sea level, and threaten cities such as New York in the United States and Kolkata in India. If the sea level rises to 5 to 7 meters, most coastal cities on the earth will become a vast ocean and swamp. In order to study and predict the collapse time of the "Doomsday Glacier", the International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration (ITGC), composed of 100 people, was established in 2018, aiming to explore the glacier and its future development trend through field surveys, remote sensing, computer modeling, etc. In addition, more than a dozen research groups and research teams of dozens or hundreds of people from top research institutions around the world are also using the most advanced computer models to conduct a large number of numerical simulations of the Antarctic ice sheet, including the Thwaites Glacier. Preliminary results from a modeling team at ITGC show that the Thwaites Glacier will steadily melt and retreat over the next few decades. Although it will not collapse immediately, it is expected that global sea levels will rise by 6 cm by the end of the 21st century. This will happen even if humans uniformly stop greenhouse gas emissions. Scientists involved in the survey are pessimistic about the future of the Thwaites Glacier and the consequences of rising sea levels. In the long run, the situation remains grim. The only good news is that humans can buy time and do something to control the rate at which the Thwaites Glacier disappears. A large amount of Antarctic ice melts into the ocean Forty years of hard work On Earth, Antarctica is the last continent that humans have set foot on. It is not only a paradise for adventurers, but also a dream place for scientists. In the eyes of scientific researchers, although it is cold and desolate, its special geographical environment and climatic conditions make it a natural scientific laboratory. Antarctic scientific research can help humans better understand the ecological environment of the earth. Since the first Antarctic scientific expedition was launched in 1984, my country's Antarctic scientific expedition has gone through 40 years. Over the years, expedition members selected from various units across the country have successively rushed to this "last pure land on earth" to help human exploration and scientific investigation. The Antarctic region is vast, with a total area of 14.245 million square kilometers. It is difficult for a single scientific research station to complete a comprehensive scientific expedition mission. my country has successively established five research stations in Antarctica - the Great Wall Station built in 1985, the Zhongshan Station built in 1989, the Kunlun Station built in 2009, the Taishan Station built in 2014, and the Qinling Station opened on February 7 this year. The Great Wall Station was built earlier and is outside the Antarctic Circle, making it easier for researchers to reach. Zhongshan Station can be used for summer and winter, where researchers can complete observations of the high-altitude atmosphere, ice and snow physics, etc. Kunlun Station and Taishan Station are both seasonal stations and can be used in the summer. Kunlun Station is located in the heart of Antarctica and is the summer station established by my country at the highest point in Antarctica. Taishan Station is located between Zhongshan Station and Kunlun Station in the heart of Antarctica and can be used as a relay station. The newly opened Qinling Station is located in the Ross Sea coastal area of Antarctica, with a construction area of more than 5,000 square meters. It is my country's third permanent Antarctic research station and the first research station facing the Pacific sector. Qinling Station will make full use of the geographical advantages of being adjacent to the Terra Nova polynya in the east and the marine laboratory owned by the research station, focusing on oceanographic observation and research, while carrying out observation and research in atmospheric science, glaciology, geology and space physics, etc., and will play an important role in my country's Antarctic scientific research. Antarctic expedition members can be divided into oceanic teams, summer teams, inland teams, wintering teams and fixed-wing aircraft teams according to the nature of their operations. The oceanic team mainly follows the ship to collect data along the way and carry out ocean exploration tasks; the summer team generally conducts scientific research near the station area and is also responsible for station maintenance and other work; the inland team will continue to advance inland after arriving at the Antarctic continent and go to Taishan Station and Kunlun Station to carry out tasks; the wintering team will continue to stay in Antarctica for the winter after other teams have completed their summer scientific research and return, until the next year when the "Snow Dragon" sends a new batch of team members to take over with them. my country's fifth research station in Antarctica - Qinling Station Scientific research is like giving Antarctica a "physical examination" every year. As the "physical examination doctor" of Antarctica, scientific researchers often have a complex mood, hoping that it will maintain its original appearance, but also looking forward to discovering its unknown side. On the one hand, they hope that all indicators of Antarctica will be stable and not show any abnormalities. On the other hand, facing the vast Antarctic continent, there are always corners that humans have not set foot on, and scientists always want to explore more unknown secrets hidden in the frozen continent. Understand Antarctica and protect Antarctica! Protecting Antarctica means protecting the Earth and protecting ourselves. All scientific research in Antarctica must follow strict environmental protection principles and minimize the impact on the local ecology. Taking the Antarctic Zhongshan Base Station as an example, researchers said they would give full play to the benefits of Antarctic meteorological observation data and draw the "Antarctic Zhongshan Curve" to help better understand, protect and utilize the polar regions, and make new and greater contributions to benefiting mankind and promoting the building of a community with a shared future for mankind. |
<<: Barnard 68, mistakenly thought to be a black hole, is actually a mass...
Recommend
Do you think being a vegetarian is healthy? Wrong! You can also get fatty liver!
Expert of this article: Huang Jia, Doctor of Medi...
The two core elements of product promotion: content and channels
Product promotion is a difficult problem. It look...
A guide to placing ads on Xiaohongshu for brands like Huaxizi!
From the earliest example of Perfect Diary to Hua...
iOS WeChat 7.0.15 update is launched: chat menu has a new UI, tap to add bubble reminders
On August 11, the iOS WeChat version 7.0.15 updat...
7 steps to completely dismantle live streaming sales
Live streaming sales are very popular. It's m...
Where did the transparent glass ball on the moon come from?
A research team led by Dr. Xiao Zhiyong of Sun Ya...
Double points trading started, 56 companies failed to meet fuel consumption standards
On July 2, the Ministry of Industry and Informati...
There are more and more bad domestic films: Are these young actors not good enough?
In July this year, the summer box office fell sha...
Guangdong University Rankings 2019, which undergraduate universities are there in Guangzhou?
Which universities in Guangdong Province are amon...
About to be "launched", what happened to the United Launch Alliance?
Recently, according to foreign media reports, the...
Marketing promotion: 13 tips for building your personal IP
Regarding the creation of personal IP, various co...
If you don’t understand, just ask: Where does the electricity for the subway come from?
In our city, subway lines that run day and night ...
Practical cases will help you master the headlines information flow!
This article mainly briefly introduces the backgr...
Is the effect of bidding advertising promotion terrible? Pay attention to these 4 points
I often hear advertisers complain that SEM promot...
![Hu Chao's Golden Rules of Time Management [Audio] Baidu Cloud Download](/upload/images/67cc240468685.webp)